Diploma thesis
Diploma thesis
Diploma thesis
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
3 Theory<br />
3.1 Three-wave mixing<br />
Nonlinear optics is the science of light-matter and light-light interaction in nonlinear<br />
materials. Effects are ”nonlinear” in the sense that the response of the material<br />
depends nonlinearly upon the applied electric field. Interactions of this kind are<br />
embedded in a wide range of phenomena, from the Kerr-effect to frequency mixing<br />
processes. In this work, we focus solely on three-wave mixing processes.<br />
3.1.1 Sum frequency generation<br />
Since its discovery in 1961 by Franken et al. [13], second harmonic generation<br />
(SHG) or sum frequency generation (SFG) became one of the most commonly used<br />
nonlinear optical effects. Its use ranges from tiny green laser pointers to expensive<br />
mode locked pulsed Nd:YAG laser systems. SFG describes the combination of two<br />
photons to a third photon with higher energy, inside a nonlinear material, under<br />
the restrictions of energy and momentum conservation. In the special case of two<br />
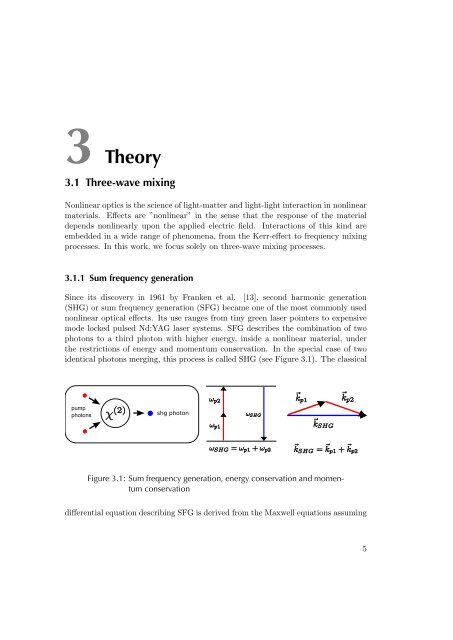
identical photons merging, this process is called SHG (see Figure 3.1). The classical<br />
Figure 3.1: Sum frequency generation, energy conservation and momentum<br />
conservation<br />
differential equation describing SFG is derived from the Maxwell equations assuming<br />
5