Scania annual report 2004
Scania annual report 2004
Scania annual report 2004
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
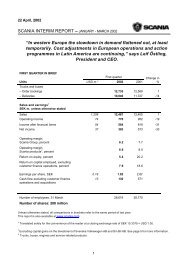
coinciding with the carrying amount, and these instruments are therefore<br />
not included in the table below.<br />
<strong>2004</strong> 2003<br />
Book Fair Book Fair<br />
Fair value value value value value<br />
Assets<br />
Long-term holdings<br />
of securities 1 25 25 56 69<br />
Long-term interestbearing<br />
receivables 2 12,756 12,630 11,796 11,917<br />
Interest-bearing current<br />
receivables 2 7,875 8,090 7,502 7,887<br />
Short-term investments 1,379 1,384 704 703<br />
Cash and bank balances 1,119 1,119 1,212 1,212<br />
Currency forward contract<br />
for hedging of net foreign<br />
investments 3 0 0 – 1 – 1<br />
Currency derivatives for<br />
hedging of commercial<br />
exposure 3, 4 31 110 54 113<br />
Currency derivatives<br />
for hedging of financial<br />
exposure 3 109 110 58 58<br />
Currency interest rate<br />
swap agreements 3 – 108 – 117 – 62 – 64<br />
Interest rate-related<br />
derivatives 3 186 752 223 641<br />
Total assets 23,372 24,103 21,542 22,535<br />
Liabilities<br />
Short-term borrowing 5,804 5,962 5,380 5,369<br />
Long-term borrowing 19,809 21,093 20,827 22,370<br />
Total liabilities 25,613 27,055 26,207 27,739<br />
1 Reported in the balance sheet under “Holdings in associated companies etc”.<br />
2 Operating leases amounting to SEK 5,809 m. (6,604) are not included in the table.<br />
3 Reported in the balance sheet under “Other current receivables”.<br />
4 Fair value of hedging instruments that were not included in the balance sheet on<br />
the closing date totalled SEK 79 (76) m.<br />
The main reason why the fair value of interest-bearing assets and liabilities<br />
exceeded the book value is that general interest rates were lower at<br />
year-end than when the contracts were entered into.<br />
In some cases, the carrying amounts of assets with fixed interest rates<br />
exceeded fair value as a consequence of changes in market interest<br />
rates. Write-downs of these assets occur only when there is reason to<br />
believe that the counterparty will not fulfil its contractual commitments,<br />
not as a consequence of changes in market interest rates.<br />
As a result of the transition to IAS 39 as per 1 January 2005, certain<br />
financial assets and liabilities will be valued at fair value while others are<br />
valued at accrued acquisition value. Valuation according to IAS 39 is<br />
determined by how the asset or liability is classified and whether hedge<br />
accounting is applied or not. The above table discloses the fair value of<br />
financial assets and liabilities, regardless of valuation according to IAS 39.<br />
Reporting and valuation<br />
Financial assets are <strong>report</strong>ed in the balance sheet on the sales or<br />
transaction date at their acquisition value, which is equivalent to fair<br />
value on that date. After the acquisition date, financial fixed assets are<br />
valued at accrued acquisition value after subtracting probable credit<br />
losses. Financial current assets are valued at the lower of accrued<br />
acquisition value and market value.<br />
Financial liabilities are recognised in the balance sheet at accrued<br />
acquisition value. Premiums or deficits, including transaction costs, are<br />
accrued over the life of the loan. Financial assets and liabilities in foreign<br />
currencies are <strong>report</strong>ed at the closing day rate.<br />
<strong>Scania</strong> uses derivative instruments to control changes in exchange<br />
rates and interest rates. Expected future payments in foreign currencies<br />
are hedged mainly by selling currencies in forward contracts. Unrealised<br />
gains or losses on contracts intended for hedging purposes are not<br />
<strong>report</strong>ed continuously in the income statement, but only on the same<br />
date as the result of the hedged flow. In currency hedging of receivables<br />
and liabilities with forward contracts, <strong>Scania</strong> uses the exchange rate on<br />
the date the currency hedging occurs, at the valuation of the underlying<br />
