Plant basal resistance - Universiteit Utrecht
Plant basal resistance - Universiteit Utrecht
Plant basal resistance - Universiteit Utrecht
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
113<br />
General discussion<br />
of Arabidopsis mutants in genes that are closely co-regulated with CYP81D11 at the gene<br />
expression level, e.g. At1g05560 (UGT1), At2g29420 (GSTU7), and At4g34138 (UGT73B1),<br />
might be an approach to identify other genes in the pathway.<br />
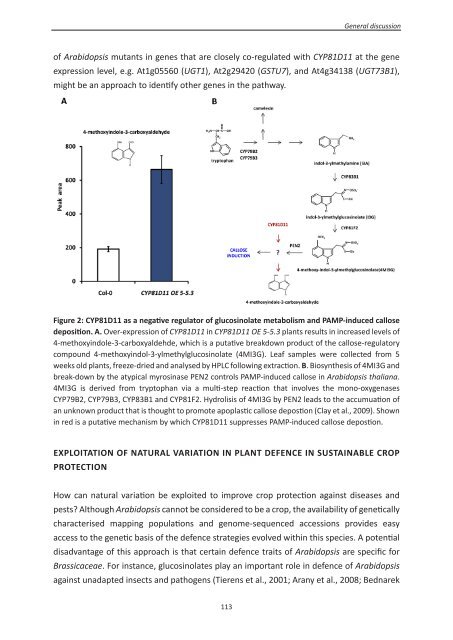
Figure 2: CYP81D11 as a negative regulator of glucosinolate metabolism and PAMP-induced callose<br />
deposition. A. Over-expression of CYP81D11 in CYP81D11 OE 5-5.3 plants results in increased levels of<br />
4-methoxyindole-3-carboxyaldehde, which is a putative breakdown product of the callose-regulatory<br />
compound 4-methoxyindol-3-ylmethylglucosinolate (4MI3G). Leaf samples were collected from 5<br />
weeks old plants, freeze-dried and analysed by HPLC following extraction. B. Biosynthesis of 4MI3G and<br />
break-down by the atypical myrosinase PEN2 controls PAMP-induced callose in Arabidopsis thaliana.<br />
4MI3G is derived from tryptophan via a multi-step reaction that involves the mono-oxygenases<br />
CYP79B2, CYP79B3, CYP83B1 and CYP81F2. Hydrolisis of 4MI3G by PEN2 leads to the accumuation of<br />
an unknown product that is thought to promote apoplastic callose depostion (Clay et al., 2009). Shown<br />
in red is a putative mechanism by which CYP81D11 suppresses PAMP-induced callose depostion.<br />
EXPLOITATION OF NATURAL VARIATION IN PLANT DEFENCE IN SUSTAINABLE CROP<br />
PROTECTION<br />
How can natural variation be exploited to improve crop protection against diseases and<br />
pests? Although Arabidopsis cannot be considered to be a crop, the availability of genetically<br />
characterised mapping populations and genome-sequenced accessions provides easy<br />
access to the genetic basis of the defence strategies evolved within this species. A potential<br />
disadvantage of this approach is that certain defence traits of Arabidopsis are specific for<br />
Brassicaceae. For instance, glucosinolates play an important role in defence of Arabidopsis<br />
against unadapted insects and pathogens (Tierens et al., 2001; Arany et al., 2008; Bednarek