- Page 1 and 2:
TM Methods in Molecular Biology VOL
- Page 3 and 4:
4 Sachse 2. Selection of Target Seq
- Page 5 and 6:
Table 1 Target Sequences Used in PC
- Page 7 and 8:
8 Sachse Fig. 1. Structural organiz
- Page 9 and 10:
10 Sachse proteins (66-68), invasio
- Page 11 and 12:
12 Sachse Since there appears to be
- Page 13 and 14:
14 Sachse In the context of identif
- Page 15 and 16:
16 Sachse to partially compensate t
- Page 17 and 18:
18 Sachse nostic potential of PCR.
- Page 19 and 20:
20 Sachse product has to be confirm
- Page 21 and 22:
22 Sachse 7. van Camp, G., Fierens,
- Page 23 and 24:
24 Sachse 33. Rappelli, P., Are, R.
- Page 25 and 26:
26 Sachse 60. Furrer, B., Candrian,
- Page 27 and 28:
28 Sachse 89. Bloch, W. (1991) A bi
- Page 29 and 30:
30 Sachse
- Page 31 and 32:
32 Rådström et al. Fig. 1. Illust
- Page 33 and 34:
34 Rådström et al. immunoglobulin
- Page 35 and 36:
36 Rådström et al. and the captur
- Page 37 and 38:
Table 2 Comparison of the Performan
- Page 39 and 40:
40 Rådström et al. explain these
- Page 41 and 42:
42 Rådström et al. 5.1. Proteins
- Page 43 and 44:
44 Rådström et al. neous. Consequ
- Page 45 and 46:
46 Rådström et al. 11. Powell, H.
- Page 47 and 48:
48 Rådström et al. 39. Katcher, H
- Page 49 and 50:
50 Rådström et al. 73. Nagai, M.,
- Page 51 and 52:
52 Hoorfar and Cook 2. FOOD-PCR: A
- Page 53 and 54:
54 Hoorfar and Cook Fig. 2. Practic
- Page 55 and 56:
56 Hoorfar and Cook Fig. 4. The str
- Page 57 and 58:
Table 58 3 Hoorfar and Cook Test Co
- Page 59 and 60:
60 Hoorfar and Cook The choosing an
- Page 61 and 62:
62 Hoorfar and Cook 10. Demanding L
- Page 63 and 64:
64 Hoorfar and Cook 15. Anon. (1995
- Page 65 and 66:
66 Lübeck and Hoorfar ods for the
- Page 67 and 68:
68 Lübeck and Hoorfar amplificatio
- Page 69 and 70:
70 Lübeck and Hoorfar It may be ne
- Page 71 and 72:
72 Lübeck and Hoorfar specificity
- Page 73 and 74:
74 Lübeck and Hoorfar The latter i
- Page 75 and 76:
76 Lübeck and Hoorfar A simple che
- Page 77 and 78:
78 Lübeck and Hoorfar 13. Hanai, K
- Page 79 and 80:
80 Lübeck and Hoorfar 43. Mitchell
- Page 81 and 82:
82 Lübeck and Hoorfar 70. Lawrence
- Page 83 and 84:
84 Lübeck and Hoorfar 98. Lantz, P
- Page 85 and 86:
88 Frey Table 1 Presence of the Var
- Page 87 and 88:
90 Frey 13. Lysis buffer: 100 mM Tr
- Page 89 and 90:
92 Frey as template for PCR. In add
- Page 91 and 92:
94 Frey strains, including all sero
- Page 93 and 94:
96 Frey
- Page 95 and 96:
98 Ewalt and Bricker (named for the
- Page 97 and 98:
100 Ewalt and Bricker 4. Ethidium b
- Page 99 and 100:
102 Ewalt and Bricker Primer Cockta
- Page 101 and 102:
104 Ewalt and Bricker Fig. 2. Typic
- Page 103 and 104:
106 Ewalt and Bricker with betaine
- Page 105 and 106:
108 Ewalt and Bricker unused ethidi
- Page 107 and 108:
110 Englen et al. which campylobact
- Page 109 and 110:
112 Englen et al. 18. Dehydrated cu
- Page 111 and 112:
114 Englen et al. 3.1.3. Fecal Samp
- Page 113 and 114:
116 Englen et al. respectively), an
- Page 115 and 116:
118 Englen et al. Fig. 1. Identific
- Page 117 and 118:
120 Englen et al. 3. Goossens, H.,
- Page 119 and 120:
