Review of the Food-borne Zoonoses Research ... - ARCHIVE: Defra
Review of the Food-borne Zoonoses Research ... - ARCHIVE: Defra
Review of the Food-borne Zoonoses Research ... - ARCHIVE: Defra
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
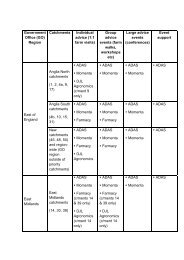
Project code:<br />
VTEC O157 <strong>Research</strong> Projects<br />
OZ0703<br />
Project title: Plant antibody delivery <strong>of</strong> passive immunisation<br />
against E. coli O157:H7: a novel means <strong>of</strong> control in<br />
<strong>the</strong> animal<br />
Start date (dd/mm/yy): 01/09/1999<br />
End date (dd/mm/yy): 01/06/2003<br />
£354,108<br />
Total cost:<br />
Affiliation: Veterinary Laboratories Agency<br />
Sub-contractor(s): ADAS Consulting<br />
Abstract <strong>of</strong> research<br />
Biology Department, University <strong>of</strong> Leicester<br />
Intimin, TIR and EspA proteins are expressed by Enterohaemorrhagic E. coli O157:H7.<br />
EspA proteins are part <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> type three secretion system needle complex that delivers<br />
TIR to <strong>the</strong> host epi<strong>the</strong>lial cell whilst surface arrayed intimin docks <strong>the</strong> bacterium to <strong>the</strong><br />
translocated TIR. This process leads to intimate attachment resulting in attaching and<br />
effacing lesions which are essential for colonisation and persistence in ruminants.<br />
Recombinant forms <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>se effector proteins from E. coli O157:H7 were produced and<br />
used to elicit immune responses in rabbits and immune phage-display antibody libraries<br />
were produced. Screening <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>se immune libraries by phage-antibody panning and<br />
colony filter screening produced a panel <strong>of</strong> antibodies with specificity for EspA or intimin.<br />
Antibodies recognising different C-terminal epitopes on intimin bound specifically to <strong>the</strong><br />
gamma intimin <strong>of</strong> O157:H7 and not to o<strong>the</strong>r classes <strong>of</strong> intimin whereas antibodies raised<br />
against EspA recognised EspA analogues from o<strong>the</strong>r serotypes also. Anti-intimin<br />
antibodies were also produced as fusion proteins coupled to <strong>the</strong> reporter molecule<br />
alkaline phosphatase, allowing <strong>the</strong> one-step detection <strong>of</strong> γ-intimin. The isolated<br />
recombinant monoclonal antibodies were functional in a range <strong>of</strong> assay formats including<br />
ELISA, Western blot and dot blots demonstrating diagnostic potential.<br />
We assessed whe<strong>the</strong>r <strong>the</strong>se antibody constructs could be used to disrupt <strong>the</strong> intimate<br />
association <strong>of</strong> E. coli O157:H7 with <strong>the</strong> host cell but nei<strong>the</strong>r anti-γ intimin or anti-EspA<br />
antibodies did so although <strong>the</strong> anti-EspA antibodies significantly reduced <strong>the</strong> extent <strong>of</strong> E.<br />
coli O157:H7-induced host cell actin rearrangement. In tests with traditionally made<br />
antibodies, both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies completely blocked adherence<br />
and cytoskeletal changes within <strong>the</strong> host cell. Both polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies<br />
could be used to label E. coli O157 EspA filaments and <strong>the</strong>se immunoreagents did not<br />
inhibit <strong>the</strong> formation <strong>of</strong> such filaments. This is <strong>the</strong> first report <strong>of</strong> monoclonal antibodies to<br />
EspA capable <strong>of</strong> disrupting <strong>the</strong> TTSS function <strong>of</strong> E. coli O157:H7.<br />
87