CHAPTER X CHAPTER 4 - Cancer et environnement
CHAPTER X CHAPTER 4 - Cancer et environnement
CHAPTER X CHAPTER 4 - Cancer et environnement
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
testicular parenchyma and tumour tends<br />
to be blurred where the tumour infiltrates<br />
the testicular interstitium. Nodular<br />
excrescences may stud the tunics and<br />
the spermatic cord.<br />
Histopathology<br />
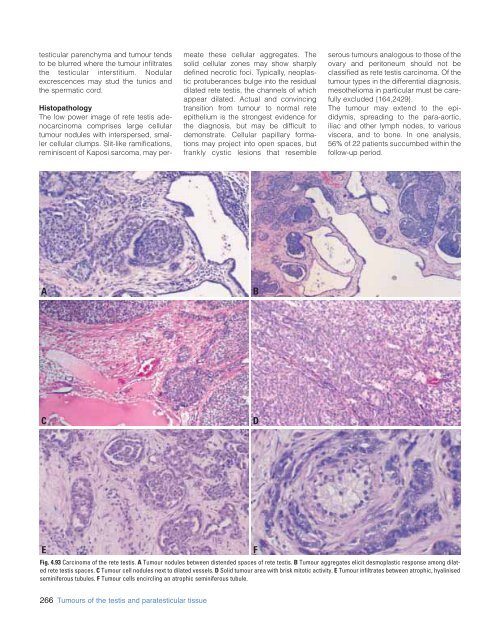
The low power image of r<strong>et</strong>e testis adenocarcinoma<br />
comprises large cellular<br />
tumour nodules with interspersed, smaller<br />
cellular clumps. Slit-like ramifications,<br />
reminiscent of Kaposi sarcoma, may permeate<br />
these cellular aggregates. The<br />
solid cellular zones may show sharply<br />
defined necrotic foci. Typically, neoplastic<br />
protuberances bulge into the residual<br />
dilated r<strong>et</strong>e testis, the channels of which<br />
appear dilated. Actual and convincing<br />
transition from tumour to normal r<strong>et</strong>e<br />
epithelium is the strongest evidence for<br />
the diagnosis, but may be difficult to<br />
demonstrate. Cellular papillary formations<br />
may project into open spaces, but<br />
frankly cystic lesions that resemble<br />
serous tumours analogous to those of the<br />
ovary and peritoneum should not be<br />
classified as r<strong>et</strong>e testis carcinoma. Of the<br />
tumour types in the differential diagnosis,<br />
mesothelioma in particular must be carefully<br />
excluded {164,2429}.<br />
The tumour may extend to the epididymis,<br />
spreading to the para-aortic,<br />
iliac and other lymph nodes, to various<br />
viscera, and to bone. In one analysis,<br />
56% of 22 patients succumbed within the<br />
follow-up period.<br />
A<br />
B<br />
C<br />
D<br />
E<br />
Fig. 4.93 Carcinoma of the r<strong>et</strong>e testis. A Tumour nodules b<strong>et</strong>ween distended spaces of r<strong>et</strong>e testis. B Tumour aggregates elicit desmoplastic response among dilated<br />
r<strong>et</strong>e testis spaces. C Tumour cell nodules next to dilated vessels. D Solid tumour area with brisk mitotic activity. E Tumour infiltrates b<strong>et</strong>ween atrophic, hyalinised<br />
seminiferous tubules. F Tumour cells encircling an atrophic seminiferous tubule.<br />
F<br />
266 Tumours of the testis and paratesticular tissue