Download Here - James L. Schaller, M.D., M.A.R., P.C
Download Here - James L. Schaller, M.D., M.A.R., P.C
Download Here - James L. Schaller, M.D., M.A.R., P.C
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
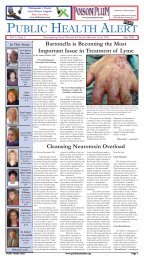
Environmentally Friendly Mold Remediation Techniques That Significantly Reduce Childhood AsthmaMVOCs: Microbial Volatile Organic Compounds: chemicals that canbe produced by actively growing molds and bacteria, which arereleased as gases into the air and are responsible for the characteristicmoldy or musty odor.MYCOTOXIN: A harmful substance produced by a fungus, whichaffects the structural or functional integrity of cells or tissues.Mycotoxins are usually found in the spores, filamentous structures,and/or the surrounding growth material.MYCOLOGIST: A microbiologist who studies or has “expert”knowledge of fungi.NADCA: National Air Duct Cleaners Association. Trade group thatpublishes the standard "Assessment, Cleaning, and Restoration ofHVAC Systems" (ACR-2002).NEGATIVE PRESSURE: An atmosphere created in an enclosuresuch that the air pressure within the enclosure is less than the airpressure outside the enclosure, resulting in the tendency for airborneparticles to be drawn in rather than out.NIOSH: National Institute for Occupational Safety and HealthODTS: Organic Dust Toxic Syndrome (a.k.a. pulmonary mycotoxicosis,"humidifier fever," or "silo unloader's disease"). Illness characterizedby chest tightness, flu-like symptoms, and possibly other symptomsfollowing a single, very heavy microbial exposure (including mold).Such extreme conditions are rarely found in homes or offices.PATHOGENIC: A microbe capable of causing disease by directcontact, typically through infection. The molds most often regardedas pathogenic are those most frequently known to cause opportunisticfungal infections, primarily among immuno-compromisedindividuals (e.g., Aspergillus fumigatus). A microbe that producestoxins that cause disease in the absence of the microbe is not definedas pathogenic.POROUS: Strictly defined, porous refers to the ability of a materialto allow fluids to pass through (permeability to liquids or gases). Forthe purposes of this document, porous materials are items that absorb158