CHAPTER X CHAPTER 4 - Cancer et environnement
CHAPTER X CHAPTER 4 - Cancer et environnement
CHAPTER X CHAPTER 4 - Cancer et environnement
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
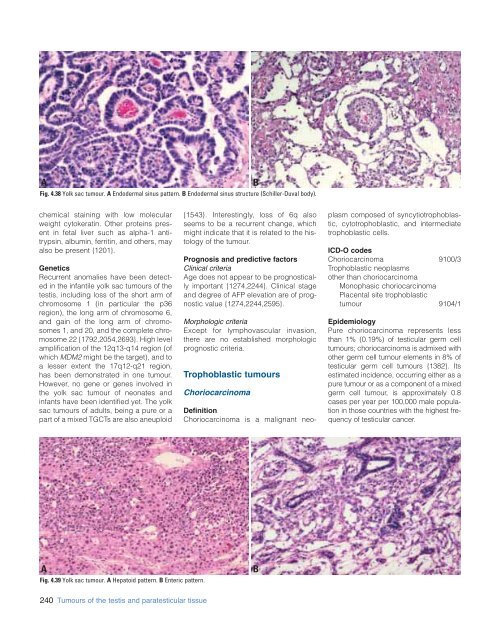
A<br />
B<br />
Fig. 4.38 Yolk sac tumour. A Endodermal sinus pattern. B Endodermal sinus structure (Schiller-Duval body).<br />
chemical staining with low molecular<br />
weight cytokeratin. Other proteins present<br />
in f<strong>et</strong>al liver such as alpha-1 antitrypsin,<br />
albumin, ferritin, and others, may<br />
also be present {1201}.<br />
Gen<strong>et</strong>ics<br />
Recurrent anomalies have been d<strong>et</strong>ected<br />
in the infantile yolk sac tumours of the<br />
testis, including loss of the short arm of<br />
chromosome 1 (in particular the p36<br />
region), the long arm of chromosome 6,<br />
and gain of the long arm of chromosomes<br />
1, and 20, and the compl<strong>et</strong>e chromosome<br />
22 {1792,2054,2693}. High level<br />
amplification of the 12q13-q14 region (of<br />
which MDM2 might be the targ<strong>et</strong>), and to<br />
a lesser extent the 17q12-q21 region,<br />
has been demonstrated in one tumour.<br />
However, no gene or genes involved in<br />
the yolk sac tumour of neonates and<br />
infants have been identified y<strong>et</strong>. The yolk<br />
sac tumours of adults, being a pure or a<br />
part of a mixed TGCTs are also aneuploid<br />
{1543}. Interestingly, loss of 6q also<br />
seems to be a recurrent change, which<br />
might indicate that it is related to the histology<br />
of the tumour.<br />
Prognosis and predictive factors<br />
Clinical criteria<br />
Age does not appear to be prognostically<br />
important {1274,2244}. Clinical stage<br />
and degree of AFP elevation are of prognostic<br />
value {1274,2244,2595}.<br />
Morphologic criteria<br />
Except for lymphovascular invasion,<br />
there are no established morphologic<br />
prognostic criteria.<br />
Trophoblastic tumours<br />
Choriocarcinoma<br />
Definition<br />
Choriocarcinoma is a malignant neoplasm<br />
composed of syncytiotrophoblastic,<br />
cytotrophoblastic, and intermediate<br />
trophoblastic cells.<br />
ICD-O codes<br />
Choriocarcinoma 9100/3<br />
Trophoblastic neoplasms<br />
other than choriocarcinoma<br />
Monophasic choriocarcinoma<br />
Placental site trophoblastic<br />
tumour 9104/1<br />
Epidemiology<br />
Pure choriocarcinoma represents less<br />
than 1% (0.19%) of testicular germ cell<br />
tumours; choriocarcinoma is admixed with<br />
other germ cell tumour elements in 8% of<br />
testicular germ cell tumours {1382}. Its<br />
estimated incidence, occurring either as a<br />
pure tumour or as a component of a mixed<br />
germ cell tumour, is approximately 0.8<br />
cases per year per 100,000 male population<br />
in those countries with the highest frequency<br />
of testicular cancer.<br />
A<br />
Fig. 4.39 Yolk sac tumour. A Hepatoid pattern. B Enteric pattern.<br />
B<br />
240 Tumours of the testis and paratesticular tissue