ILCD Handbook: Framework and requirements for LCIA models and ...
ILCD Handbook: Framework and requirements for LCIA models and ...
ILCD Handbook: Framework and requirements for LCIA models and ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>ILCD</strong> <strong>H<strong>and</strong>book</strong>: <strong>Framework</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>requirements</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>LCIA</strong> <strong>models</strong> <strong>and</strong> indicators First edition<br />
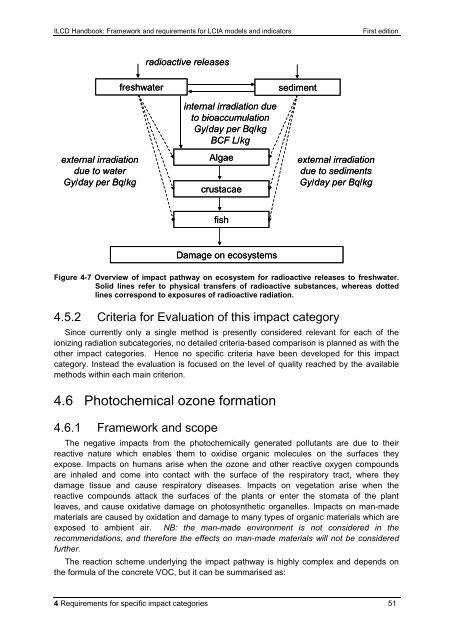
external irradiation<br />
due to water<br />
Gy/day per Bq/kg<br />
freshwater<br />
radioactive releases<br />
internal irradiation due<br />
to bioaccumulation<br />
Gy/day per Bq/kg<br />
BCF L/kg<br />
Algae<br />
crustacae<br />
fish<br />
Damage on ecosystems<br />
sediment<br />
external irradiation<br />
due to sediments<br />
Gy/day per Bq/kg<br />
Figure 4-7 Overview of impact pathway on ecosystem <strong>for</strong> radioactive releases to freshwater.<br />
Solid lines refer to physical transfers of radioactive substances, whereas dotted<br />
lines correspond to exposures of radioactive radiation.<br />
4.5.2 Criteria <strong>for</strong> Evaluation of this impact category<br />
Since currently only a single method is presently considered relevant <strong>for</strong> each of the<br />
ionizing radiation subcategories, no detailed criteria-based comparison is planned as with the<br />
other impact categories. Hence no specific criteria have been developed <strong>for</strong> this impact<br />
category. Instead the evaluation is focused on the level of quality reached by the available<br />
methods within each main criterion.<br />
4.6 Photochemical ozone <strong>for</strong>mation<br />
4.6.1 <strong>Framework</strong> <strong>and</strong> scope<br />
The negative impacts from the photochemically generated pollutants are due to their<br />
reactive nature which enables them to oxidise organic molecules on the surfaces they<br />
expose. Impacts on humans arise when the ozone <strong>and</strong> other reactive oxygen compounds<br />
are inhaled <strong>and</strong> come into contact with the surface of the respiratory tract, where they<br />
damage tissue <strong>and</strong> cause respiratory diseases. Impacts on vegetation arise when the<br />
reactive compounds attack the surfaces of the plants or enter the stomata of the plant<br />
leaves, <strong>and</strong> cause oxidative damage on photosynthetic organelles. Impacts on man-made<br />
materials are caused by oxidation <strong>and</strong> damage to many types of organic materials which are<br />
exposed to ambient air. NB: the man-made environment is not considered in the<br />
recommendations, <strong>and</strong> there<strong>for</strong>e the effects on man-made materials will not be considered<br />
further.<br />
The reaction scheme underlying the impact pathway is highly complex <strong>and</strong> depends on<br />
the <strong>for</strong>mula of the concrete VOC, but it can be summarised as:<br />
4 Requirements <strong>for</strong> specific impact categories 51