- Page 1 and 2: y WaterGroup WATER CONDITIONING PRO
- Page 3 and 4: Facilities Directory United States
- Page 5 and 6: Hydrotech ® , “Your Clear Choice
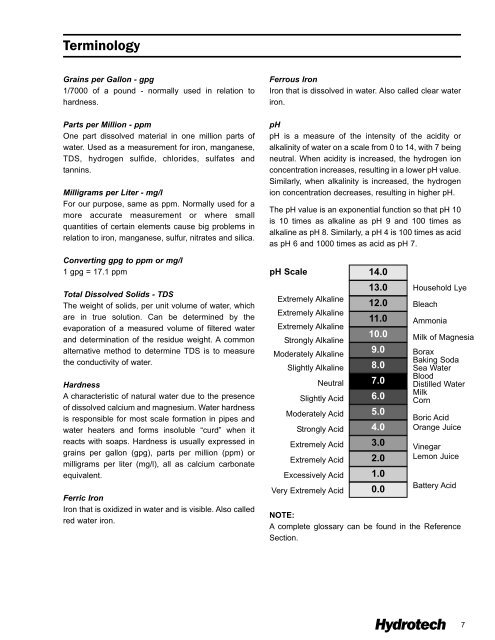
- Page 7: Guidelines for Solving Water Proble
- Page 11 and 12: 5. Standard Laboratory Tests Total
- Page 13 and 14: Fundamentals of Ion Exchange in Wat
- Page 15 and 16: The Benefits of Hydrotech ® The fo
- Page 17 and 18: Notes 16 Hydrotech
- Page 19 and 20: Assembled Water Softeners - Introdu
- Page 21 and 22: 5600 Softeners - Automatic Mechanic
- Page 23 and 24: Specifications - 5600SXT Valve Wate
- Page 25 and 26: 5600SXT Softeners - Automatic Elect
- Page 27 and 28: 2510 Softeners - Automatic Mechanic
- Page 29 and 30: Specifications - ProFlo SXT Valve W
- Page 31 and 32: ProFlo SXT Softeners - Automatic El
- Page 33 and 34: 6700XTR Softeners - Automatic Elect
- Page 35 and 36: Specifications - 7000SXT Valve Wate
- Page 37 and 38: 7000 Softeners - Automatic Electron
- Page 39 and 40: 9000 Softeners - Twin Alternating E
- Page 41 and 42: Specifications - TMI 9100 Valve Wat
- Page 43 and 44: 9100 Softeners - Twin Alternating A
- Page 45 and 46: Specifications - Hot Water Softener
- Page 47 and 48: Notes 46 Hydrotech
- Page 49 and 50: Specifications - 5600 & 2510 Valve
- Page 51 and 52: Iron and Sulfur Filters Additional
- Page 53 and 54: Activated Carbon Filters Unpleasant
- Page 55 and 56: Turbidity (Multi-Media) Filters 251
- Page 57 and 58: Neutralizing Filters Neutralizing f
- Page 59 and 60:
Specifications - 2510 Valve Chemica
- Page 61 and 62:
Chemical Free Iron Filters Addition
- Page 63 and 64:
Air Pump & Retention Tank Assembly
- Page 65 and 66:
Water Conditioning Pressure Tanks O
- Page 67 and 68:
Water Conditioning Tank Jackets Hyd
- Page 69 and 70:
Brine Tanks Brine Tank: Regular Len
- Page 71 and 72:
Bottom Stack Distributors These bot
- Page 73 and 74:
Tank Closures & Adapters #81039 Tan
- Page 75 and 76:
5600SXT - Simple Electronic Control
- Page 77 and 78:
ProFlo SXT - High Performance Contr
- Page 79 and 80:
7000SXT - High Flow Rate Control Va
- Page 81 and 82:
9100SXT - Light Commercial/Resident
- Page 83 and 84:
Mazzei Injectors Mazzei injectors (
- Page 85 and 86:
Aquafine ® Ion Exchange Resin AQ10
- Page 87 and 88:
C-100 E-FM Fine Mesh Softener Resin
- Page 89 and 90:
A-520E Macroporous Strong Base Anio
- Page 91 and 92:
RED FLINT - Filter Sand & Gravel In
- Page 93 and 94:
GreensandPlus Physical Characterist
- Page 95 and 96:
Magnesium Oxide & Calcium Carbonate
- Page 97 and 98:
GW 12 x 40 Granular Activated Carbo
- Page 99 and 100:
KDF ® 55 and 85 Process Media What
- Page 101 and 102:
Media Item # Description Quantity W
- Page 103 and 104:
Notes 102 Hydrotech
- Page 105 and 106:
Reverse Osmosis Drinking Water Syst
- Page 107 and 108:
Reverse Osmosis Drinking Water Syst
- Page 109 and 110:
Economy RO Drinking Water Systems E
- Page 111 and 112:
Value Faucets The Value Faucets are
- Page 113 and 114:
Aquatec - Reverse Osmosis Booster P
- Page 115 and 116:
Reverse Osmosis Storage Tanks For C
- Page 117 and 118:
Aqua Flo Under Sink Filter Systems
- Page 119 and 120:
Bottle-Free Point-of-Use Coolers Th
- Page 121 and 122:
Leak Controller The first line of d
- Page 123 and 124:
Notes 122 Hydrotech
- Page 125 and 126:
