40Natalia Kruszewska, Jan Styczynski2004-2008 w Klinice Pediatrii, Hematologii i Onkologii.146/305 pacjentów było urodzonych przed 1995 rokiem.Przeanalizowano obecność w surowicy krwi markerów zakażeniawirusami HBV i HCV oznaczonych w trakcie hospitalizacji.Zakażenie HBV rozpoznawano na podstawie obecnościantygenu HBsAg lub przeciwciał anty-HBc-IgM, natomiastzakażenie HCV na podstawie obecności przeciwciałanty-HCV.W y n i k i . W badanej grupie 305 dzieci u 3 (0,98%)stwierdzono zakażenie wirusem HBV, wszyscy należeli dogrupy urodzonych przed 1995 rokiem. We wszystkich przypadkachzakażenia wykryto przed przyjęciem do Kliniki,przy czym 2/3 zakażonych pacjentów pochodziło z innychośrodków. Ponadto u 150/159 (94,3%) dzieci objętych programemszczepień stwierdzono obecność przeciwciał anty-HBs; w 72 przypadkach stężenie ochronne. U 4 (1,3%) pacjentówstwierdzono zakażenie wirusem HCV: u 3 urodzonychprzed 1995 rokiem i u 1 urodzonego później. U 3/4dzieci zakażenie nastąpiło w trakcie terapii.Wnioski. (1) Wprowadzenie szczepień ochronnychprzeciwko zakażeniom HBV przyczyniło się do opanowaniaendemii zakażeń HBV wśród dzieci z chorobami nowotworowymi.(2) Równocześnie odsetek zakażeń HCV w tejgrupie pacjentów uległ obniżeniu, co przemawia za dużymznaczeniem również niespecyficznych metod profilaktycznych.(3) Aktualne ryzyko zakażenia HBV i HCV w trakcieterapii przeciwnowotworowej jest porównywalne z ryzykiemw populacji ogólnej.Key words: HBV, HCV, vaccination, cancer, children, epidemiologySłowa kluczowe: HBV, HCV, szczepienia, nowotwór, dzieci, epidemiologiaINTRODUCTIONChildren with malignancy carry a high risk of hepatitisB virus (HBV) <strong>and</strong> hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections.Factors that promote the infections include: frequentcontact with a highly endemic environment dueto many hospitalizations, all necessary diagnostic <strong>and</strong>therapeutic manipulations that injure tissues [1,2].Immunosuppression <strong>and</strong> treatment harmful to liverwhich patients have to undergo, might cause an unfavorableprogression of hepatitis. Although hepatitis isusually asymptomatic during anticancer treatment, itcan rapidly progress to fulminant type after cessationof chemotherapy <strong>and</strong> cause liver necrosis with hepaticcoma [2]. A high rate of the infection might progressto the chronic phase, which is further associated withthe development of liver cirrhosis <strong>and</strong> hepatocellularcarcinoma [3]. Thus, HBV <strong>and</strong> HCV infections canplay an adverse prognostic role in criteria of diseasefreesurvival [4]. It can essentially abolish the effectsof treatment of the basic disease or become the finalcause of death [3].Prior to 1995, viral hepatitis infections among childrenwith cancer were a serious clinical problem inPol<strong>and</strong>. At that time, HBV infections were found in62,2% of oncological patients in our clinic, while54,3% were infected with HCV [1]. This situationforced introduction of many prophylactic methods,which included the use of new-generation disposalequipment, strict hygienic rules in nursing patients,proper blood donors screening, <strong>and</strong> specific passive<strong>and</strong> active immunization [2].Apart from that, an obligatory vaccination of allneonates in Pol<strong>and</strong> was introduced. It started in 1994<strong>and</strong> covered the whole country in 1996. It was introducedin the Bydgoszcz area in the beginning of 1995[3].The aim of this study was to analyze the presentepidemiology of HBV <strong>and</strong> HCV infections amongchildren with malignancy, with respect to m<strong>and</strong>atoryvaccination program against HBV of neonates <strong>and</strong>infants introduced in 1995.MATERIALS AND PATIENTSA retrospective study was carried out in 305 childrenwith malignant diseases that were hospitalizedbetween August 2004 <strong>and</strong> January 2008 in the Chair<strong>and</strong> Clinic of Pediatric Hematology <strong>and</strong> Oncology inBydgoszcz, Pol<strong>and</strong>. 146 patients out of 305 (48%)were born prior to 1995. The remaining 159 (52%)patients were born in 1995 or later <strong>and</strong> had thereforebeen immunized according to m<strong>and</strong>atory vaccinationschedule (3 doses of vaccine administrated during thefirst days of life, <strong>and</strong> then in 2 nd <strong>and</strong> 6 th month afterbirth). The patients were diagnosed as follows: leukemia122 (40%), lymphoma 57 (19%), brain tumors 31(10%), nephroblastoma 18 (6%), <strong>and</strong> other solid tumors(25%).All patients were screened for hepatitis B <strong>and</strong> C virusesby testing for the presence of HBsAg, anti-HBs,anti-HBe, HBeAg, anti-HBc-IgM, anti-HBc-IgG <strong>and</strong>anti-HCV in serum. The tests were performed at thebeginning of the first admission to the hospital <strong>and</strong>were then repeated during further therapy. A patient
