Diploma thesis
Diploma thesis
Diploma thesis
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Material: KTP<br />
Polarizations: y → y + z<br />
400 nm → 800 nm + 800 nm<br />
Λ: 8.85 µm<br />
m: 1<br />
Pump FWHM: 1.5 nm<br />
Dimensions: 4 µm x 4 µm x 3.5 mm<br />
Table 3.3: Investigated crystal and pump parameters<br />
We define the loss in brightness as<br />
Iloss =<br />
� ∞ � ∞<br />
0<br />
dωs dωi e −2 (ω i −ω f )2<br />
2σ 2 f f(ωs, ωi) 2<br />
�0 ∞ � ∞<br />
dωs dωif(ωs, ωi) 2<br />
0<br />
0<br />
(3.56)<br />
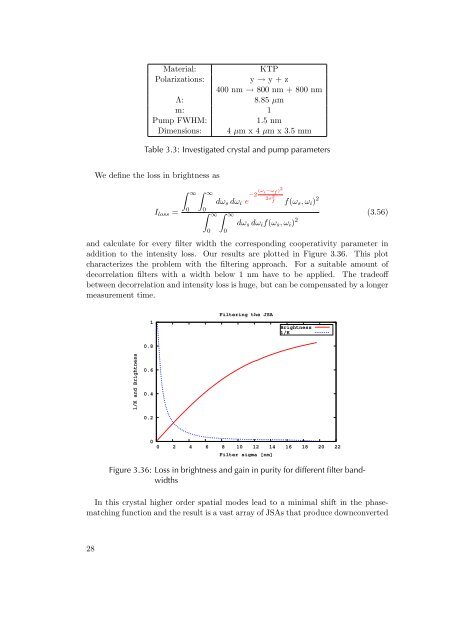
and calculate for every filter width the corresponding cooperativity parameter in<br />
addition to the intensity loss. Our results are plotted in Figure 3.36. This plot<br />
characterizes the problem with the filtering approach. For a suitable amount of<br />
decorrelation filters with a width below 1 nm have to be applied. The tradeoff<br />
between decorrelation and intensity loss is huge, but can be compensated by a longer<br />
measurement time.<br />
1/K and Brightness<br />
1<br />
0.8<br />
0.6<br />
0.4<br />
0.2<br />
Filtering the JSA<br />
0<br />
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22<br />
Filter sigma [nm]<br />
Brightness<br />
1/K<br />
Figure 3.36: Loss in brightness and gain in purity for different filter bandwidths<br />
In this crystal higher order spatial modes lead to a minimal shift in the phasematching<br />
function and the result is a vast array of JSAs that produce downconverted<br />
28