Research Report 2010 2011 - Helmholtz-Zentrum für ...
Research Report 2010 2011 - Helmholtz-Zentrum für ...
Research Report 2010 2011 - Helmholtz-Zentrum für ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
78 SCIENTIFIC REPORTS | Infection and Immunity | Microbial Pathogenesis<br />
01.10 Molecular Mechanisms of Host-cell Pathogen<br />
Interactions<br />
PROJECT LEADER | Prof. Dr. Klemens Rottner | Former <strong>Research</strong> Group Cytoskeleton Dynamics |<br />
krottner@uni-bonn.de<br />
PROJECT MEMBERS | Dr. Jennifer Block | Dr. Stefan Köstler | Markus Ladwein | Margit Oelkers |<br />
Dr. Malgorzata Szczodrak<br />
This project aims at characterising the precise molecular<br />
mechanisms driving actin reorganisation during different<br />
types of motility processes and the interaction of different<br />
pathogens with their hosts.<br />
Actin polymerisation is catalysed by protein complexes<br />
enhancing actin filament nucleation, such as the Arp2/3-<br />
complex or formins. Prominent important actin regulators<br />
include activators of Arp2/3-complex, e.g. WASP and<br />
WAVE family members, which can operate downstream<br />
of the Rho-GTPases Cdc42 and Rac1. Novel members of<br />
this Arp2/3-complex activators include proteins of the<br />
WHAMM/JMY subfamily and WASH (Rottner et al., <strong>2010</strong>),<br />
the latter of which we could recently identify to contribute<br />
to Salmonella invasion (Hänisch et al., <strong>2010</strong>).<br />
Another prominent Arp2/3-complex binding protein that<br />
had previously been implicated in dynamic actin reorganization<br />
events such as lamellipodium protrusion or different<br />
types of host-pathogen interaction is the Src-substrate<br />
cortactin. We have generated cells and mice harbouring a<br />
conditional mutation of the cortactin gene. To our surprise,<br />
genetic removal of cortactin in fibroblasts did not abolish<br />
Arp2/3-complex activation and actin polymerization<br />
stimulated by constitutively active Rac1. However, cortactin<br />
deletion abrogated signal transduction to activation of<br />
Rac or Cdc42 small GTPases, for instance downstream of<br />
growth factor activation, thus affecting migration and actin<br />
reorganization more indirectly than previously thought (Lai<br />
et al., 2009).<br />
These results are consistent with more recent data obtained<br />
by employing a novel actin assembly assay that we could<br />
recently develop. We demonstrated that cortactin is incapable<br />
of driving Arp2/3-complex-dependent actin assembly<br />
at ectopic sites in living cytoplasm (Oelkers et al., submitted).<br />
They also confirmed our previous data on the relative<br />
turnover of cortactin and Arp2/3-complex in the lamellipodium,<br />
which had already indicated that the majority of the<br />
cortactin molecules associating with the structure cannot<br />
engage in Arp2/3-complex activation at the lamellipodium<br />
tip (Lai et al., 2008).<br />
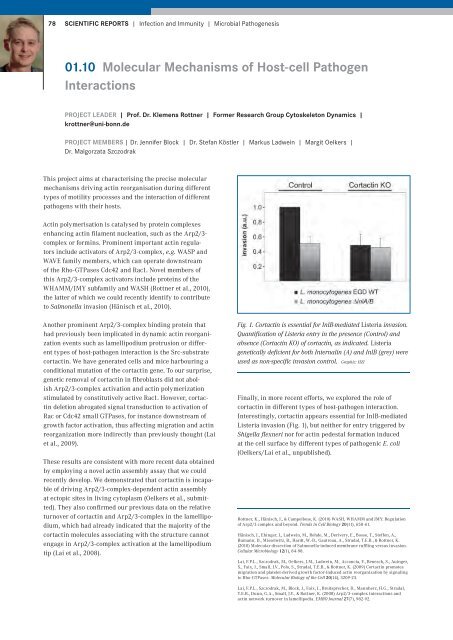
Fig. 1. Cortactin is essential for InlB-mediated Listeria invasion.<br />
Quantification of Listeria entry in the presence (Control) and<br />
absence (Cortactin KO) of cortactin, as indicated. Listeria<br />
genetically deficient for both Internalin (A) and InlB (grey) were<br />
used as non-specific invasion control. Graphic: HZI<br />
Finally, in more recent efforts, we explored the role of<br />
cortactin in different types of host-pathogen interaction.<br />
Interestingly, cortactin appears essential for InlB-mediated<br />
Listeria invasion (Fig. 1), but neither for entry triggered by<br />
Shigella flexneri nor for actin pedestal formation induced<br />
at the cell surface by different types of pathogenic E. coli<br />
(Oelkers/Lai et al., unpublished).<br />
Rottner, K., Hänisch, J., & Campellone, K. (<strong>2010</strong>) WASH, WHAMM and JMY: Regulation<br />
of Arp2/3 complex and beyond. Trends in Cell Biology 20(11), 650-61.<br />
Hänisch, J., Ehinger, J., Ladwein, M., Rohde, M., Derivery, E., Bosse, T., Steffen, A.,<br />
Bumann, D., Misselwitz, B., Hardt, W.-D., Gautreau, A., Stradal, T.E.B., & Rottner, K.<br />
(<strong>2010</strong>) Molecular dissection of Salmonella-induced membrane ruffling versus invasion.<br />
Cellular Microbiology 12(1), 84-98.<br />
Lai, F.P.L., Szczodrak, M., Oelkers, J.M., Ladwein, M., Acconcia, F., Benesch, S., Auinger,<br />
S., Faix, J., Small, J.V., Polo, S., Stradal, T.E.B., & Rottner, K. (2009) Cortactin promotes<br />
migration and platelet-derived growth factor-induced actin reorganization by signaling<br />
to Rho-GTPases. Molecular Biology of the Cell 20(14), 3209-23.<br />
Lai, F.P.L., Szczodrak, M., Block, J., Faix, J., Breitsprecher, D., Mannherz, H.G., Stradal,<br />
T.E.B., Dunn, G.A., Small, J.V., & Rottner, K. (2008) Arp2/3-complex interactions and<br />
actin network turnover in lamellipodia. EMBO Journal 27(7), 982-92.