Organizational Change for Participatory Irrigation Management
Organizational Change for Participatory Irrigation Management
Organizational Change for Participatory Irrigation Management
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
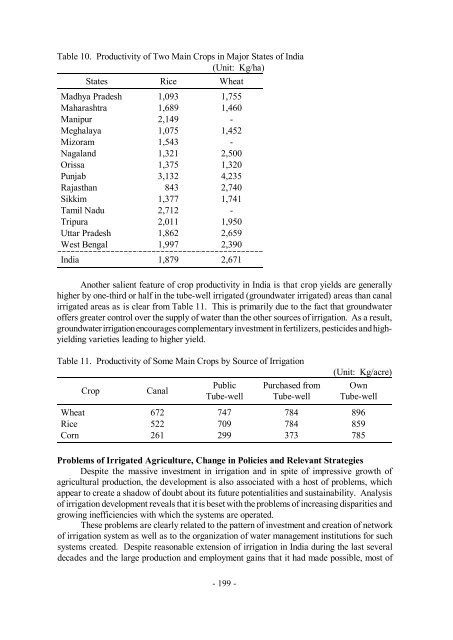
Table 10. Productivity of Two Main Crops in Major States of India<br />
(Unit: Kg/ha)<br />
States Rice Wheat<br />
Madhya Pradesh 1,093 1,755<br />
Maharashtra 1,689 1,460<br />
Manipur 2,149 -<br />
Meghalaya 1,075 1,452<br />
Mizoram 1,543 -<br />
Nagaland 1,321 2,500<br />
Orissa 1,375 1,320<br />
Punjab 3,132 4,235<br />
Rajasthan 843 2,740<br />
Sikkim 1,377 1,741<br />
Tamil Nadu 2,712 -<br />
Tripura 2,011 1,950<br />
Uttar Pradesh 1,862 2,659<br />
West Bengal 1,997 2,390<br />
India 1,879 2,671<br />
Another salient feature of crop productivity in India is that crop yields are generally<br />
higher by one-third or half in the tube-well irrigated (groundwater irrigated) areas than canal<br />
irrigated areas as is clear from Table 11. This is primarily due to the fact that groundwater<br />
offers greater control over the supply of water than the other sources of irrigation. As a result,<br />
groundwater irrigation encourages complementary investment in fertilizers, pesticides and highyielding<br />
varieties leading to higher yield.<br />
Table 11. Productivity of Some Main Crops by Source of <strong>Irrigation</strong><br />
Crop Canal<br />
Public<br />
Tube-well<br />
- 199 -<br />
Purchased from<br />
Tube-well<br />
(Unit: Kg/acre)<br />
Own<br />
Tube-well<br />
Wheat 672 747 784 896<br />
Rice 522 709 784 859<br />
Corn 261 299 373 785<br />
Problems of Irrigated Agriculture, <strong>Change</strong> in Policies and Relevant Strategies<br />
Despite the massive investment in irrigation and in spite of impressive growth of<br />
agricultural production, the development is also associated with a host of problems, which<br />
appear to create a shadow of doubt about its future potentialities and sustainability. Analysis<br />
of irrigation development reveals that it is beset with the problems of increasing disparities and<br />
growing inefficiencies with which the systems are operated.<br />
These problems are clearly related to the pattern of investment and creation of network<br />
of irrigation system as well as to the organization of water management institutions <strong>for</strong> such<br />
systems created. Despite reasonable extension of irrigation in India during the last several<br />
decades and the large production and employment gains that it had made possible, most of