- Page 1 and 2:
WHO/RHR/00.7Distr: GeneralIntegrate
- Page 4 and 5: ©World Health Organization, 2000Th
- Page 6 and 7: iiTable of contentsLoss of fetal mo
- Page 8 and 9: ivPreface
- Page 10 and 11: viIntroduction
- Page 12 and 13: viiiHow to use the manualprocedure,
- Page 14 and 15: xAbbreviations
- Page 16 and 17: xiiList of diagnoses
- Page 18 and 19: RAPID INITIAL ASSESSMENT C-1When a
- Page 20 and 21: Rapid initial assessmentC-3Abdomina
- Page 22 and 23: TALKING WITH WOMEN AND THEIR FAMILI
- Page 24 and 25: EMOTIONAL AND PSYCHOLOGICAL SUPPORT
- Page 26 and 27: Emotional and psychological support
- Page 28 and 29: Emotional and psychological support
- Page 30 and 31: Emotional and psychological support
- Page 33 and 34: C-16 Emotional and psychological su
- Page 35 and 36: C-16 Emergencies• If the woman is
- Page 37 and 38: C-18 General care principles- after
- Page 39 and 40: C-20 General care principlesaGloves
- Page 41 and 42: C-22 General care principles- weari
- Page 43 and 44: C-24 General care principles• Nev
- Page 45 and 46: C-24 Clinical use of blood, blood p
- Page 47 and 48: C-26 Clinical use of blood, blood p
- Page 49 and 50: C-28 Clinical use of blood, blood p
- Page 51 and 52: C-30 Clinical use of blood, blood p
- Page 53: C-32 Clinical use of blood, blood p
- Page 57 and 58: ANTIBIOTIC THERAPY C-35Infection du
- Page 59 and 60: ANAESTHESIA AND ANALGESIA C-37Pain
- Page 61 and 62: Anaesthesia and analgesiaC-39• Gi
- Page 63 and 64: Anaesthesia and analgesiaC-41TABLE
- Page 65 and 66: Anaesthesia and analgesiaC-43MANAGE
- Page 67 and 68: Anaesthesia and analgesiaC-45- Give
- Page 69 and 70: Anaesthesia and analgesiaC-47Proced
- Page 71 and 72: OPERATIVE CARE PRINCIPLES C-47The w
- Page 73 and 74: Operative care principlesC-49• Ho
- Page 75 and 76: Operative care principlesC-51HAEMOS
- Page 77 and 78: Operative care principlesC-53- Plac
- Page 79 and 80: Operative care principlesC-55A urin
- Page 81 and 82: NORMAL LABOUR AND CHILDBIRTH C-57NO
- Page 83 and 84: Normal labour and childbirthC-59- E
- Page 85 and 86: Normal labour and childbirthC-61•
- Page 87 and 88: Normal labour and childbirthC-63•
- Page 89 and 90: Normal labour and childbirthC-65•
- Page 91 and 92: Normal labour and childbirthC-67•
- Page 93 and 94: Normal labour and childbirthC-69FIG
- Page 95 and 96: Normal labour and childbirthC-71FIG
- Page 97 and 98: Normal labour and childbirthC-73•
- Page 99 and 100: Normal labour and childbirthC-75Not
- Page 101 and 102: Normal labour and childbirthC-77Nev
- Page 103 and 104: NEWBORN CARE PRINCIPLES C-77When a
- Page 105 and 106:
PROVIDER AND COMMUNITY LINKAGES C-7
- Page 107 and 108:
Provider and community linkagesC-81
- Page 109 and 110:
SHOCK S-1Shock is characterized by
- Page 111 and 112:
ShockS-3BEDSIDE CLOTTING TEST• As
- Page 113 and 114:
ShockS-5• If trauma is suspected
- Page 115 and 116:
VAGINAL BLEEDING IN EARLY PREGNANCY
- Page 117 and 118:
Vaginal bleeding in early pregnancy
- Page 119 and 120:
Vaginal bleeding in early pregnancy
- Page 121 and 122:
Vaginal bleeding in early pregnancy
- Page 123 and 124:
Vaginal bleeding in early pregnancy
- Page 125 and 126:
Vaginal bleeding in early pregnancy
- Page 127 and 128:
S-18 Vaginal bleeding in later preg
- Page 129 and 130:
S-20 Vaginal bleeding in later preg
- Page 131 and 132:
S-22 Vaginal bleeding in later preg
- Page 133 and 134:
S-24 Vaginal bleeding in later preg
- Page 135 and 136:
S-26 Vaginal bleeding after childbi
- Page 137 and 138:
S-28 Vaginal bleeding after childbi
- Page 139 and 140:
S-30 Vaginal bleeding after childbi
- Page 141 and 142:
S-32 Vaginal bleeding after childbi
- Page 143 and 144:
S-34 Vaginal bleeding after childbi
- Page 145 and 146:
HEADACHE, BLURRED VISION, CONVULSIO
- Page 147 and 148:
Headache, blurred vision, convulsio
