Ecological Transport Information Tool for Worldwide ... - Schenker
Ecological Transport Information Tool for Worldwide ... - Schenker
Ecological Transport Information Tool for Worldwide ... - Schenker
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Page 6<br />
IFEU Heidelberg, Öko-Institut, IVE, RMCON<br />
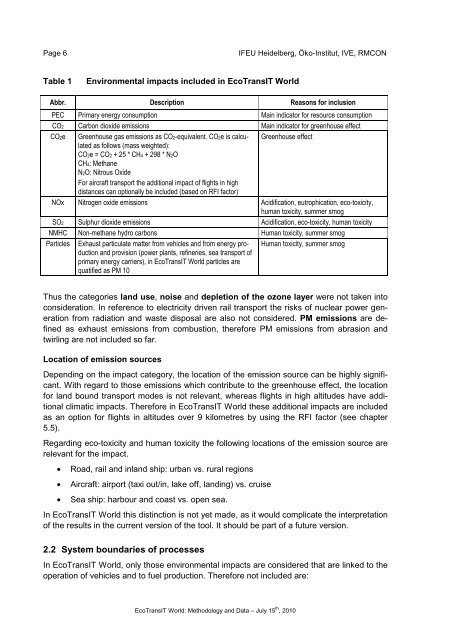
Table 1<br />
Environmental impacts included in EcoTransIT World<br />
Abbr. Description Reasons <strong>for</strong> inclusion<br />
PEC Primary energy consumption Main indicator <strong>for</strong> resource consumption<br />
CO2 Carbon dioxide emissions Main indicator <strong>for</strong> greenhouse effect<br />
CO2e Greenhouse gas emissions as CO2-equivalent. CO2e is calculated<br />
Greenhouse effect<br />
as follows (mass weighted):<br />
CO2e = CO2 + 25 * CH4 + 298 * N2O<br />
CH4: Methane<br />
N2O: Nitrous Oxide<br />
For aircraft transport the additional impact of flights in high<br />
distances can optionally be included (based on RFI factor)<br />
NOx Nitrogen oxide emissions Acidification, eutrophication, eco-toxicity,<br />
human toxicity, summer smog<br />
SO2 Sulphur dioxide emissions Acidification, eco-toxicity, human toxicity<br />
NMHC Non-methane hydro carbons Human toxicity, summer smog<br />
Particles Exhaust particulate matter from vehicles and from energy production<br />
and provision (power plants, refineries, sea transport of<br />
primary energy carriers), in EcoTransIT World particles are<br />
quatified as PM 10<br />
Human toxicity, summer smog<br />
Thus the categories land use, noise and depletion of the ozone layer were not taken into<br />
consideration. In reference to electricity driven rail transport the risks of nuclear power generation<br />
from radiation and waste disposal are also not considered. PM emissions are defined<br />
as exhaust emissions from combustion, there<strong>for</strong>e PM emissions from abrasion and<br />
twirling are not included so far.<br />
Location of emission sources<br />
Depending on the impact category, the location of the emission source can be highly significant.<br />
With regard to those emissions which contribute to the greenhouse effect, the location<br />
<strong>for</strong> land bound transport modes is not relevant, whereas flights in high altitudes have additional<br />
climatic impacts. There<strong>for</strong>e in EcoTransIT World these additional impacts are included<br />
as an option <strong>for</strong> flights in altitudes over 9 kilometres by using the RFI factor (see chapter<br />
5.5).<br />
Regarding eco-toxicity and human toxicity the following locations of the emission source are<br />
relevant <strong>for</strong> the impact.<br />
• Road, rail and inland ship: urban vs. rural regions<br />
• Aircraft: airport (taxi out/in, lake off, landing) vs. cruise<br />
• Sea ship: harbour and coast vs. open sea.<br />
In EcoTransIT World this distinction is not yet made, as it would complicate the interpretation<br />
of the results in the current version of the tool. It should be part of a future version.<br />
2.2 System boundaries of processes<br />
In EcoTransIT World, only those environmental impacts are considered that are linked to the<br />
operation of vehicles and to fuel production. There<strong>for</strong>e not included are:<br />
EcoTransIT World: Methodology and Data – July 15 th , 2010