122 Englen et al.
- Page 121 and 122:
124 Sachse and Hotzel Table 1 Compa
- Page 123 and 124:
126 Sachse and Hotzel Table 2 Prime
- Page 125 and 126: 128 Sachse and Hotzel 7. Phenol: sa
- Page 127 and 128: 130 Sachse and Hotzel 4. Vortex mix
- Page 129 and 130: 132 Sachse and Hotzel Fig. 2. Speci
- Page 131 and 132: 134 Sachse and Hotzel In the latter
- Page 133 and 134: 136 Sachse and Hotzel 17. Longbotto
- Page 135 and 136: 138 Popoff spastic paralysis. The g
- Page 137 and 138: Table 3 Primers for Toxin Gene Dete
- Page 139 and 140: 142 Popoff 18. Agarose gel loading
- Page 141 and 142: 144 Popoff Taq reaction buffer 1X,
- Page 143 and 144: 146 Popoff almost all C. perfringen
- Page 145 and 146: 148 Popoff 2. Add to each PCR tube
- Page 147 and 148: 150 Popoff 7. Hielm, S., Hyyttia, E
- Page 149 and 150: 152 Popoff 35. Wieckowski, E., Bill
- Page 151 and 152: 154 Berri et al. 2. Materials 1. C.
- Page 153 and 154: 156 Berri et al. 3.3.2. Vaginal Swa
- Page 155 and 156: 158 Berri et al. Fig. 1. Trans-PCR.
- Page 157 and 158: 160 Berri et al. Fig. 3. Sensitivit
- Page 159 and 160: 162 Berri et al.
- Page 161 and 162: 164 Gallien The first description o
- Page 163 and 164: 166 Gallien
- Page 165 and 166: 168 Gallien 2. Materials 2.1. Bacte
- Page 167 and 168: 170 Gallien 10. Ethidium bromide: 1
- Page 169 and 170: Table 2 Components (in µL) of 25-
- Page 171 and 172: Table 4 Components (in µL) of 25-
- Page 173 and 174: 176 Gallien 3.3. Specific Isolation
- Page 175: Table 6 PCR Conditions for Subtypin
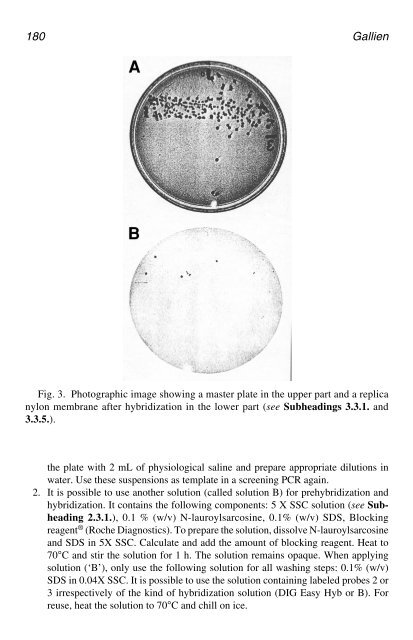
- Page 179 and 180: 182 Gallien 3. Boyce, T. G., Swerdl
- Page 181 and 182: 184 Gallien enteropathogenic E. col
- Page 183 and 184: 186 O'Connor This chapter will desc
- Page 185 and 186: 188 O'Connor 2.2. PCR of Enriched F
- Page 187 and 188: 190 O'Connor 4. Notes 1. In enrichi
- Page 189 and 190: 192 O'Connor 4. O’Sullivan, N., F
- Page 191 and 192: 194 Lester and LeFebvre titers (4).
- Page 193 and 194: 196 Lester and LeFebvre 3.1.2. Samp
- Page 195 and 196: Fig. 1. Sensitivity of the PCR assa
- Page 197 and 198: 200 Lester and LeFebvre 5. Swart, K
- Page 199 and 200: 202 Skuce et al. Table 1 Significan
- Page 201 and 202: 204 Skuce et al. commercial kits. E
- Page 203 and 204: 206 Skuce et al. Fig. 1. Schematic
- Page 205 and 206: 208 Skuce et al. 5. Disposable ster
- Page 207 and 208: 210 Skuce et al. 2.5.2. Sequence An
- Page 209 and 210: 212 Skuce et al. 2. Carefully trans
- Page 211 and 212: Table 4 Recommended PCR Amplificati
- Page 213 and 214: 216 Skuce et al. Fig. 3. PCR produc
- Page 215 and 216: 218 Skuce et al. Fig. 5. Spoligotyp
- Page 217 and 218: 220 Skuce et al. 14. Aranaz, A., Li
- Page 219 and 220: 222 Skuce et al.
