Pedestrian safety - Global Road Safety Partnership
Pedestrian safety - Global Road Safety Partnership
Pedestrian safety - Global Road Safety Partnership
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Why is addressing pedestrian <strong>safety</strong> necessary?<br />
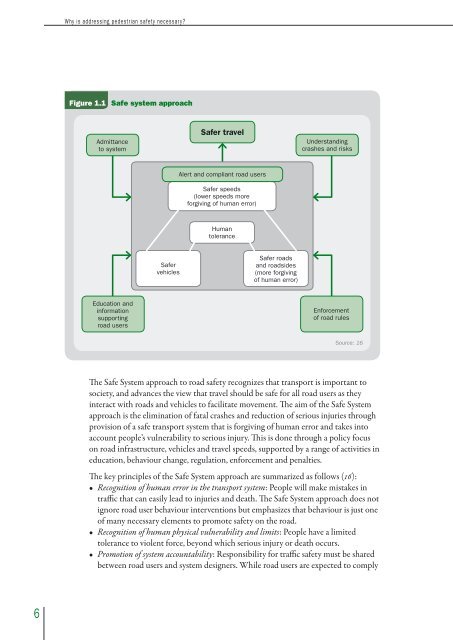
Figure 1.1 Safe system approach<br />
Admittance<br />
to system<br />
Safer travel<br />
Understanding<br />
crashes and risks<br />
Alert and compliant road users<br />
Safer speeds<br />
(lower speeds more<br />
forgiving of human error)<br />
Human<br />
tolerance<br />
Safer<br />
vehicles<br />
Safer roads<br />
and roadsides<br />
(more forgiving<br />
of human error)<br />
Education and<br />
information<br />
supporting<br />
road users<br />
Enforcement<br />
of road rules<br />
Source: 16<br />
The Safe System approach to road <strong>safety</strong> recognizes that transport is important to<br />
society, and advances the view that travel should be safe for all road users as they<br />
interact with roads and vehicles to facilitate movement. The aim of the Safe System<br />
approach is the elimination of fatal crashes and reduction of serious injuries through<br />
provision of a safe transport system that is forgiving of human error and takes into<br />
account people’s vulnerability to serious injury. This is done through a policy focus<br />
on road infrastructure, vehicles and travel speeds, supported by a range of activities in<br />
education, behaviour change, regulation, enforcement and penalties.<br />
The key principles of the Safe System approach are summarized as follows (16):<br />
• Recognition of human error in the transport system: People will make mistakes in<br />
traffic that can easily lead to injuries and death. The Safe System approach does not<br />
ignore road user behaviour interventions but emphasizes that behaviour is just one<br />
of many necessary elements to promote <strong>safety</strong> on the road.<br />
• Recognition of human physical vulnerability and limits: People have a limited<br />
tolerance to violent force, beyond which serious injury or death occurs.<br />
• Promotion of system accountability: Responsibility for traffic <strong>safety</strong> must be shared<br />
between road users and system designers. While road users are expected to comply<br />
6