receivable or liability. The difference between the spot market rate and<br />
the forward rate when the contract is entered into is accrued over the<br />
life of the contract. Option premiums received and paid are accrued in a<br />
corresponding way.<br />
<strong>Scania</strong> uses interest rate swap agreements to achieve the desired<br />
interest rate refixing period. Interest income and expenses related to<br />
interest rate swap agreements are accrued continuously according to<br />
the contract terms. To adapt borrowing to the desired funding currency,<br />
currency swap agreements are used. When a loan in one currency has<br />
been converted to another currency by means of swap agreements,<br />
the loan and the swap agreement are valued at the exchange rate<br />
prevailing on the closing day for the new currency.<br />
Hedging of net assets in foreign subsidiaries occurs only to the<br />
extent that a subsidiary has significant monetary assets in local currency.<br />
The exchange rate difference in the forward contract is <strong>report</strong>ed directly<br />
against shareholders’ equity. The interest rate portion of the forward<br />
contract is accrued over the life of the contract and is <strong>report</strong>ed among<br />
financial income and expenses.<br />
Derivatives for which the requirements for hedge accounting are not<br />
deemed as being fulfilled are valued in the balance sheet at the lower of<br />
acquisition value and fair value.<br />
NOTE 30 Net assets in foreign currencies<br />
Net assets outside Sweden consist of net Group-external assets in<br />
foreign subsidiaries, as well as net Group-external receivables and<br />
liabilities of Swedish companies that are not hedged by funding in the<br />
corresponding currency.<br />
<strong>2004</strong> 2003 2002<br />
Euro (EUR) 3,236 5,361 5,675<br />
British pound (GBP) 936 846 863<br />
Other European currencies 1,161 966 1,051<br />
US dollar (USD) 191 – 285 103<br />
South American local currencies 2,094 2,050 2,659<br />
Other currencies 1,143 1,202 1,046<br />
Total 8,761 10,140 11,397<br />
For information on accumulated exchange rate differences that are<br />
<strong>report</strong>ed directly against shareholders’ equity, see Note 14.<br />
NOTE 31 Currency exposure in operating income<br />
The table below shows the net amount of operating revenue and<br />
operating expenses exposed to foreign currencies, by currency.<br />
<strong>2004</strong> 2003 2002<br />
Euro (EUR) 8,300 8,400 7,900<br />
British pound (GBP) 4,900 4,600 3,400<br />
Other European currencies 2,300 2,100 2,100<br />
Korean won (KRW) 800 1,500 1,300<br />
US dollar (USD) 600 300 500<br />
South American local currencies 1 300 0 –<br />
Other currencies 1,900 1,400 1,200<br />
Total 19,100 18,300 16,400<br />
1 During 2002, local South American currencies fluctuated sharply, with significant<br />
price and cost changes as a consequence. This means that a description of the<br />
currency effect/exposure alone for that year is not meaningful.<br />
In <strong>2004</strong>, currency spot rate effects totalled about SEK –135 m., compared<br />
to 2003. This was offset by positive currency hedging income of SEK<br />
65 m., resulting in a negative net effect of SEK 70 m. During 2003,<br />
currency hedging had a positive impact of SEK 620 m. Compared to<br />
2002, the total currency rate effect was thus SEK – 690 m.<br />
NOTE 32 Effect of exchange rate differences<br />
NOTE 32 on net income<br />
Net income was affected by exchange rate differences (excluding<br />
flow-related forward contracts) as shown in the following table:<br />
<strong>2004</strong> 2003 2002<br />
Sales revenue – 85 – 80 45<br />
Cost of goods sold 8 137 2<br />
Selling expenses 0 – 16 26<br />
Income from Customer Finance – 5 – 1 3<br />
Operating income – 82 40 76<br />
Financial income and expenses 18 – 58 – 160<br />
Taxes 1 5 – 14<br />
Effect on net income – 63 – 13 – 98<br />
For information on accumulated exchange rate differences that are<br />
<strong>report</strong>ed directly against shareholders’ equity, see Note 14.<br />
73 NOTES • SCANIA ANNUAL REPORT <strong>2004</strong>