- Page 221 and 222: 224 Khan Simultaneous detection of
- Page 223 and 224: 226 Khan 10. Incubate for 20 min at
- Page 225 and 226: 228 Khan 5. Periodically, multiplex
- Page 227 and 228:
230 Khan
- Page 229 and 230:
232 Hotzel et al. tis (2). Particul
- Page 231 and 232:
234 Hotzel et al. 8. Sodium dodecyl
- Page 233 and 234:
236 Hotzel et al. 3. Methods 3.1. D
- Page 235 and 236:
238 Hotzel et al. 3.1.5. Semen (see
- Page 237 and 238:
240 Hotzel et al. Fig. 1 Detection
- Page 239 and 240:
242 Hotzel et al. 4. Notes 1. The u
- Page 241 and 242:
244 Hotzel et al. in Mycoplasma Pro
- Page 243 and 244:
246 Hotzel et al.
- Page 245 and 246:
248 Kobisch and Frey PCR assay to d
- Page 247 and 248:
250 Kobisch and Frey Table 1 Oligon
- Page 249 and 250:
252 Kobisch and Frey 3.2.1. Prepara
- Page 251 and 252:
254 Kobisch and Frey First round of
- Page 253 and 254:
256 Kobisch and Frey References 1.
- Page 255 and 256:
258 Christensen et al. thrombotic m
- Page 257 and 258:
260 Christensen et al. Table 1 Spec
- Page 259 and 260:
Table 2 Oligonucleotide Primers for
- Page 261 and 262:
264 Christensen et al. 3.2. Extract
- Page 263 and 264:
Table 3 PCR Protocols for the Patho
- Page 265 and 266:
268 Christensen et al. 2. Apply fra
- Page 267 and 268:
270 Christensen et al. 7. To reduce
- Page 269 and 270:
272 Christensen et al. 24. Fisher,
- Page 271 and 272:
274 Christensen et al. 54. Hunt, M.
- Page 273 and 274:
276 Malorny and Helmuth valent meta
- Page 275 and 276:
278 Malorny and Helmuth 12. Apparat
- Page 277 and 278:
280 Malorny and Helmuth 3.3. Amplif
- Page 279 and 280:
282 Malorny and Helmuth Table 2 Vol
- Page 281 and 282:
284 Malorny and Helmuth Table 4 PCR
- Page 283 and 284:
286 Malorny and Helmuth 3. Wallace,
- Page 285 and 286:
288 Malorny and Helmuth
- Page 287 and 288:
290 Wastling and Mattsson is an imp
- Page 289 and 290:
292 Wastling and Mattsson 2. Remove
- Page 291 and 292:
294 Wastling and Mattsson Fig. 1. B
- Page 293 and 294:
296 Wastling and Mattsson time PCR
- Page 295 and 296:
298 Wastling and Mattsson
- Page 297 and 298:
300 Pozio and La Rosa Table 1 Princ
- Page 299 and 300:
302 Pozio and La Rosa regions; spot
- Page 301 and 302:
304 Pozio and La Rosa 3. Proteinase
- Page 303 and 304:
306 Pozio and La Rosa Table 3 PCR-R
- Page 305 and 306:
308 Pozio and La Rosa 2. Pepsin sho
- Page 307 and 308:
310 Pozio and La Rosa
- Page 309 and 310:
312 Knutsson and Rådström The ref
- Page 311 and 312:
314 Knutsson and Rådström Fig. 1.
- Page 313 and 314:
316 Knutsson and Rådström 2.4. El
- Page 315 and 316:
318 Knutsson and Rådström the swa
- Page 317 and 318:
320 Knutsson and Rådström Fig. 3.
- Page 319 and 320:
322 Knutsson and Rådström 4. Alek
- Page 321:
324 Knutsson and Rådström 34. Hee