Druck-Materie 20b.qxd - JUWEL - Forschungszentrum Jülich
Druck-Materie 20b.qxd - JUWEL - Forschungszentrum Jülich
Druck-Materie 20b.qxd - JUWEL - Forschungszentrum Jülich
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
2. EXPERIMENTAL<br />
Methane hydrate was prepared by contacting methane gas with crashed ice in a high<br />
pressure container under a condition of pressure of5 MPa and temperature of 268K. The<br />
methane contents in the hydrate were at least 80% and contents of many of samples were<br />
around 90%. We prepared CH4-H2O and CH4-D2O, and also prepared H2O and D2O ice for<br />
comparison.<br />
Neutron scattering experiments were performed on the MARI spectrometer at ISIS, and<br />
on the LAM-80 at KENS. The energy resolution of LAM-80 is about 0.02 meV. The sample<br />
temperature was mainly about 12K. Higher temperatures were also examined on MARI to<br />
study the effect of the temperature on the rotational level, although the results are not described<br />
here..<br />
3. EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS<br />
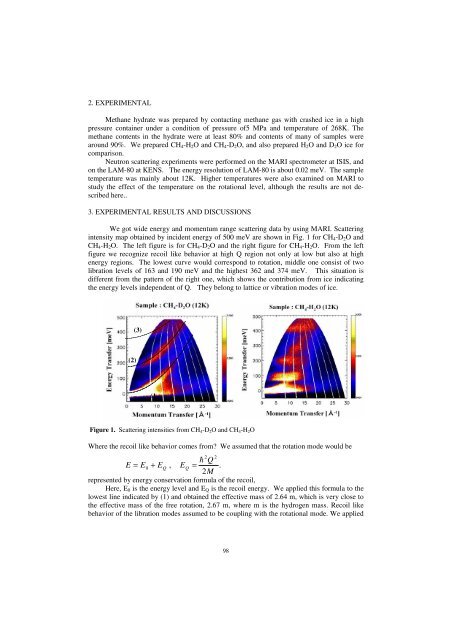
We got wide energy and momentum range scattering data by using MARI. Scattering<br />
intensity map obtained by incident energy of 500 meV are shown in Fig. 1 for CH4-D2O and<br />
CH4-H2O. The left figure is for CH4-D2O and the right figure for CH4-H2O. From the left<br />
figure we recognize recoil like behavior at high Q region not only at low but also at high<br />
energy regions. The lowest curve would correspond to rotation, middle one consist of two<br />
libration levels of 163 and 190 meV and the highest 362 and 374 meV. This situation is<br />
different from the pattern of the right one, which shows the contribution from ice indicating<br />
the energy levels independent of Q. They belong to lattice or vibration modes of ice.<br />
(2)<br />
(3)<br />
)<br />
(1<br />
Figure 1. Scattering intensities from CH4-D2O and CH4-H2O<br />
Where the recoil like behavior comes from? We assumed that the rotation mode would be<br />
2 2<br />
h Q<br />
E = E0<br />
+ EQ<br />
, EQ<br />
= .<br />
2M<br />
represented by energy conservation formula of the recoil,<br />
Here, E0 is the energy level and EQ is the recoil energy. We applied this formula to the<br />
lowest line indicated by (1) and obtained the effective mass of 2.64 m, which is very close to<br />
the effective mass of the free rotation, 2.67 m, where m is the hydrogen mass. Recoil like<br />
behavior of the libration modes assumed to be coupling with the rotational mode. We applied<br />
98