(CRAM) For Wetlands User's Manual Version 5.0.2
(CRAM) For Wetlands User's Manual Version 5.0.2
(CRAM) For Wetlands User's Manual Version 5.0.2
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
California Rapid Assessment Method for <strong>Wetlands</strong> v. <strong>5.0.2</strong> – Chapter 4<br />
counted once when calculating the Number of Co-dominant Species for the AA. Ni matter how<br />
many layers a given species dominates, it should only be counted once as a co-dominant.<br />
4.4.1.3 Percent Invasion<br />
<strong>For</strong> the third submetric, Percent Invasion, the number of invasive co-dominant species for all<br />
plant layers combined is assessed as a percentage of the total number of co-dominants, based on<br />
the results of the Number of Co-dominant Species sub-metric. The invasive status for many<br />
California wetland and riparian plant species is based on the Cal-IPC list (Appendix V).<br />
However, the best professional judgment of local experts may be used instead to determine<br />
whether or not a co-dominant species is invasive. To the extent possible, photographs of known<br />
invasive plant species will be available through the e<strong>CRAM</strong> software to minimize the amount of<br />
botanical expertise needed to determine the status of co-dominant plants as invasive. If the<br />
status cannot be determined in the field, then a voucher specimen and field photographs of the<br />
plants in question should be used in conjunction with the Jepson <strong>Manual</strong> (Hickman 1993) or in<br />
consultation with appropriate experts to determine invasive status. Even if they appear in<br />
multiple layers plant species should only be counted once when calculating the Number of Codominant<br />
Species.<br />
4.4.1.4 Native Plant Species Richness<br />
This submetric only applies to Vernal Pools and Vernal Pool System. These wetlands are<br />
distinguished from all other wetland types by a unique native flora. This submetric is based on<br />
the total number of native plant species listed in Appendix V that appear in the AA. <strong>For</strong> Vernal<br />
Pool Systems, native species richness is assessed for all the replicate pools combined.<br />
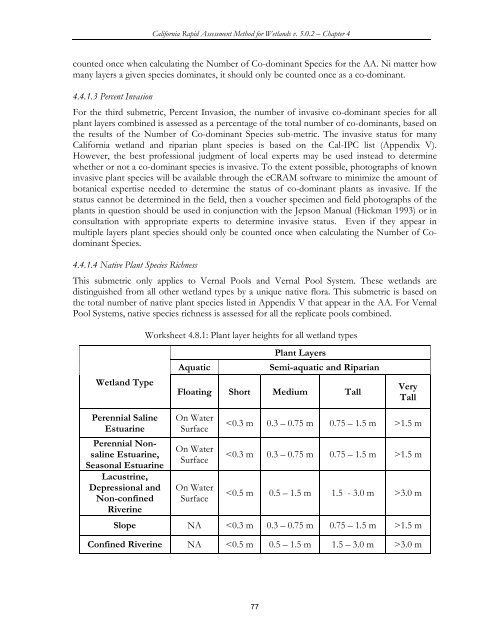
Wetland Type<br />
Perennial Saline<br />
Estuarine<br />
Perennial Nonsaline<br />
Estuarine,<br />
Seasonal Estuarine<br />
Lacustrine,<br />
Depressional and<br />
Non-confined<br />
Riverine<br />
Worksheet 4.8.1: Plant layer heights for all wetland types<br />
Plant Layers<br />
Aquatic Semi-aquatic and Riparian<br />
Floating Short Medium Tall<br />
On Water<br />
Surface<br />
On Water<br />
Surface<br />
On Water<br />
Surface<br />
77<br />
Very<br />
Tall<br />
1.5 m<br />
1.5 m<br />
3.0 m<br />
Slope NA 1.5 m<br />
Confined Riverine NA 3.0 m