Annual Report 2006 - Plataforma Solar de AlmerÃa
Annual Report 2006 - Plataforma Solar de AlmerÃa
Annual Report 2006 - Plataforma Solar de AlmerÃa
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
ENVIRONMENTAL APPLICATIONS OF SOLAR ENERGY<br />
Duration: January <strong>2006</strong> - December 2009<br />
Background: This work concerns the <strong>de</strong>velopment of a new system for treatment<br />
of dangerous and toxic substances, such as H 2 S, mercaptans, etc.,<br />
which cause the malodorous sewage plant emissions that make these installations<br />
socially unacceptable. Besi<strong>de</strong>s, these emissions can contribute to the<br />
corrosion of the instruments, causing a relevant economical in the wastewater<br />
treatment facilities.<br />
Purposes: Develop a photocatalytic treatment system activated by sun light or<br />
UVA lamps that operates un<strong>de</strong>r real process conditions.<br />
• Develop an adsorption treatment system that allows retention of the<br />
noxious components of the atmospheres found in wastewater treatment<br />
plants.<br />
• Based on the results of both systems, a new mixed photocatalysisadsorption<br />
system will be <strong>de</strong>veloped. This combined reactor should<br />
take advantage of the synergies between both processes, enhancing<br />
the efficiency of each system. The achievement of these goals should<br />
lead to a drastic reduction in the volume of the costly and irritant<br />
chemicals currently used to control these emissions, and consequently<br />
a safer environment for the plant workers will be created.<br />
Achievements in <strong>2006</strong>: During this first year of the project, the main effort<br />
focused on the selection of high-efficiency, durable supported photocatalysts.<br />
Different UV-transparent carriers were initially selected and sol-gel-coated<br />
TiO 2 . In parallel, several adsorbents based on high-strength surface materials<br />
(silicates, carbon…) were prepared by extrusion as either plates or monoliths.<br />
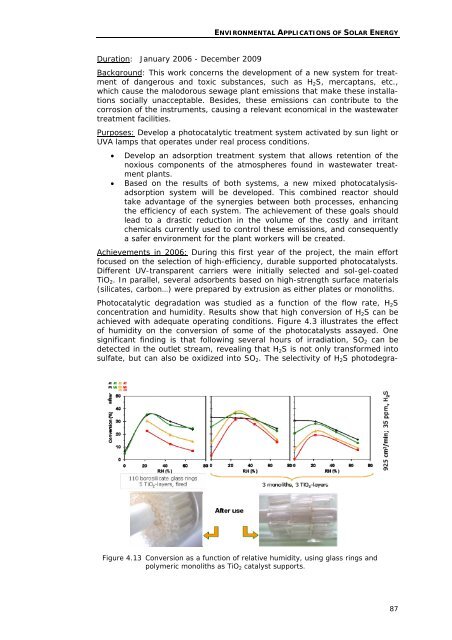
Photocatalytic <strong>de</strong>gradation was studied as a function of the flow rate, H 2 S<br />
concentration and humidity. Results show that high conversion of H 2 S can be<br />
achieved with a<strong>de</strong>quate operating conditions. Figure 4.3 illustrates the effect<br />
of humidity on the conversion of some of the photocatalysts assayed. One<br />
significant finding is that following several hours of irradiation, SO 2 can be<br />
<strong>de</strong>tected in the outlet stream, revealing that H 2 S is not only transformed into<br />
sulfate, but can also be oxidized into SO 2 . The selectivity of H 2 S photo<strong>de</strong>gra-<br />
Figure 4.13 Conversion as a function of relative humidity, using glass rings and<br />
polymeric monoliths as TiO 2 catalyst supports.<br />
87