The economic effects of EU-reforms in corporate income tax systems
The economic effects of EU-reforms in corporate income tax systems
The economic effects of EU-reforms in corporate income tax systems
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>effects</strong> on <strong>in</strong>vestment and, consequently, on welfare. In the second sensitivity analysis, the<br />
<strong>effects</strong> are similar for the same reasons as expla<strong>in</strong>ed <strong>in</strong> section 3.<br />
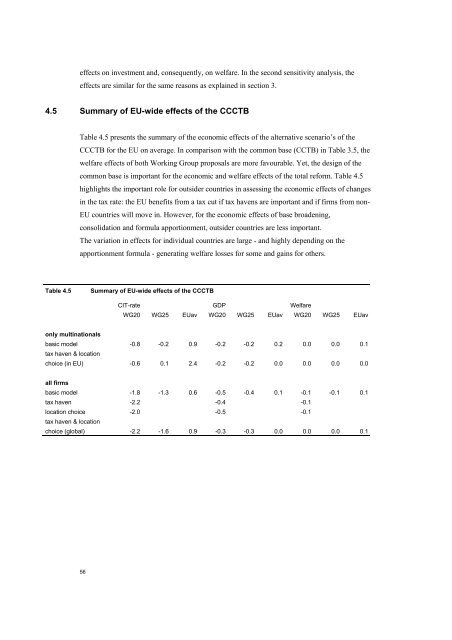
4.5 Summary <strong>of</strong> <strong>EU</strong>-wide <strong>effects</strong> <strong>of</strong> the CCCTB<br />
Table 4.5 presents the summary <strong>of</strong> the <strong>economic</strong> <strong>effects</strong> <strong>of</strong> the alternative scenario’s <strong>of</strong> the<br />
CCCTB for the <strong>EU</strong> on average. In comparison with the common base (CCTB) <strong>in</strong> Table 3.5, the<br />
welfare <strong>effects</strong> <strong>of</strong> both Work<strong>in</strong>g Group proposals are more favourable. Yet, the design <strong>of</strong> the<br />
common base is important for the <strong>economic</strong> and welfare <strong>effects</strong> <strong>of</strong> the total reform. Table 4.5<br />
highlights the important role for outsider countries <strong>in</strong> assess<strong>in</strong>g the <strong>economic</strong> <strong>effects</strong> <strong>of</strong> changes<br />
<strong>in</strong> the <strong>tax</strong> rate: the <strong>EU</strong> benefits from a <strong>tax</strong> cut if <strong>tax</strong> havens are important and if firms from non-<br />
<strong>EU</strong> countries will move <strong>in</strong>. However, for the <strong>economic</strong> <strong>effects</strong> <strong>of</strong> base broaden<strong>in</strong>g,<br />
consolidation and formula apportionment, outsider countries are less important.<br />
<strong>The</strong> variation <strong>in</strong> <strong>effects</strong> for <strong>in</strong>dividual countries are large - and highly depend<strong>in</strong>g on the<br />
apportionment formula - generat<strong>in</strong>g welfare losses for some and ga<strong>in</strong>s for others.<br />
Table 4.5<br />
Summary <strong>of</strong> <strong>EU</strong>-wide <strong>effects</strong> <strong>of</strong> the CCCTB<br />
CIT-rate GDP Welfare<br />
WG20 WG25 <strong>EU</strong>av WG20 WG25 <strong>EU</strong>av WG20 WG25 <strong>EU</strong>av<br />
only mult<strong>in</strong>ationals<br />
basic model -0.8 -0.2 0.9 -0.2 -0.2 0.2 0.0 0.0 0.1<br />
<strong>tax</strong> haven & location<br />
choice (<strong>in</strong> <strong>EU</strong>) -0.6 0.1 2.4 -0.2 -0.2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0<br />
all firms<br />
basic model -1.8 -1.3 0.6 -0.5 -0.4 0.1 -0.1 -0.1 0.1<br />
<strong>tax</strong> haven -2.2 -0.4 -0.1<br />
location choice -2.0 -0.5 -0.1<br />
<strong>tax</strong> haven & location<br />
choice (global) -2.2 -1.6 0.9 -0.3 -0.3 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.1<br />
56