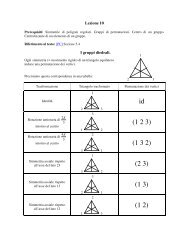
lucidi 5 - Dipartimento di Matematica
lucidi 5 - Dipartimento di Matematica
lucidi 5 - Dipartimento di Matematica
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Test della derivata prima<br />
Sia f : A → R una funzione continua e sia x 0 interno ad A can<strong>di</strong>dato<br />
punto <strong>di</strong> estremo locale. Supponiamo f derivabile vicino a x 0 .<br />
Se, per x vicino a x 0 , f ′ (x) ha segni <strong>di</strong>scor<strong>di</strong> a sinistra e a destra <strong>di</strong><br />
x 0 , allora x 0 è un punto <strong>di</strong> estremo locale. Precisamente:<br />
segno <strong>di</strong> f ′ segno <strong>di</strong> f ′ classificazione <strong>di</strong> x 0<br />
vicino a x 0 , a sinistra vicino a x 0 , a destra<br />
f ′ (x) > 0 f ′ (x) < 0 punto <strong>di</strong> massimo locale<br />
f ′ (x) < 0 f ′ (x) > 0 punto <strong>di</strong> minimo locale<br />
Se, per x vicino a x 0 , f ′ (x) ha lo stesso segno a sinistra e a destra <strong>di</strong><br />
x 0 , allora x 0 non è un punto <strong>di</strong> estremo locale.<br />
Esempio<br />
Classificare i can<strong>di</strong>dati punti <strong>di</strong> estremo locale per la funzione<br />
f 1 (x) = |x|(1 − x 2 ).<br />
23 / 35