Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
The different studies also applied varying doses of radiation to the affected region,<br />
ranging from 3,600 to 6,000 rads. Moreover, treatments were spread over differing<br />
numbers of days and used dissimilar fractions. In the study by Plenk, 117 patients were<br />
exposed to two different radiation doses and dosing schedules based on their exposure to<br />
HBO or air.<br />
Assessment of heterogeneity<br />
Due to the inadequacy with which study populations, methodologies, and intervention<br />
and comparison protocols were described, this review does not attempt to arrive at a<br />
common effect estimate through statistical methods. The results of each study are<br />
described below.<br />
Review of published clinical experience<br />
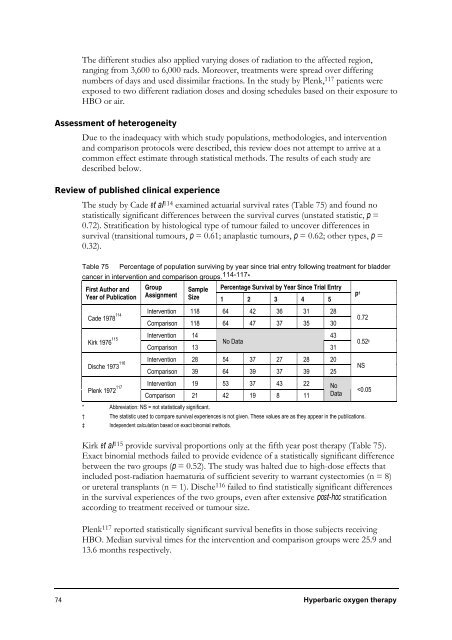
The study by Cade et al114 examined actuarial survival rates (Table 75) and found no<br />
statistically significant differences between the survival curves (unstated statistic, p =<br />
0.72). Stratification by histological type of tumour failed to uncover differences in<br />
survival (transitional tumours, p = 0.61; anaplastic tumours, p = 0.62; other types, p =<br />
0.32).<br />
Table 75 Percentage of population surviving by year since trial entry following treatment for bladder<br />
cancer in intervention and comparison groups. 114-117 *<br />
First Author and<br />
Year of Publication<br />
Group<br />
Assignment<br />
Sample<br />
Size<br />
Percentage Survival by Year Since Trial Entry<br />
1 2 3 4 5<br />
p †<br />
Cade 1978 114<br />
Kirk 1976 115<br />
Dische 1973 116<br />
Plenk 1972 117<br />
Intervention 118 64 42 36 31 28<br />
Comparison 118 64 47 37 35 30<br />
Intervention 14 43<br />
No Data<br />
Comparison 13<br />
31<br />
Intervention 28 54 37 27 28 20<br />
Comparison 39 64 39 37 39 25<br />
Intervention 19 53 37 43 22<br />
Comparison 21 42 19 8 11<br />
* Abbreviation: NS = not statistically significant.<br />
74 <strong>Hyperbaric</strong> oxygen therapy<br />
No<br />
Data<br />
† The statistic used to compare survival experiences is not given. These values are as they appear in the publications.<br />
‡ Independent calculation based on exact binomial methods.<br />
Kirk et al 115 provide survival proportions only at the fifth year post therapy (Table 75).<br />
Exact binomial methods failed to provide evidence of a statistically significant difference<br />
between the two groups (p = 0.52). The study was halted due to high-dose effects that<br />
included post-radiation haematuria of sufficient severity to warrant cystectomies (n = 8)<br />
or ureteral transplants (n = 1). Dische 116 failed to find statistically significant differences<br />
in the survival experiences of the two groups, even after extensive post-hoc stratification<br />
according to treatment received or tumour size.<br />
Plenk 117 reported statistically significant survival benefits in those subjects receiving<br />
HBO. Median survival times for the intervention and comparison groups were 25.9 and<br />
13.6 months respectively.<br />
0.72<br />
0.52 ‡<br />
NS<br />