Soil Management Handbook - Ministry of Agriculture and Lands
Soil Management Handbook - Ministry of Agriculture and Lands
Soil Management Handbook - Ministry of Agriculture and Lands
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
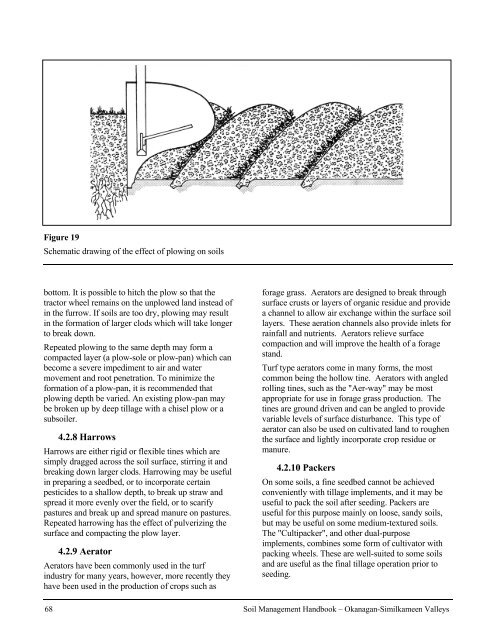
Figure 19<br />
Schematic drawing <strong>of</strong> the effect <strong>of</strong> plowing on soils<br />
bottom. It is possible to hitch the plow so that the<br />
tractor wheel remains on the unplowed l<strong>and</strong> instead <strong>of</strong><br />
in the furrow. If soils are too dry, plowing may result<br />
in the formation <strong>of</strong> larger clods which will take longer<br />
to break down.<br />
Repeated plowing to the same depth may form a<br />
compacted layer (a plow-sole or plow-pan) which can<br />
become a severe impediment to air <strong>and</strong> water<br />
movement <strong>and</strong> root penetration. To minimize the<br />
formation <strong>of</strong> a plow-pan, it is recommended that<br />
plowing depth be varied. An existing plow-pan may<br />
be broken up by deep tillage with a chisel plow or a<br />
subsoiler.<br />
4.2.8 Harrows<br />
Harrows are either rigid or flexible tines which are<br />
simply dragged across the soil surface, stirring it <strong>and</strong><br />
breaking down larger clods. Harrowing may be useful<br />
in preparing a seedbed, or to incorporate certain<br />
pesticides to a shallow depth, to break up straw <strong>and</strong><br />
spread it more evenly over the field, or to scarify<br />
pastures <strong>and</strong> break up <strong>and</strong> spread manure on pastures.<br />
Repeated harrowing has the effect <strong>of</strong> pulverizing the<br />
surface <strong>and</strong> compacting the plow layer.<br />
4.2.9 Aerator<br />
Aerators have been commonly used in the turf<br />
industry for many years, however, more recently they<br />
have been used in the production <strong>of</strong> crops such as<br />
forage grass. Aerators are designed to break through<br />
surface crusts or layers <strong>of</strong> organic residue <strong>and</strong> provide<br />
a channel to allow air exchange within the surface soil<br />
layers. These aeration channels also provide inlets for<br />
rainfall <strong>and</strong> nutrients. Aerators relieve surface<br />
compaction <strong>and</strong> will improve the health <strong>of</strong> a forage<br />
st<strong>and</strong>.<br />
Turf type aerators come in many forms, the most<br />
common being the hollow tine. Aerators with angled<br />
rolling tines, such as the "Aer-way" may be most<br />
appropriate for use in forage grass production. The<br />
tines are ground driven <strong>and</strong> can be angled to provide<br />
variable levels <strong>of</strong> surface disturbance. This type <strong>of</strong><br />
aerator can also be used on cultivated l<strong>and</strong> to roughen<br />
the surface <strong>and</strong> lightly incorporate crop residue or<br />
manure.<br />
4.2.10 Packers<br />
On some soils, a fine seedbed cannot be achieved<br />
conveniently with tillage implements, <strong>and</strong> it may be<br />
useful to pack the soil after seeding. Packers are<br />
useful for this purpose mainly on loose, s<strong>and</strong>y soils,<br />
but may be useful on some medium-textured soils.<br />
The "Cultipacker", <strong>and</strong> other dual-purpose<br />
implements, combines some form <strong>of</strong> cultivator with<br />
packing wheels. These are well-suited to some soils<br />
<strong>and</strong> are useful as the final tillage operation prior to<br />
seeding.<br />
68 <strong>Soil</strong> <strong>Management</strong> <strong>H<strong>and</strong>book</strong> – Okanagan-Similkameen Valleys