Scania annual report 2003
Scania annual report 2003
Scania annual report 2003
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Fair value of financial instruments<br />
The carrying amount of interest-bearing assets and liabilities in the<br />
balance sheet may deviate from their fair value, among other things as<br />
a consequence of changes in market interest rates.<br />
There is also a fair value for items that are not recognised in the balance<br />
sheet, such as hedging instruments that do not correspond to net<br />
assets in the balance sheet and that meet the requirements for hedge<br />
accounting. To establish the fair value of financial assets and liabilities,<br />
official market quotations have been used for those assets and liabilities<br />
that are traded in an active market.<br />
In those cases where market quotations do not exist, fair value has<br />
been established by discounting future payment flows at current market<br />
interest rates and exchange rates for similar instruments. Fair value of<br />
financial instruments such as accounts receivable, accounts payable<br />
and other non-interest-bearing financial assets and liabilities that are<br />
recognised at acquisition value, minus any write-downs, is regarded as<br />
coinciding with the carrying amount, and these instruments are therefore<br />
not included in the table below.<br />
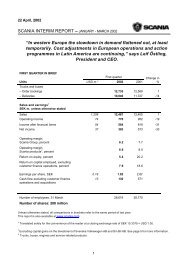
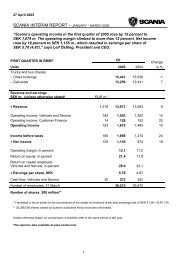
<strong>2003</strong><br />
Carrying<br />
Fair<br />
amount value 1<br />
Assets<br />
Long-term holdings of securities 2 56 69<br />
Long-term interest-bearing receivables 3 11,796 11,917<br />
Interest-bearing current receivables 3 7,502 7,887<br />
Short-term investments 704 703<br />
Cash and bank balances 1,212 1,212<br />
Currency forward contract for hedging<br />
of net foreign investments 4 –1 –1<br />
Currency derivatives for hedging of<br />
future cash flows related to operating<br />
activities 4, 5 54 113<br />
Currency derivatives for hedging<br />
of loans etc 4 58 58<br />
Currency interest rate swaps 4 –62 –64<br />
Interest rate-related derivatives 4 223 641<br />
Total assets 21,542 22,535<br />
Liabilities<br />
Short-term borrowing 5,380 5,369<br />
Long-term borrowing 20,827 22,370<br />
Total liabilities 26,207 27,739<br />
1 Interest-bearing financial assets and liabilities have been discounted to market<br />
interest rates, without taking credit margins into account.<br />
2 In the balance sheet under “Holdings in associated companies etc”.<br />
3 Operating leases amounting to SEK 6,604 m. are not included in the table.<br />
4 In the balance sheet under “Other current receivables”.<br />
5 Fair value of hedging instruments that were not included in the balance sheet<br />
on the closing date totalled SEK 76 m.<br />
In some cases, carrying amount of assets with fixed interest rates exceeded<br />
fair value as a consequence of changes in market interest rates.<br />
Write-downs of these assets occur only when there is reason to believe<br />
that the counterparty will not fulfil its contractual commitments, not as a<br />
consequence of changes in market interest rates.<br />
Accounting and valuation<br />
Financial assets are recognised in the balance sheet on the sales or<br />
transaction date at their acquisition value, which is equivalent to fair<br />
value on that date. After the acquisition date, financial fixed assets are<br />
valued at accrued acquisition value after subtracting probable credit<br />
losses. Financial current assets are valued at the lower of accrued<br />
acquisition value and market value.<br />
Financial liabilities are recognised in the balance sheet at accrued<br />
acquisition value. Premiums or deficits, including transaction costs, are<br />
accrued over the life of the loan. Financial assets and liabilities in foreign<br />
currencies are <strong>report</strong>ed at the closing day rate.<br />
<strong>Scania</strong> uses derivative instruments to control changes in exchange<br />
rates and interest rates. Expected future payments in foreign currencies<br />
are hedged mainly by selling currencies in forward contracts. Unrealised<br />
gains or losses on contracts intended for hedging purposes are not<br />
recognised continuously in the income statement, but only on the same<br />
date as the result of the hedged flow. In currency hedging of receivables<br />
and liabilities with forward contracts, <strong>Scania</strong> uses the exchange rate on<br />
the date the currency hedging occurs at the valuation of the underlying<br />
receivable or liability. The difference between the spot market rate and<br />
the forward rate when the contract is entered into is accrued over the<br />
life of the contract. Option premiums received and paid are accrued in a<br />
corresponding way.<br />
<strong>Scania</strong> uses interest rate swaps to achieve the desired interest rate<br />
refixing period. Interest income and expenses related to interest rate<br />
swaps are accrued continuously according to the contract terms. To<br />
adapt borrowing to the desired funding currency, currency swaps are<br />
used. When a loan in one currency has been converted to another currency<br />
by means of swap agreements, the loan and the swap agreement<br />
are valued at the exchange rate prevailing on the closing day for the new<br />
currency.<br />
Hedging of net assets in foreign subsidiaries occurs only to the extent<br />
that a subsidiary has significant monetary assets in local currency. The<br />
exchange rate difference in the forward contract is <strong>report</strong>ed directly<br />
against shareholders’ equity. The interest rate portion of the forward<br />
contract is accrued over the life of the contract and is <strong>report</strong>ed among<br />
financial income and expenses.<br />
Derivatives for which the requirements for hedge acounting are not<br />
fulfilled are valued in the balance sheet at the lower of acquisition value<br />
and fair value.<br />
The main reason why the fair value of interest-bearing assets and liabilities<br />
exceeded the carrying amount is that general interest rates were<br />
lower at year-end than when the contracts were entered into.<br />
73 ANNUAL REPORT <strong>2003</strong>