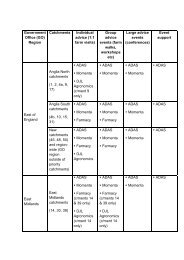
Review of the Food-borne Zoonoses Research ... - ARCHIVE: Defra
Review of the Food-borne Zoonoses Research ... - ARCHIVE: Defra
Review of the Food-borne Zoonoses Research ... - ARCHIVE: Defra
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Review</strong> summary<br />
While poultry meat is generally accepted as <strong>the</strong> primary source <strong>of</strong> infection for cases <strong>of</strong><br />
human campylobacteriosis, <strong>the</strong>re is also evidence to suggest that a significant proportion<br />
<strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>se infections originate from alternative sources. The primary aim <strong>of</strong> this project was<br />
to determine carriage <strong>of</strong> Campylobacter spp. by <strong>the</strong> UK dog population, and any risk this<br />
may cause to human health.<br />
Results to-date indicate that dogs are not an important source <strong>of</strong> C. jejuni or C. coli, <strong>the</strong><br />
common cause <strong>of</strong> infection in humans. C. upsaliensis was <strong>the</strong> most common<br />
campylobacter species detected in dogs. While this organism is zoonotic, it is recovered<br />
much less frequently from human campylobacter infections.<br />
86