Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
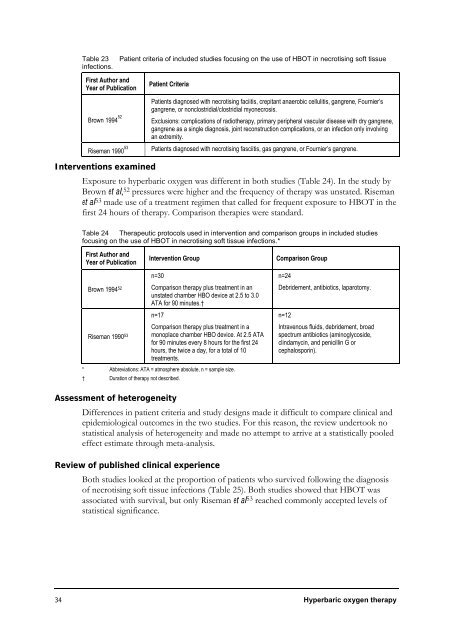
Table 23 Patient criteria of included studies focusing on the use of HBOT in necrotising soft tissue<br />
infections.<br />
First Author and<br />
Year of Publication<br />
Brown 1994 52<br />
Patient Criteria<br />
Patients diagnosed with necrotising faciitis, crepitant anaerobic cellulitis, gangrene, Fournier’s<br />
gangrene, or nonclostridial/clostridial myonecrosis.<br />
Exclusions: complications of radiotherapy, primary peripheral vascular disease with dry gangrene,<br />
gangrene as a single diagnosis, joint reconstruction complications, or an infection only involving<br />
an extremity.<br />
Riseman 1990 53 Patients diagnosed with necrotising fasciitis, gas gangrene, or Fournier’s gangrene.<br />
Interventions examined<br />
Exposure to hyperbaric oxygen was different in both studies (Table 24). In the study by<br />
Brown et al, 52 pressures were higher and the frequency of therapy was unstated. Riseman<br />
et al53 made use of a treatment regimen that called for frequent exposure to HBOT in the<br />
first 24 hours of therapy. Comparison therapies were standard.<br />
Table 24 Therapeutic protocols used in intervention and comparison groups in included studies<br />
focusing on the use of HBOT in necrotising soft tissue infections.*<br />
First Author and<br />
Year of Publication<br />
Brown 1994 52<br />
Riseman 1990 53<br />
Intervention Group Comparison Group<br />
n=30<br />
Comparison therapy plus treatment in an<br />
unstated chamber HBO device at 2.5 to 3.0<br />
ATA for 90 minutes.†<br />
n=17<br />
Comparison therapy plus treatment in a<br />
monoplace chamber HBO device. At 2.5 ATA<br />
for 90 minutes every 8 hours for the first 24<br />
hours, the twice a day, for a total of 10<br />
treatments.<br />
* Abbreviations: ATA = atmosphere absolute, n = sample size.<br />
† Duration of therapy not described.<br />
n=24<br />
Debridement, antibiotics, laparotomy.<br />
n=12<br />
Intravenous fluids, debridement, broad<br />
spectrum antibiotics (aminoglycoside,<br />
clindamycin, and penicillin G or<br />
cephalosporin).<br />
Assessment of heterogeneity<br />
Differences in patient criteria and study designs made it difficult to compare clinical and<br />
epidemiological outcomes in the two studies. For this reason, the review undertook no<br />
statistical analysis of heterogeneity and made no attempt to arrive at a statistically pooled<br />
effect estimate through meta-analysis.<br />
Review of published clinical experience<br />
Both studies looked at the proportion of patients who survived following the diagnosis<br />
of necrotising soft tissue infections (Table 25). Both studies showed that HBOT was<br />
associated with survival, but only Riseman et al53 reached commonly accepted levels of<br />
statistical significance.<br />
34 <strong>Hyperbaric</strong> oxygen therapy