You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Non-metals, which lack only one or two electrons in the outer energy level have little tendency to<br />
lose electrons - the ionization potential would be very high. Instead non-metals have a tendency to<br />
gain electrons. The ELECTRON AFFINITY is the energy given off by an atom when it gains<br />
electrons.<br />
Non-metal Atom + e- --- Non-metal (-) ion + energy<br />
The energy required to produce positive ions (ionization potential) is roughly balanced by the energy<br />
given off to produce negative ions (electron affinity). The energy released by the net force of<br />
attraction by the ions provides the overall stabilizing energy of the compound.<br />
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zpaHPXVR8W U<br />
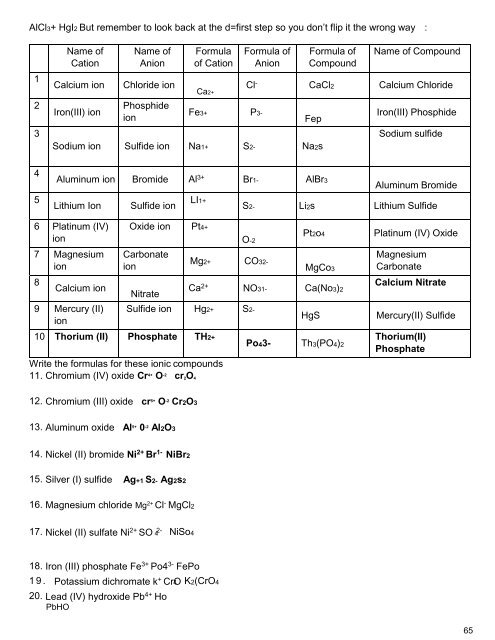
Writing Ionic Compounds<br />
An easy technique for creating a neutral combination of two charged ions is called the criss-cross<br />
technique. When writing a formula for an ionic compound the charges from each ion are simply<br />
switched to become the subscript values written to designate the number of atoms present in a<br />
compound. See the example below.<br />
Naming Ionic Compounds<br />
Naming Binary Ionic Compounds<br />
Learning to name ionic compounds is both easy and hard depending on the complexity of the<br />
compound. Before we start, though, I just wanted to review a few terms. Remember that positively<br />
charged ions are called cations. Negatively charged ions are called anions. An ionic compound is a<br />
compound held together by ionic bonds. A simple binary compound is just what it seems - a simple<br />
compound with two elements in it.<br />
Binary compounds are easy to name. The cation is always named first and gets its name from the<br />
name of the element. For example, K + is called a potassium ion. An anion also takes its name from<br />
its element, but it adds the suffix -ide to it. So, Cl - is called a chloride ion; O 2- is an oxide ion.<br />
Take the binary compound NaCl. The Na + is a sodium cation. The Cl - is a chlorine anion, which<br />
gets the suffix -ide added to it. When you put them together, it becomes sodium chloride. Here are<br />
some examples for you:<br />
Zn 2+ is zinc. S 2- is sulfide. Put them together for zinc sulfide (ZnS).<br />
63