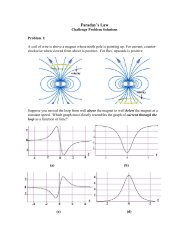
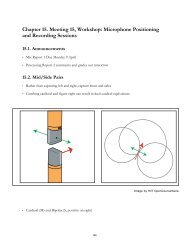
- Page 1 and 2:
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.e
- Page 3 and 4:
VNR Computer Library Advanced Topic
- Page 5 and 6:
To Ava andKaya for the patienceto s
- Page 7 and 8:
vi VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 9 and 10:
viE VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 11 and 12:
VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTEgS
- Page 14 and 15:
Speaking of Talk As we enter the ne
- Page 16 and 17:
Speaking ofTalk The short-term fix
- Page 18 and 19:
Preface This book began as graduate
- Page 20:
RFe[e ih This is just the beginning
- Page 23 and 24:
xxii VOICE OMMUNICEAIIO WITH COMPUT
- Page 25 and 26:
2 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTER
- Page 27 and 28:
4 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTEI
- Page 29 and 30:
6 VOICE (OMMUNICAIION WITH COMPUTER
- Page 31 and 32:
S YVOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 33 and 34:
10 VOICE COMMUHICATION WITH (OMPUIE
- Page 35 and 36:
12 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 37 and 38:
14 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 39 and 40:
16 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 41 and 42:
18 YVOII (OMMUNICATION WITH (OMPUTE
- Page 43 and 44:
20 VOIC[ COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 45 and 46:
22 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 47 and 48:
24 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 49 and 50:
26 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 51 and 52:
28 VOICE (OMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 53 and 54:
30 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH (OMPUTE
- Page 55 and 56:
32 VOICE (OMMUHICATIOI WITH (OMPUTE
- Page 57 and 58:
34 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 59 and 60:
3 Speech Coding This chapter introd
- Page 61 and 62:
38 VOICE (OMMUNICATlON WITH COMPUTE
- Page 63 and 64:
40 VOICE COMMURItATION WITH (OMPUTE
- Page 65 and 66:
42 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 67 and 68:
44 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 69 and 70:
46 VOICE (OMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 71 and 72:
48 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITi COMPUTE
- Page 73 and 74:
IT -010 !Mm1-tgq Vm-0 50 VOICE COMM
- Page 75 and 76:
52 VOICE (OMMUNICAlION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 77 and 78:
54 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 79 and 80:
56 VOICE COMMUNI(ATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 81 and 82:
58 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH (OMPUTE
- Page 83 and 84:
4 Applications and Editing of Store
- Page 85 and 86:
62 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 87 and 88:
64 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 89 and 90:
66 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 91 and 92:
68 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 93 and 94:
70 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 95 and 96:
72 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 97 and 98:
74 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 99 and 100:
76 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH (OMPUTE
- Page 101 and 102:
78 YOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 103 and 104:
80 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 105 and 106:
5 Speech Synthesis The previous two
- Page 107 and 108:
84 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 109 and 110:
6 YVOICE (OMMUNICATION WITH [OMPUTE
- Page 111 and 112:
n VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTER
- Page 113 and 114:
90 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 115 and 116:
92 VOICE (OMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 117 and 118:
94 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 119 and 120:
96 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 121 and 122:
98 VOICE COMMUlICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 123 and 124:
Interactive Voice Response This cha
- Page 125 and 126: 102 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 127 and 128: 104 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH (OMPUT
- Page 129 and 130: 106 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 131 and 132: 108 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 133 and 134: 110 VOICE (DMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 135 and 136: 112 VOICE COMMUNICATIOH WITH COMPUT
- Page 137 and 138: 114 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 139 and 140: 116 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 141 and 142: 118 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 143 and 144: 120 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 145 and 146: 122 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 147 and 148: 124 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 149 and 150: 126 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 151 and 152: 128 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 153 and 154: 13 VOICE COMMUNICAIIOR WITH COMPUTE
- Page 155 and 156: 7 Speech Recognition This chapter i
- Page 157 and 158: 134 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 159 and 160: 136 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 161 and 162: 138 VOICE (OMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 163 and 164: 140 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 165 and 166: 142 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 167 and 168: 144 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 169 and 170: 146 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 171 and 172: 148 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 173 and 174: 150 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 175: 152 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH (OMPUT