- Page 149 and 150:
Headache, blurred vision, convulsio
- Page 151 and 152:
Headache, blurred vision, convulsio
- Page 153 and 154:
Headache, blurred vision, convulsio
- Page 155 and 156:
Headache, blurred vision, convulsio
- Page 157 and 158:
Headache, blurred vision, convulsio
- Page 159 and 160:
Headache, blurred vision, convulsio
- Page 161 and 162:
Headache, blurred vision, convulsio
- Page 163 and 164:
Headache, blurred vision, convulsio
- Page 165 and 166:
Headache, blurred vision, convulsio
- Page 167 and 168:
Headache, blurred vision, convulsio
- Page 169 and 170:
Headache, blurred vision, convulsio
- Page 171 and 172:
UNSATISFACTORY PROGRESS OF LABOUR S
- Page 173 and 174:
Unsatisfactory progress of labourS-
- Page 175 and 176:
Unsatisfactory progress of labourS-
- Page 177 and 178:
Unsatisfactory progress of labourS-
- Page 179 and 180:
Unsatisfactory progress of labourS-
- Page 181 and 182:
Unsatisfactory progress of labourS-
- Page 183 and 184:
MALPOSITIONS AND MALPRESENTATIONS S
- Page 185 and 186:
Malpositions and malpresentationsS-
- Page 187 and 188:
Malpositions and malpresentationsS-
- Page 189 and 190:
Malpositions and malpresentationsS-
- Page 191 and 192:
Malpositions and malpresentationsS-
- Page 193 and 194:
Malpositions and malpresentationsS-
- Page 195 and 196:
Malpositions and malpresentationsS-
- Page 197 and 198:
Malpositions and malpresentationsS-
- Page 199 and 200:
S-84 Shoulder dystociaFIGURE S-26As
- Page 201 and 202:
S-86 Shoulder dystocia
- Page 203 and 204:
S-88 Labour with an overdistended u
- Page 205 and 206:
S-90 Labour with an overdistended u
- Page 207 and 208:
S-92 Labour with an overdistended u
- Page 209 and 210:
S-94 Labour with a scarred uterus-
- Page 211 and 212:
S-96 Fetal distress in labour- If t
- Page 213 and 214:
S-98 Prolapsed cord- If breech pres
- Page 215 and 216:
S-100 Fever during pregnancy and la
- Page 217 and 218:
S-102 Fever during pregnancy and la
- Page 219 and 220:
S-104 Fever during pregnancy and la
- Page 221 and 222:
S-106 Fever during pregnancy and la
- Page 223 and 224:
FEVER AFTER CHILDBIRTH S-107PROBLEM
- Page 225 and 226:
Fever after childbirthS-109Presenti
- Page 227 and 228:
Fever after childbirthS-111aGive he
- Page 229 and 230:
Fever after childbirthS-113• If t
- Page 231 and 232:
Fever after childbirthS-115- apply
- Page 233 and 234:
Fever after childbirthS-117• Remo
- Page 235 and 236:
ABDOMINAL PAIN IN EARLY PREGNANCY S
- Page 237 and 238:
Abdominal pain in early pregnancyS-
- Page 239 and 240:
Abdominal pain in early pregnancyS-
- Page 241 and 242:
S-120 Abdominal pain in later pregn
- Page 243 and 244:
S-122 Abdominal pain in later pregn
- Page 245 and 246:
S-124 Abdominal pain in later pregn
- Page 247 and 248:
S-126 Abdominal pain in later pregn
- Page 249 and 250:
S-126 Difficulty in breathingDIAGNO
- Page 251 and 252:
S-128 Difficulty in breathing- Give
- Page 253 and 254:
S-130 Difficulty in breathing
- Page 255 and 256:
LOSS OF FETAL MOVEMENTS S-131PROBLE
- Page 257 and 258:
Loss of fetal movementsS-133• Alt
- Page 259 and 260:
PRELABOUR RUPTURE OF MEMBRANES S-13
- Page 261 and 262:
Prelabour rupture of membranesS-137
- Page 263 and 264:
Prelabour rupture of membranesS-139
- Page 265 and 266:
IMMEDIATE NEWBORN CONDITIONS OR S-1
- Page 267 and 268:
Immediate newborn conditions or pro
- Page 269 and 270:
Immediate newborn conditions or pro
- Page 271 and 272:
Immediate newborn conditions or pro
- Page 273 and 274:
Immediate newborn conditions or pro
- Page 275 and 276:
Immediate newborn conditions or pro
- Page 277 and 278:
SECTION 3PROCEDURES
- Page 279 and 280:
P-2 Paracervical blocktry again. Ne
- Page 281 and 282:
P-4 Pudendal blockFIGURE P-2Perinea
- Page 283 and 284:
P-6 Pudendal block• Inject 10 mL
- Page 285 and 286:
P-8 Local anaesthesia for caesarean
