Capitolo_11-Generatori_di_segnali_sinusoidali
Capitolo_11-Generatori_di_segnali_sinusoidali
Capitolo_11-Generatori_di_segnali_sinusoidali
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
72 <strong>Capitolo</strong> <strong>11</strong><br />
Un'oscillazione <strong>di</strong> pulsazione W o può mantenersi nel tempo con ampiezza costante in un anello<br />
<strong>di</strong> reazione positiva se si verificano le seguenti con<strong>di</strong>zioni:<br />
ITJ / fiA (jwo) = 180 0 ,<br />
C[J /fiA(jw o ) = 0°,<br />
m/fiA (jwo) = 0°,<br />
[QJ /fiA(jwo) =0°,<br />
1 fiA (jwo) 1 > 1<br />
1 fiA(jw o ) 1 = 1<br />
1 fiA(jwo) 1 > l<br />
1 fiA (jwo) 1 < l<br />
Un oscillatore a sfasamento è <strong>di</strong> norma costituito da:<br />
ITJ un amplificatore invertente con una rete <strong>di</strong> reazione a tre celle CR.<br />
C[J un amplificatore non invertente con una rete <strong>di</strong> reazione RLC.<br />
m un amplificatore invertente con una rete <strong>di</strong> reazione a due celle CR.<br />
[QJ un amplificatore non invertente con una rete <strong>di</strong> reazione a tre celle CR.<br />
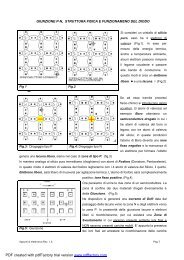
La struttura circuitale <strong>di</strong> figura (supposto per l'amplificatore Ri = 00, Ro = O):<br />
ITJ non può <strong>11</strong>1 alcun caso oscillare.<br />
C[J può oscillare solo sostituendo una bobina con una capacità.<br />
m potrebbe oscillare se l'amplificatore fosse non invertente.<br />
[QJ può entrare in oscillazione.<br />
L'oscillatore <strong>di</strong> Wien è formato da:<br />
ITJ un amplificatore invertente con una rete <strong>di</strong> reazione positiva RC passa-basso a due celle.<br />
C[J un amplificatore non invertente con una rete <strong>di</strong> reazione positiva RC passa-banda.<br />
m un amplificatore invertente con una rete <strong>di</strong> reazione positiva Re passa-banda.<br />
[QJ un amplificatore invertente con una rete <strong>di</strong> reazione positiva RLC.<br />
La frequenza <strong>di</strong> oscillazione fa <strong>di</strong> un oscillatore <strong>di</strong> Wien è espressa dalla seguente relazione:<br />
ITJ fa = 1/2n JLC<br />
C[J fa = 1/2n RC<br />
m lo = 1/2n fl/\c<br />
[QJ fa = 1/2n.)Re<br />
L