Part I - IPA SA
Part I - IPA SA
Part I - IPA SA
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
REVISTA ROMÂN DE AUTOMATIC<br />
15<br />
2.2 Controlling and Security System with<br />
data base and processes analysis<br />
Security and monitoring system is connected<br />
to the controlling system from control room<br />
in tritium removal pilot plant. The main<br />
function of this system is to monitor all<br />
parameters in installation.<br />
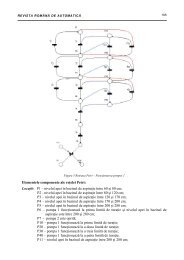
In figure 3 is presented the diagram block<br />
with the virtual security system and<br />
monitoring system and in Figure 4 is shown a<br />
capture screen from security software from<br />
control room.<br />
Control<br />
room<br />
Protection<br />
System<br />
Virtual<br />
Security<br />
System<br />
Monitoring<br />
system<br />
Tritium Removal Plant<br />
Data<br />
Base<br />
Figure 3. Block diagram with virtual security system (VSS)<br />
Figure 4. Monitoring system for isotopic exchange<br />
installation with security system<br />
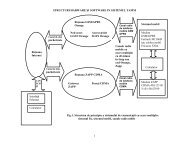
The control software will also include the<br />
security and monitoring architecture of a<br />
radioactive fluids-processing plant, mainly<br />
composed of the following principal systems:<br />
a. Interlocking and interconditioning<br />
system – ensures the plant control for good<br />
operation with minimum toxic fluids leaks; it<br />
controls and commands the fluids recovery from<br />
the plant and/or building after accidents as well.<br />
The system must perform the following<br />
functions:<br />
- automatically control the technological<br />
process with the help of the computer;<br />
- command, at the reach of the actuating<br />
threshold, the emergency shutdown and<br />
drainage of the plant;<br />
- command the sealing-off of the bay and<br />
modules, individually;<br />
- to command the closure of the bay<br />
during operation;<br />
- to indicate the levels in the liquid<br />
effluent-collecting tanks;<br />
- to command the ventilation system;<br />
- to command the control system of access<br />
into the technological bay.<br />
These requests are fulfilled by establishing<br />
some measurement parameters, of safe<br />
operation and auto-triggering mode.<br />
Processing the signals coming from the<br />
sensors of process and of toxic emission<br />
concentration, by its own software, secures<br />
the intervention of the protection systems.<br />
b. Dosimetric and emission quality<br />
survey – ensures the dosimetric survey of the<br />
personnel, checks the toxicity level from<br />
within the building and also the gas release<br />
into the environment; it also supplies the<br />
warning values for the radioactive/toxic<br />
substance concentrations.<br />
The system must perform the following<br />
functions:<br />
- the dosimeter survey and of the toxicity<br />
levels in the air and of the operation<br />
personnel;<br />
- monitoring of the working areas;<br />
- supplying the actuating values for<br />
radioactive/toxic fluids concentrations;<br />
- monitoring the toxic gas and liquid leaks.<br />
The system allows for the automatic tripping<br />
(simultaneously with the signal from a<br />
process transducer) of the plant through the<br />
interlocking system. In case of accident, it<br />
triggers the shut-down/discharge of the plant<br />
and its sealing-off.