Download Here - James L. Schaller, M.D., M.A.R., P.C
Download Here - James L. Schaller, M.D., M.A.R., P.C
Download Here - James L. Schaller, M.D., M.A.R., P.C
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
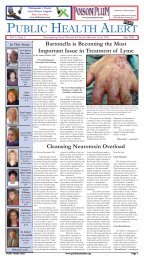
Environmentally Friendly Mold Remediation Techniques That Significantly Reduce Childhood Asthmapersons often need help from toxin binding medicine to clean thetoxins from their systems.A significant amount of recent work on the subject of mold toxinbinding is being done in Europe. The work, published in major peerreviewedU.S. (English language) scientific journals, confirms theefficacy of activated charcoal and also establishes the toxin bindingresin Cholestyramine as perhaps the preferred toxin binding agent tokeep mycotoxin exposed farm animals healthy. 3,4,5,6,7Toxin binders such as Cholestyramine are now being prescribed byphysicians (not just veterinarians) involved in treating mold-relatedillnesses. Plus, some mold remediators routinely take toxin binders toprevent health problems from mold toxin exposure.A thorough discussion of mold toxin binders and human health canbe found in our other book: When Traditional Medicine Fails: YourGuide to Mold Toxins.A Small WorldMold spores are extremely small – more than 200 times smaller thana human hair. Because toxin containing mold spores cannot be seen,some people have a hard time taking mycotoxin contaminationseriously. However, “invisible” particles such as bacteria, viruses, andallergens make people sick all the time. Furthermore, mold spores arejust one type of particulate associated with adverse human healtheffects from mold. Scientists from the University of Cincinnati’sDepartment of Health 8 have shown a very high release level of nonsporefungal fragments from mold-contaminated materials. Thesescientists inoculated agar plates with the mold Aspergillus versicolorand incubated them for varying time periods to produce moldcultures of different ages.The study revealed that fungal micro-fragments were released inmuch higher concentrations than spores in all the cultures no matterwhat age. Fragment release was triggered by air flow over the mold.Furthermore, prior research by the U. of Cincinnati scientists showed36