PHD Thesis - Institute for Computer Graphics and Vision - Graz ...
PHD Thesis - Institute for Computer Graphics and Vision - Graz ...
PHD Thesis - Institute for Computer Graphics and Vision - Graz ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
7.2. Localization 124<br />
(a)<br />
(b)<br />
(c)<br />
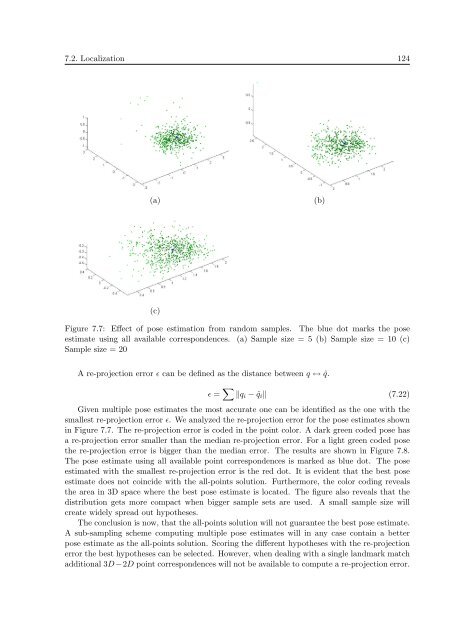
Figure 7.7: Effect of pose estimation from r<strong>and</strong>om samples. The blue dot marks the pose<br />
estimate using all available correspondences. (a) Sample size = 5 (b) Sample size = 10 (c)<br />
Sample size = 20<br />
A re-projection error ɛ can be defined as the distance between q ↔ ˆq.<br />
ɛ = ∑ ‖q i − ˆq i ‖ (7.22)<br />
Given multiple pose estimates the most accurate one can be identified as the one with the<br />
smallest re-projection error ɛ. We analyzed the re-projection error <strong>for</strong> the pose estimates shown<br />
in Figure 7.7. The re-projection error is coded in the point color. A dark green coded pose has<br />
a re-projection error smaller than the median re-projection error. For a light green coded pose<br />
the re-projection error is bigger than the median error. The results are shown in Figure 7.8.<br />
The pose estimate using all available point correspondences is marked as blue dot. The pose<br />
estimated with the smallest re-projection error is the red dot. It is evident that the best pose<br />
estimate does not coincide with the all-points solution. Furthermore, the color coding reveals<br />
the area in 3D space where the best pose estimate is located. The figure also reveals that the<br />
distribution gets more compact when bigger sample sets are used. A small sample size will<br />
create widely spread out hypotheses.<br />
The conclusion is now, that the all-points solution will not guarantee the best pose estimate.<br />
A sub-sampling scheme computing multiple pose estimates will in any case contain a better<br />
pose estimate as the all-points solution. Scoring the different hypotheses with the re-projection<br />
error the best hypotheses can be selected. However, when dealing with a single l<strong>and</strong>mark match<br />
additional 3D −2D point correspondences will not be available to compute a re-projection error.