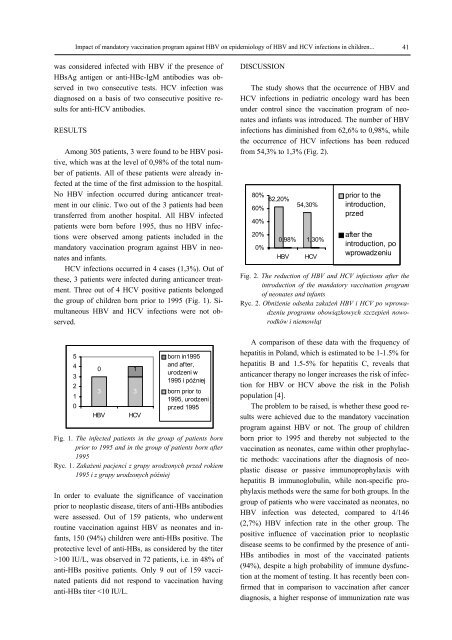
Impact of m<strong>and</strong>atory vaccination program against HBV on epidemiology of HBV <strong>and</strong> HCV infections in children... 41was considered infected with HBV if the presence ofHBsAg antigen or anti-HBc-IgM antibodies was observedin two consecutive tests. HCV infection wasdiagnosed on a basis of two consecutive positive resultsfor anti-HCV antibodies.RESULTSAmong 305 patients, 3 were found to be HBV positive,which was at the level of 0,98% of the total numberof patients. All of these patients were already infectedat the time of the first admission to the hospital.No HBV infection occurred during anticancer treatmentin our clinic. Two out of the 3 patients had beentransferred from another hospital. All HBV infectedpatients were born before 1995, thus no HBV infectionswere observed among patients included in them<strong>and</strong>atory vaccination program against HBV in neonates<strong>and</strong> infants.HCV infections occurred in 4 cases (1,3%). Out ofthese, 3 patients were infected during anticancer treatment.Three out of 4 HCV positive patients belongedthe group of children born prior to 1995 (Fig. 1). SimultaneousHBV <strong>and</strong> HCV infections were not observed.DISCUSSIONThe study shows that the occurrence of HBV <strong>and</strong>HCV infections in pediatric oncology ward has beenunder control since the vaccination program of neonates<strong>and</strong> infants was introduced. The number of HBVinfections has diminished from 62,6% to 0,98%, whilethe occurrence of HCV infections has been reducedfrom 54,3% to 1,3% (Fig. 2).80%60%40%20%0%62,20%0,98%HBV54,30%1,30%HCVprior to theintroduction,przedafter theintroduction, powprowadzeniuFig. 2. The reduction of HBV <strong>and</strong> HCV infections after theintroduction of the m<strong>and</strong>atory vaccination programof neonates <strong>and</strong> infantsRyc. 2. Obniżenie odsetka zakażeń HBV i HCV po wprowadzeniuprogramu obowiązkowych szczepień noworodkówi niemowląt5432100 13 3HBVHCVborn in1995<strong>and</strong> after,urodzeni w1995 i późniejborn prior to1995, urodzeniprzed 1995Fig. 1. The infected patients in the group of patients bornprior to 1995 <strong>and</strong> in the group of patients born after1995Ryc. 1. Zakażeni pacjenci z grupy urodzonych przed rokiem1995 i z grupy urodzonych późniejIn order to evaluate the significance of vaccinationprior to neoplastic disease, titers of anti-HBs antibodieswere assessed. Out of 159 patients, who underwentroutine vaccination against HBV as neonates <strong>and</strong> infants,150 (94%) children were anti-HBs positive. Theprotective level of anti-HBs, as considered by the titer>100 IU/L, was observed in 72 patients, i.e. in 48% ofanti-HBs positive patients. Only 9 out of 159 vaccinatedpatients did not respond to vaccination havinganti-HBs titer
- Page 8: 8Wojciech J. Baranowskirating) move
- Page 13 and 14: The benefits resulting from introdu
- Page 15 and 16: The benefits resulting from introdu
- Page 17 and 18: Medical and Biological Sciences, 20
- Page 19 and 20: The history and the present of hern
- Page 21 and 22: The history and the present of hern
- Page 23: The history and the present of hern
- Page 26: 26Anna Budzyńska et al.Gram-dodatn
- Page 32 and 33: 32Piotr Kamiński et al.Streszczeni
- Page 34 and 35: 34Piotr Kamiński et al.both in Pom
- Page 36 and 37: 36Piotr Kamiński et al.hemoglobin
- Page 39: Medical and Biological Sciences, 20
- Page 43 and 44: Medical and Biological Sciences, 20
- Page 45 and 46: Bone turnover during pregnancy 45ra
- Page 47: Bone turnover during pregnancy 47pl
- Page 50 and 51: 50Jan Styczyński, Anna Jaworska(p
- Page 52 and 53: 52Jan Styczyński, Anna JaworskaRES
- Page 55 and 56: Medical and Biological Sciences, 20
- Page 57 and 58: Analysis of immunophenotype at seco
- Page 59: Analysis of immunophenotype at seco
- Page 62 and 63: 62Ana-Maria ŠimundićINTRODUCTIOND
- Page 64 and 65: 64Ana-Maria ŠimundićThe shape of
- Page 67 and 68: Medical and Biological Sciences, 20
- Page 69 and 70: Quantitative anatomy of the aortic
- Page 71 and 72: Quantitative anatomy of the aortic
- Page 73 and 74: Medical and Biological Sciences, 20
- Page 75 and 76: Volumetric growth of various aortic
- Page 77 and 78: Volumetric growth of various aortic
- Page 79 and 80: Medical and Biological Sciences, 20
- Page 81 and 82: Effect of Low Level Laser Therapy a
- Page 83 and 84: Effect of Low Level Laser Therapy a
- Page 85 and 86: Medical and Biological Sciences, 20
- Page 87 and 88: Body weight support during treadmil
- Page 89 and 90: Body weight support during treadmil
- Page 91 and 92:
Medical and Biological Sciences, 20