Empowering citizens Engaging governments Rebuilding communities
Empowering citizens Engaging governments Rebuilding communities
Empowering citizens Engaging governments Rebuilding communities
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
IRD oversaw CSP operations in 15 cities<br />
nationwide, reaching millions of Iraqis<br />
through employment, training, business<br />
development, and youth projects<br />
Box 4<br />
CSP: At a glance<br />
2<br />
Awarded to IRD by USAID in 2006, CSP grew into a $644 million delivery mechanism for quick-impact projects, a<br />
“nonlethal, counterinsurgency program that reduces the incentives for participation in violent conflict by employing<br />
or engaging at risk youth between the ages of 17 and 35,” according to the contract’s scope of work. In short, CSP<br />
was designed to address the root cause of the insurgency through a four-pronged strategy that focused on:<br />
• Assisting the government of Iraq at all levels in fulfilling its duties, thus improving <strong>citizens</strong>’ perceptions of government<br />
efficacy and legitimacy.<br />
• Mitigating the major economic factors contributing to the insurgency.<br />
• Stimulating preconditions for economic stability.<br />
• Facilitating constructive dialogue and peaceful interactions through civic education and community-oriented<br />
activities.<br />
A complete stabilization package<br />
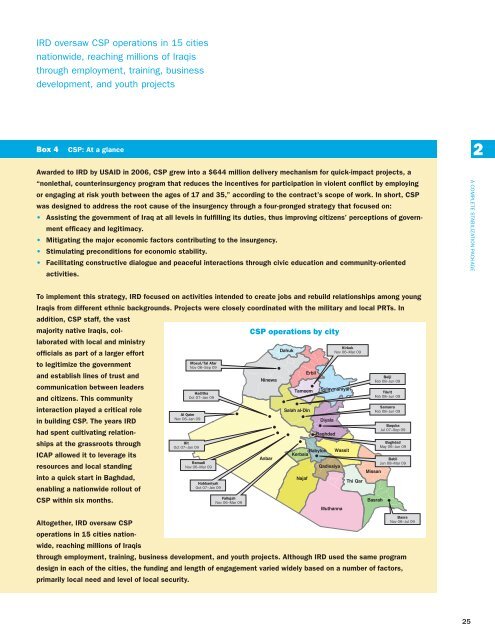
To implement this strategy, IRD focused on activities intended to create jobs and rebuild relationships among young<br />
Iraqis from different ethnic backgrounds. Projects were closely coordinated with the military and local PRTs. In<br />
addition, CSP staff, the vast<br />
majority native Iraqis, collaborated<br />
with local and ministry<br />
CSP operations by city<br />
Kirkuk<br />
Nov 06–Mar 09<br />
officials as part of a larger effort<br />
Mosul/Tal Afar<br />
to legitimize the government<br />
Nov 06–Sep 09<br />
and establish lines of trust and<br />
Beiji<br />
Feb 08–Jun 09<br />
communication between leaders<br />
Haditha<br />
Tikrit<br />
Oct 07–Jan 09<br />
Feb 08–Jun 09<br />
and <strong>citizens</strong>. This community<br />
Samarra<br />
interaction played a critical role<br />
Feb 08–Jun 09<br />
Al Qaim<br />
Nov 06–Jan 09<br />
in building CSP. The years IRD<br />
Baquba<br />
Jul 07–Sep 09<br />
had spent cultivating relationships<br />
at the grassroots through<br />
Baghdad<br />
Hit<br />
Oct 07–Jan 09<br />
May 06–Jun 09<br />
ICAP allowed it to leverage its<br />
Babil<br />
Ramadi<br />
Jan 08–Mar 09<br />
resources and local standing<br />
Nov 06–Mar 09<br />
into a quick start in Baghdad,<br />
Habbaniyah<br />
Oct 07–Jan 09<br />
enabling a nationwide rollout of<br />
CSP within six months.<br />
Fallujah<br />
Nov 06–Mar 09<br />
Basra<br />
Nov 06–Jul 09<br />
Altogether, IRD oversaw CSP<br />
operations in 15 cities nationwide,<br />
reaching millions of Iraqis<br />
through employment, training, business development, and youth projects. Although IRD used the same program<br />
design in each of the cities, the funding and length of engagement varied widely based on a number of factors,<br />
primarily local need and level of local security.<br />
25





![Guide bonne pratique production d'oignon qualité_VF_4_2411012[1]](https://img.yumpu.com/23506639/1/184x260/guide-bonne-pratique-production-doignon-qualitac-vf-4-24110121.jpg?quality=85)









