Dispensa di modelli lineari in R - Dipartimento di Statistica
Dispensa di modelli lineari in R - Dipartimento di Statistica
Dispensa di modelli lineari in R - Dipartimento di Statistica
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
CAPITOLO 5. COSTRUZIONE DEL MODELLO E ANALISI DEI RESIDUI 48<br />
Si può procedere ora con l’analisi grafica dei residui, mostrata <strong>in</strong> Figura 5.6.<br />
> par(mfrow = c(1, 2))<br />
> vento.rstand vento.fit plot(vento.fit, vento.rstand)<br />
> plot(w<strong>in</strong>d, vento.rstand)<br />
vento.rstand<br />
−2 −1 0 1<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
● ●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
● ●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5<br />
vento.fit<br />
−2 −1 0 1<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
● ●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
● ●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
4 6 8 10<br />
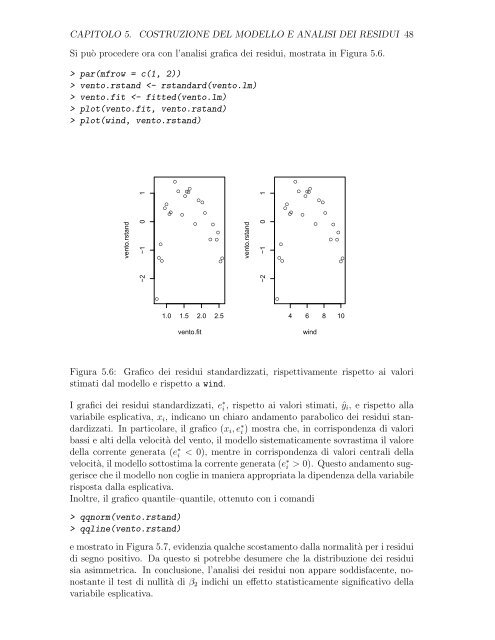
Figura 5.6: Grafico dei residui standar<strong>di</strong>zzati, rispettivamente rispetto ai valori<br />
stimati dal modello e rispetto a w<strong>in</strong>d.<br />
vento.rstand<br />
I grafici dei residui standar<strong>di</strong>zzati, e ∗ i , rispetto ai valori stimati, ˆyi, e rispetto alla<br />
variabile esplicativa, xi, <strong>in</strong><strong>di</strong>cano un chiaro andamento parabolico dei residui standar<strong>di</strong>zzati.<br />
In particolare, il grafico (xi, e ∗ i ) mostra che, <strong>in</strong> corrispondenza <strong>di</strong> valori<br />
bassi e alti della velocità del vento, il modello sistematicamente sovrastima il valore<br />
della corrente generata (e ∗ i < 0), mentre <strong>in</strong> corrispondenza <strong>di</strong> valori centrali della<br />
velocità, il modello sottostima la corrente generata (e ∗ i > 0). Questo andamento suggerisce<br />
che il modello non coglie <strong>in</strong> maniera appropriata la <strong>di</strong>pendenza della variabile<br />
risposta dalla esplicativa.<br />
Inoltre, il grafico quantile–quantile, ottenuto con i coman<strong>di</strong><br />
> qqnorm(vento.rstand)<br />
> qql<strong>in</strong>e(vento.rstand)<br />
e mostrato <strong>in</strong> Figura 5.7, evidenzia qualche scostamento dalla normalità per i residui<br />
<strong>di</strong> segno positivo. Da questo si potrebbe desumere che la <strong>di</strong>stribuzione dei residui<br />
sia asimmetrica. In conclusione, l’analisi dei residui non appare sod<strong>di</strong>sfacente, nonostante<br />
il test <strong>di</strong> nullità <strong>di</strong> β2 <strong>in</strong><strong>di</strong>chi un effetto statisticamente significativo della<br />
variabile esplicativa.<br />
w<strong>in</strong>d