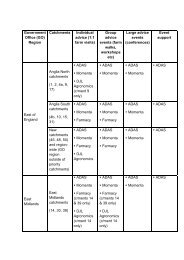
Review of the Food-borne Zoonoses Research ... - ARCHIVE: Defra
Review of the Food-borne Zoonoses Research ... - ARCHIVE: Defra
Review of the Food-borne Zoonoses Research ... - ARCHIVE: Defra
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
to elucidate <strong>the</strong> antigenic repertoire <strong>of</strong> this bacterium at one antigen locus, will provide an<br />
accurate, comprehensive, and portable typing system for C. jejuni and related organisms,<br />
with a firm <strong>the</strong>oretical basis in bacterial population biology.<br />
OZ0611<br />
Campylobacter is <strong>the</strong> most common cause <strong>of</strong> bacterial infectious intestinal disease in <strong>the</strong><br />
UK. Although various risk factors for infection, including consumption <strong>of</strong> undercooked<br />
poultry or unpasteurised milk have been identified, <strong>the</strong> epidemiology <strong>of</strong> this disease<br />
remains poorly understood. This is because (i) outbreaks are rarely detected, hence<br />
valuable information on sources and transmission routes which is obtained from outbreak<br />
investigations is generally lacking, and (ii) Campylobacter genomes are genetically<br />
diverse, and unstable, with frequent inter and intragenomic recombination, toge<strong>the</strong>r with<br />
phase variation, which complicates <strong>the</strong> interpretation <strong>of</strong> data from many typing methods.<br />
However, a suitable typing techniqe is multilocus sequence typing (MLST). MLST for<br />
Campylobacter jejuni, toge<strong>the</strong>r with a comprehensive internet accessible MLST database<br />
(http://pubmlst.org/campylobacter/) was developed with DEFRA support (contract<br />
number: OZ0604). MLST <strong>of</strong>fers advantages over previous typing techniques including<br />
100% typeability, reproducibility, and <strong>the</strong> straightforward sharing <strong>of</strong> data via <strong>the</strong> internet.<br />
The Campylobacter MLST database now contains 4434 isolates (29 th May 2007) and<br />
provides a resource for <strong>the</strong> scientific, public health, and veterinary communities as well<br />
as <strong>the</strong> food industry. Database submissions are received from laboratories<br />
internationally. The database is curated to ensure quality control, and additional MLST<br />
schemes and databases have been set up for o<strong>the</strong>r Campylobacter species including C.<br />
coli, C. fetus and C. lari. If it is to continue, and undergo fur<strong>the</strong>r expansion, this program<br />
<strong>of</strong> work will require continued support.<br />
<strong>Review</strong> Summary<br />
The work performed in OZ0604 and OZ0611 has been <strong>of</strong> fundamental importance in<br />
developing and applying a robust molecular typing method to Campylobacter. Adoption<br />
<strong>of</strong> MLST for Campylobacter at an international level demonstrates <strong>the</strong> strength <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
work performed.<br />
As OZ0611 comes to an end and fur<strong>the</strong>r work is considered, it is important that <strong>the</strong> MLST<br />
database is populated with campylobacters <strong>of</strong> public health importance. In addition, when<br />
selecting environmental isolates, quantity, source, geographical, and temporal factors<br />
must all be taken into account to ensure <strong>the</strong> database is not biased. The database must<br />
<strong>the</strong>n be interrogated to identify sources <strong>of</strong> human infection and <strong>the</strong>refore where<br />
interventions will have <strong>the</strong> greatest impact.<br />
72