- Page 287 and 288:
P-10 Local anaesthesia for caesarea
- Page 289 and 290:
P-12 Spinal anaesthesia• If the n
- Page 291 and 292:
KETAMINE P-13TABLE P-5Indications a
- Page 293 and 294:
EXTERNAL VERSION P-15• Review for
- Page 295 and 296:
INDUCTION AND AUGMENTATION OF LABOU
- Page 297 and 298:
Induction and augmentation of labou
- Page 299 and 300:
Induction and augmentation of labou
- Page 301 and 302:
Induction and augmentation of labou
- Page 303 and 304:
Induction and augmentation of labou
- Page 305 and 306:
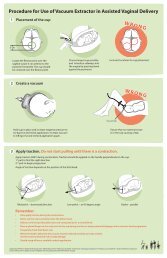
VACUUM EXTRACTION P-27Figure P-6 sh
- Page 307 and 308:
Vacuum extractionP-29• With the p
- Page 309 and 310:
Vacuum extractionP-31FAILURE• Vac
- Page 311 and 312:
FORCEPS DELIVERY P-33• Review for
- Page 313 and 314:
Forceps deliveryP-35- fetal heart r
- Page 315 and 316:
BREECH DELIVERY P-37• Review for
- Page 317 and 318:
Breech deliveryP-39• Hold the bab
- Page 319 and 320:
Breech deliveryP-41Note: Ask an ass
- Page 321 and 322:
Breech deliveryP-43extended at hip
- Page 323 and 324:
CAESAREAN SECTION P-43• Review fo
- Page 325 and 326:
Caesarean sectionP-45• Use two fi
- Page 327 and 328:
Caesarean sectionP-47• Hand the b
- Page 329 and 330:
Caesarean sectionP-49CLOSING THE AB
- Page 331 and 332:
Caesarean sectionP-51• Women with
- Page 333 and 334:
Caesarean sectionP-53• Grasp the
- Page 335 and 336:
P-54 SymphysiotomyAbduction of the
- Page 337 and 338:
P-56 Symphysiotomy• After separat
- Page 339 and 340:
P-58 Craniotomy and craniocentesis
- Page 341 and 342:
P-60 Craniotomy and craniocentesisA
- Page 343 and 344:
P-62 Dilatation and curettage- Take
- Page 345 and 346:
P-64 Dilatation and curettage- feve
- Page 347 and 348:
P-66 Manual vacuum aspiration• Di
- Page 349 and 350:
P-68 Manual vacuum aspiration• Qu
- Page 351 and 352:
CULDOCENTESIS AND COLPOTOMY P-69CUL
- Page 353 and 354:
Culdocentesis and colpotomyP-71•
- Page 355 and 356:
P-72 EpisiotomyFIGURE P-39Infiltrat
- Page 357 and 358:
P-74 Episiotomy- At the opening of
- Page 359 and 360:
P-76 Episiotomy
- Page 361 and 362:
P-78 Manual removal of placenta•
- Page 363 and 364:
P-80 Manual removal of placenta•
- Page 365 and 366:
P-2 Repair of cervical tears
- Page 367 and 368:
REPAIR OF VAGINAL AND PERINEAL TEAR
- Page 369 and 370:
P-84 Repair of vaginal and perineal
- Page 371 and 372:
P-86 Repair of vaginal and perineal
- Page 373 and 374:
P-88 Repair of vaginal and perineal
- Page 375 and 376:
P-90 Repair of vaginal and perineal
- Page 377 and 378:
CORRECTING UTERINE INVERSION P-91
- Page 379 and 380:
P-92 Correcting uterine inversionHY
- Page 381 and 382:
P-94 Correcting uterine inversion-
- Page 383 and 384:
P-96 Repair of ruptured uterus• S
- Page 385 and 386:
P-98 Repair of ruptured uterus• I
- Page 387 and 388:
UTERINE AND UTERO-OVARIAN ARTERY P-
- Page 389 and 390:
Uterine and utero-ovarian artery li
- Page 391 and 392:
POSTPARTUM HYSTERECTOMY P-103Postpa
- Page 393 and 394:
Postpartum hysterectomyP-105FIGURE
- Page 395 and 396:
Postpartum hysterectomyP-107• Clo
- Page 397 and 398:
Postpartum hysterectomyP-109POSTOPE
- Page 399 and 400:
P-110 Salpingectomy for ectopic pre
- Page 401 and 402:
P-112 Salpingectomy for ectopic pre
- Page 405 and 406:
INDEX A-3Abdominal distensiondiagno
- Page 407 and 408:
IndexA-5Atonic uterusdiagnosis, S-2
- Page 409 and 410:
IndexS-97transverse lie and, P-49tu
- Page 411 and 412:
IndexDescentassessment of, C-61Dext
- Page 413 and 414:
IndexFetal skull landmarks, C-62Fev
- Page 415 and 416:
Indexpostoperative care, P-108subto
- Page 417 and 418:
IndexA-15Maintenance fluid therapy,
- Page 419 and 420:
IndexA-17syphilis, management, S-15
- Page 421 and 422:
Indexgeneral management, S-25Pre-ec
- Page 423 and 424:
IndexA-21Stillbirthemotional consid
- Page 425 and 426:
IndexA-23anaesthesia options, C-45b