Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Sensitivity analysis<br />
Table 79 shows the results of the sensitivity analysis using the 95% CI of effectiveness<br />
from the pooled analysis of treatment effect (pages 23 to 25) varying the costs of a<br />
doctor in attendance during treatment, the number of HBOT sessions per patient and<br />
the number of chambers in the facility.<br />
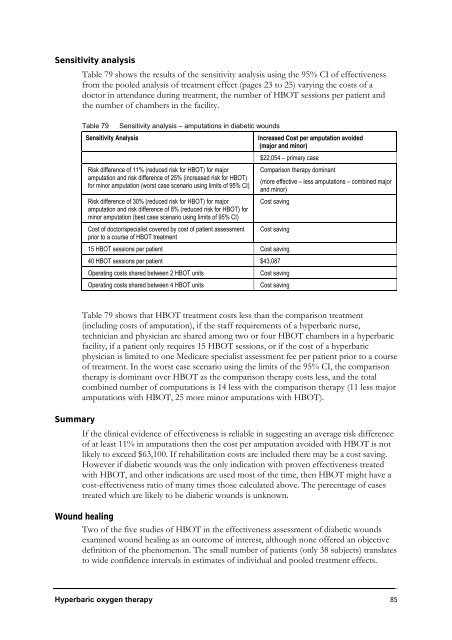
Table 79 Sensitivity analysis – amputations in diabetic wounds<br />
Sensitivity Analysis Increased Cost per amputation avoided<br />
(major and minor)<br />
Risk difference of 11% (reduced risk for HBOT) for major<br />
amputation and risk difference of 25% (increased risk for HBOT)<br />
for minor amputation (worst case scenario using limits of 95% CI)<br />
Risk difference of 30% (reduced risk for HBOT) for major<br />
amputation and risk difference of 8% (reduced risk for HBOT) for<br />
minor amputation (best case scenario using limits of 95% CI)<br />
Cost of doctor/specialist covered by cost of patient assessment<br />
prior to a course of HBOT treatment<br />
$22,054 – primary case<br />
Comparison therapy dominant<br />
(more effective – less amputations – combined major<br />
and minor)<br />
Cost saving<br />
Cost saving<br />
15 HBOT sessions per patient Cost saving<br />
40 HBOT sessions per patient $43,087<br />
Operating costs shared between 2 HBOT units Cost saving<br />
Operating costs shared between 4 HBOT units Cost saving<br />
Table 79 shows that HBOT treatment costs less than the comparison treatment<br />
(including costs of amputation), if the staff requirements of a hyperbaric nurse,<br />
technician and physician are shared among two or four HBOT chambers in a hyperbaric<br />
facility, if a patient only requires 15 HBOT sessions, or if the cost of a hyperbaric<br />
physician is limited to one Medicare specialist assessment fee per patient prior to a course<br />
of treatment. In the worst case scenario using the limits of the 95% CI, the comparison<br />
therapy is dominant over HBOT as the comparison therapy costs less, and the total<br />
combined number of computations is 14 less with the comparison therapy (11 less major<br />
amputations with HBOT, 25 more minor amputations with HBOT).<br />
Summary<br />
If the clinical evidence of effectiveness is reliable in suggesting an average risk difference<br />
of at least 11% in amputations then the cost per amputation avoided with HBOT is not<br />
likely to exceed $63,100. If rehabilitation costs are included there may be a cost saving.<br />
However if diabetic wounds was the only indication with proven effectiveness treated<br />
with HBOT, and other indications are used most of the time, then HBOT might have a<br />
cost-effectiveness ratio of many times those calculated above. The percentage of cases<br />
treated which are likely to be diabetic wounds is unknown.<br />
Wound healing<br />
Two of the five studies of HBOT in the effectiveness assessment of diabetic wounds<br />
examined wound healing as an outcome of interest, although none offered an objective<br />
definition of the phenomenon. The small number of patients (only 38 subjects) translates<br />
to wide confidence intervals in estimates of individual and pooled treatment effects.<br />
<strong>Hyperbaric</strong> oxygen therapy 85