Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
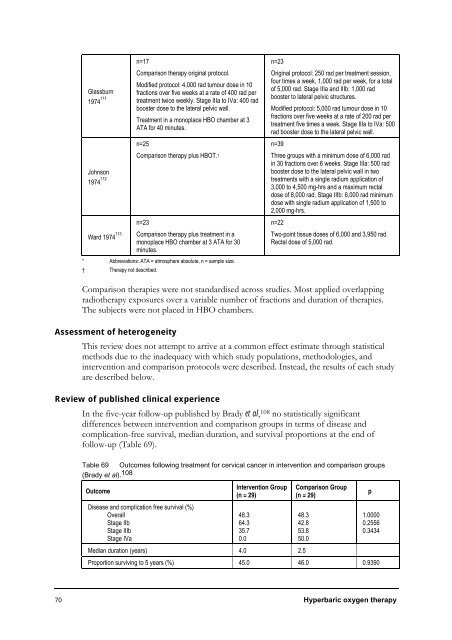
Glassburn<br />
1974 111<br />
Johnson<br />
1974 112<br />
Ward 1974 113<br />
n=17<br />
Comparison therapy original protocol.<br />
Modified protocol: 4,000 rad tumour dose in 10<br />
fractions over five weeks at a rate of 400 rad per<br />
treatment twice weekly. Stage IIIa to IVa: 400 rad<br />
booster dose to the lateral pelvic wall.<br />
Treatment in a monoplace HBO chamber at 3<br />
ATA for 40 minutes.<br />
n=25<br />
Comparison therapy plus HBOT. †<br />
n=23<br />
Comparison therapy plus treatment in a<br />
monoplace HBO chamber at 3 ATA for 30<br />
minutes.<br />
* Abbreviations: ATA = atmosphere absolute, n = sample size.<br />
† <strong>Therapy</strong> not described.<br />
n=23<br />
Original protocol: 250 rad per treatment session,<br />
four times a week, 1,000 rad per week, for a total<br />
of 5,000 rad. Stage IIIa and IIIb: 1,000 rad<br />
booster to lateral pelvic structures.<br />
Modified protocol: 5,000 rad tumour dose in 10<br />
fractions over five weeks at a rate of 200 rad per<br />
treatment five times a week. Stage IIIa to IVa: 500<br />
rad booster dose to the lateral pelvic wall.<br />
n=39<br />
Three groups with a minimum dose of 6,000 rad<br />
in 30 fractions over 6 weeks. Stage IIIa: 500 rad<br />
booster dose to the lateral pelvic wall in two<br />
treatments with a single radium application of<br />
3,000 to 4,500 mg-hrs and a maximum rectal<br />
dose of 8,000 rad. Stage IIIb: 6,000 rad minimum<br />
dose with single radium application of 1,500 to<br />
2,000 mg-hrs.<br />
n=22<br />
Two-point tissue doses of 6,000 and 3,950 rad.<br />
Rectal dose of 5,000 rad.<br />
Comparison therapies were not standardised across studies. Most applied overlapping<br />
radiotherapy exposures over a variable number of fractions and duration of therapies.<br />
The subjects were not placed in HBO chambers.<br />
Assessment of heterogeneity<br />
This review does not attempt to arrive at a common effect estimate through statistical<br />
methods due to the inadequacy with which study populations, methodologies, and<br />
intervention and comparison protocols were described. Instead, the results of each study<br />
are described below.<br />
Review of published clinical experience<br />
In the five-year follow-up published by Brady et al, 108 no statistically significant<br />
differences between intervention and comparison groups in terms of disease and<br />
complication-free survival, median duration, and survival proportions at the end of<br />
follow-up (Table 69).<br />
Table 69 Outcomes following treatment for cervical cancer in intervention and comparison groups<br />
(Brady et al). 108<br />
Outcome<br />
Disease and complication free survival (%)<br />
Overall<br />
Stage IIb<br />
Stage IIIb<br />
Stage IVa<br />
Intervention Group<br />
(n = 29)<br />
Comparison Group<br />
(n = 29)<br />
70 <strong>Hyperbaric</strong> oxygen therapy<br />
48.3<br />
64.3<br />
35.7<br />
0.0<br />
Median duration (years) 4.0 2.5<br />
48.3<br />
42.8<br />
53.8<br />
50.0<br />
p<br />
1.0000<br />
0.2556<br />
0.3434<br />
Proportion surviving to 5 years (%) 45.0 46.0 0.9390