Evaluation of Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Septic ... - Geoflow
Evaluation of Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Septic ... - Geoflow
Evaluation of Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Septic ... - Geoflow
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
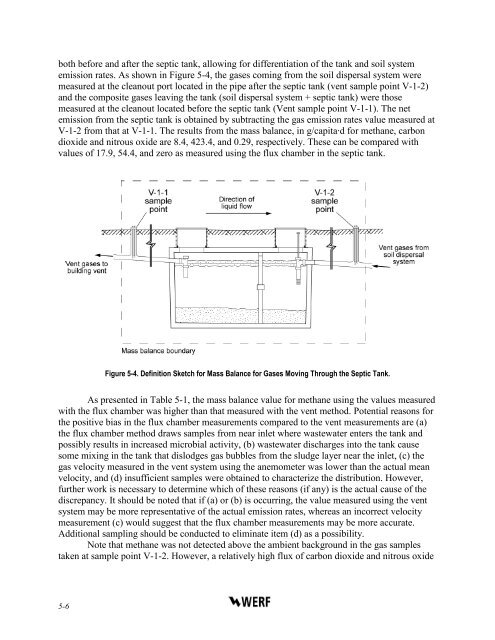
oth before and after the septic tank, allowing for differentiation <strong>of</strong> the tank and soil systememission rates. As shown in Figure 5-4, the gases coming <strong>from</strong> the soil dispersal system weremeasured at the cleanout port located in the pipe after the septic tank (vent sample point V-1-2)and the composite gases leaving the tank (soil dispersal system + septic tank) were thosemeasured at the cleanout located before the septic tank (Vent sample point V-1-1). The netemission <strong>from</strong> the septic tank is obtained by subtracting the gas emission rates value measured atV-1-2 <strong>from</strong> that at V-1-1. The results <strong>from</strong> the mass balance, in g/capita·d for methane, carbondioxide and nitrous oxide are 8.4, 423.4, and 0.29, respectively. These can be compared withvalues <strong>of</strong> 17.9, 54.4, and zero as measured using the flux chamber in the septic tank.Figure 5-4. Definition Sketch for Mass Balance for <strong>Gas</strong>es Moving Through the <strong>Septic</strong> Tank.As presented in Table 5-1, the mass balance value for methane using the values measuredwith the flux chamber was higher than that measured with the vent method. Potential reasons forthe positive bias in the flux chamber measurements compared to the vent measurements are (a)the flux chamber method draws samples <strong>from</strong> near inlet where wastewater enters the tank andpossibly results in increased microbial activity, (b) wastewater discharges into the tank causesome mixing in the tank that dislodges gas bubbles <strong>from</strong> the sludge layer near the inlet, (c) thegas velocity measured in the vent system using the anemometer was lower than the actual meanvelocity, and (d) insufficient samples were obtained to characterize the distribution. However,further work is necessary to determine which <strong>of</strong> these reasons (if any) is the actual cause <strong>of</strong> thediscrepancy. It should be noted that if (a) or (b) is occurring, the value measured using the ventsystem may be more representative <strong>of</strong> the actual emission rates, whereas an incorrect velocitymeasurement (c) would suggest that the flux chamber measurements may be more accurate.Additional sampling should be conducted to eliminate item (d) as a possibility.Note that methane was not detected above the ambient background in the gas samplestaken at sample point V-1-2. However, a relatively high flux <strong>of</strong> carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide5-6