- Page 179 and 180: 156 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 181 and 182: In VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 183 and 184: 160 VOICE [OMMUHICATION WIITH OMPUT
- Page 185 and 186: 162 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 187 and 188: 164 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 189 and 190: 166 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 191 and 192: 168 VOICE COMMUNICAlION WITH COM IU
- Page 193 and 194: 170 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 195 and 196: 172 VOICE (OMMURICAION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 197 and 198: 174 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 199 and 200: 176 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 201 and 202: 178 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 203 and 204: 180 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 205 and 206: 182 OICE (COMMUNIICAION WITH COMPUT
- Page 207 and 208: 1I4 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 209 and 210: 186 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 211 and 212: 188 VOICE COMMUNICATION WIIH (OMPUT
- Page 213 and 214: 190 VOICE COMMUNICATION WIIH (OMPUT
- Page 215 and 216: 192 VOIC0 COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 217 and 218: 194 VOI(E COMMUNIATIION WITH (OMPUT
- Page 219 and 220: 196 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 221 and 222: 198 VOICI COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 223 and 224: 200 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 225 and 226: 202 VOICE COMMUNICATIOR WIIH COMPUT
- Page 227 and 228:
204 VOICE COMMUNICAIION WIlH COMPUT
- Page 229 and 230:
206 VOIC([ OMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 231 and 232:
20 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 233 and 234:
10 Basics of Telephones This and th
- Page 235 and 236:
212 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH (OMPUT
- Page 237 and 238:
214 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 239 and 240:
216 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUI
- Page 241 and 242:
218 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 243 and 244:
220 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 245 and 246:
222 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 247 and 248:
224 VOICE COMMUNICATION WIIH (OMPUT
- Page 249 and 250:
226 VOICE (COMMUNICATION WITH COMPU
- Page 251 and 252:
228 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 253 and 254:
11 Telephones and Computers The pre
- Page 255 and 256:
232 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 257 and 258:
214 VOICE COMMUHiCATION WITH COMPUI
- Page 259 and 260:
236 VOICE COMMUNICATIOK WITH COMPUT
- Page 261 and 262:
238 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 263 and 264:
240 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 265 and 266:
242 VOICE COMMUHICATIOI WITH COMPUI
- Page 267 and 268:
244 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 269 and 270:
246 VOICE (OMMUNICAIION WITH COMPUT
- Page 271 and 272:
248 VOICE (COMMUNICATION WITH COMPU
- Page 273 and 274:
250 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 275 and 276:
252 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 277 and 278:
254 VOICE COMMUNICAIION WITH COMPUT
- Page 279 and 280:
25 VOICE (OMMUNICATIOK WITH COMPUTE
- Page 281 and 282:
258 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 283 and 284:
260 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 285 and 286:
262 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 287 and 288:
264 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 289 and 290:
266 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 291 and 292:
12 Desktop Audio Because of limitat
- Page 293 and 294:
270 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 295 and 296:
2f2 VOICE COMMUIICAIION WITH COMPUT
- Page 297 and 298:
274 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 299 and 300:
276 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 301 and 302:
278 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 303 and 304:
280 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 305 and 306:
22 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUTE
- Page 307 and 308:
284 VOIC[ COMMIUWlATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 309 and 310:
286 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 311 and 312:
211 VOICE (OMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 313 and 314:
290 VOICE COMMIUNICATIO0 WITH COMPU
- Page 315 and 316:
292 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 317 and 318:
294 VOICE (OMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 319 and 320:
296 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 321 and 322:
298 VOICE (OMMUNICATION WITH (COMPU
- Page 323 and 324:
300 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 325 and 326:
302 VOICE COMMUNICATION WITH COMPUT
- Page 328 and 329:
Bibliography Ades, S. and D. C. Swi
- Page 330 and 331:
Biliograply o30 Daly, N. A. and V W
- Page 332 and 333:
Bib~lgraphy 309 Klatt, D. H. "Revie
- Page 334 and 335:
liblgraphy 311 G.Peterson, W. Wang,
- Page 336 and 337:
Bbliography 313 Spiegel, M. F "Usin
- Page 338 and 339:
Index p-law, 45, 220, 224 acoustics
- Page 340 and 341:
Integrated Services Digital Network
- Page 342:
vocal tract, 19-24, 23 voice mail,