Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
outcomes or that decreased the risk of harmful end-points will tend to make groups<br />
more similar to each other when these outcomes are eventually compared.<br />
If the assumption is made that the technology used in the delivery of hyperbaric oxygen<br />
was similar in the two studies, then the intervention protocols used by the two research<br />
groups differ only in the dose used. However, this difference is by a factor of 16. In the<br />
study by Stavitsky et al, 77 patients were exposed to HBO at 2 ATA for 2 hours. Thurston<br />
et al 78 reports exposure to HBO at the same pressure, but prescribed for 16 continuous<br />
three-hour cycles (2/3 under pressure).<br />
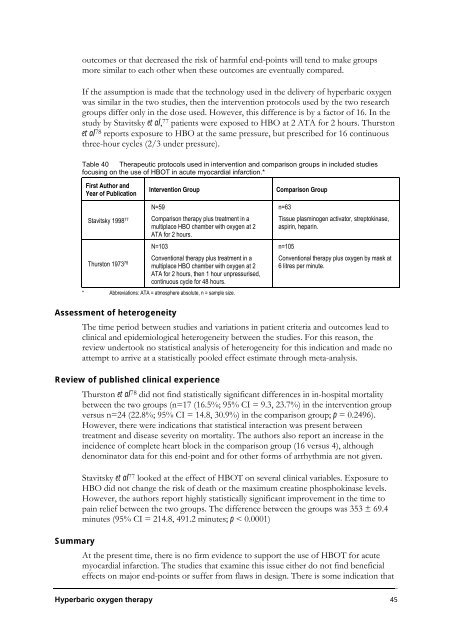
Table 40 Therapeutic protocols used in intervention and comparison groups in included studies<br />
focusing on the use of HBOT in acute myocardial infarction.*<br />
First Author and<br />
Year of Publication<br />
Stavitsky 1998 77<br />
Thurston 1973 78<br />
Intervention Group Comparison Group<br />
N=59<br />
Comparison therapy plus treatment in a<br />
multiplace HBO chamber with oxygen at 2<br />
ATA for 2 hours.<br />
N=103<br />
Conventional therapy plus treatment in a<br />
multiplace HBO chamber with oxygen at 2<br />
ATA for 2 hours, then 1 hour unpressurised,<br />
continuous cycle for 48 hours.<br />
* Abbreviations: ATA = atmosphere absolute, n = sample size.<br />
n=63<br />
Tissue plasminogen activator, streptokinase,<br />
aspirin, heparin.<br />
n=105<br />
Conventional therapy plus oxygen by mask at<br />
6 litres per minute.<br />
Assessment of heterogeneity<br />
The time period between studies and variations in patient criteria and outcomes lead to<br />
clinical and epidemiological heterogeneity between the studies. For this reason, the<br />
review undertook no statistical analysis of heterogeneity for this indication and made no<br />
attempt to arrive at a statistically pooled effect estimate through meta-analysis.<br />
Review of published clinical experience<br />
Thurston et al78 did not find statistically significant differences in in-hospital mortality<br />
between the two groups (n=17 (16.5%; 95% CI = 9.3, 23.7%) in the intervention group<br />
versus n=24 (22.8%; 95% CI = 14.8, 30.9%) in the comparison group; p = 0.2496).<br />
However, there were indications that statistical interaction was present between<br />
treatment and disease severity on mortality. The authors also report an increase in the<br />
incidence of complete heart block in the comparison group (16 versus 4), although<br />
denominator data for this end-point and for other forms of arrhythmia are not given.<br />
Stavitsky et al 77 looked at the effect of HBOT on several clinical variables. Exposure to<br />
HBO did not change the risk of death or the maximum creatine phosphokinase levels.<br />
However, the authors report highly statistically significant improvement in the time to<br />
pain relief between the two groups. The difference between the groups was 353 ± 69.4<br />
minutes (95% CI = 214.8, 491.2 minutes; p < 0.0001)<br />
Summary<br />
At the present time, there is no firm evidence to support the use of HBOT for acute<br />
myocardial infarction. The studies that examine this issue either do not find beneficial<br />
effects on major end-points or suffer from flaws in design. There is some indication that<br />
<strong>Hyperbaric</strong> oxygen therapy 45