PURA ® Ultraviolet Disinfection Sy
- Page 127 and 128:
PURA ® Ultraviolet Disinfection Sy
- Page 129 and 130:
PURA ® Ultraviolet Disinfection Sy
- Page 131 and 132:
Notes 130 Hydrotech
- Page 133 and 134:
Aqua Flo Filters & Cartridges The A
- Page 135 and 136:
Aqua Flo Filter Cartridges Aqua Flo
- Page 137 and 138:
Aqua Flo Filter Accessories 26007 S
- Page 139 and 140:
Pentek ® Filtration Products What
- Page 141 and 142:
Slim Line ® Filter Housings #20 Bl
- Page 143 and 144:
3G Standard Filter Housings We took
- Page 145 and 146:
3G Slim Line ® Standard Filter Hou
- Page 147 and 148:
Big Blue ® Filter Housings • Lar
- Page 149 and 150:
High Temperature Filter Housings
- Page 151 and 152:
ST Series Stainless Steel Filter Ho
- Page 153 and 154:
MPST-1 Multi-Purpose Stainless Stee
- Page 155 and 156:
UMS-4 BB Housing Skid System • Ca
- Page 157 and 158:
Pentek ® Filter Housings Pressure
- Page 159 and 160:
Pentek ® Accessories Cartridge Cou
- Page 161 and 162:
C Series Dual Purpose Powdered-Acti
- Page 163 and 164:
NCP Series Non-Cellulose Carbon-Imp
- Page 165 and 166:
CFB-Plus Series Modified Molded Blo
- Page 167 and 168:
CFB-PB10 Lead Reduction Modified Mo
- Page 169 and 170:
CBC Series Carbon Briquette Cartrid
- Page 171 and 172:
CBR2 Series Carbon Briquette Multim
- Page 173 and 174:
CEP-10E Series Coconut Based Carbon
- Page 175 and 176:
Chloramine Reduction Carbon Cartrid
- Page 177 and 178:
CC-10 Series Coconut Shell Granular
- Page 179 and 180:
RFC Series Radial Flow Carbon Cartr
- Page 181 and 182:
R Series Pleated Polyester Cartridg
- Page 183 and 184:
ECP Series Pleated Cellulose Polyes
- Page 185 and 186:
P Series Spun Bonded-Polypropylene
- Page 187 and 188:
DGD Series Dual-Gradient Density Ca
- Page 189 and 190:
Big Blue Polypropylene Wound Cartri
- Page 191 and 192:
Quick-Change Filtration Systems •
- Page 193 and 194:
Gold In-Line Filtration Systems •
- Page 195 and 196:
Sealed In-Line Series • Provide b
- Page 197 and 198:
Microguard Membrane Filter Cartridg
- Page 199 and 200:
PCC Series Hexametaphosphate Crysta
- Page 201 and 202:
PCF Series Mixed Bed Deionization C
- Page 203 and 204:
WS Series Water Softener Cartridges
- Page 205 and 206:
Notes 204 Hydrotech
- Page 207 and 208:
Hot Water Side Stream Filter System
- Page 209 and 210:
Absolute Rated POLY-PLEAT Cartridge
- Page 211 and 212:
Notes 210 Hydrotech
- Page 213 and 214:
Stenner Peristaltic Chemical Feed P
- Page 215 and 216:
Stenner Peristaltic Chemical Feed P
- Page 217 and 218:
Stenner Peristaltic Chemical Feed P
- Page 219 and 220:
Series C Electronic Metering Pumps
- Page 221 and 222:
Series E Electronic Metering Pumps
- Page 223 and 224:
Series E PLUS Electronic Metering P
- Page 225 and 226:
Series MP Electronic Metering Pumps
- Page 227 and 228:
Chem-Tech Series 100 Metering Pumps
- Page 229 and 230:
Retention Tanks The Universal Serie
- Page 231 and 232:
Accessories Flow Switches Johnson C
- Page 233 and 234:
Chlorination System Installation pH
- Page 235 and 236:
Chemical Resistance Guide The follo
- Page 237 and 238:
Chemical Resistance Guide COATINGS:
- Page 239 and 240:
Pro Solutions Products The followin
- Page 241 and 242:
Pro-Softener Mate Softener Mate is
- Page 243 and 244:
Pro-Pot Perm Pot Perm is a strong o
- Page 245 and 246:
Pro-Ban T Formerly Pro-Citric Acid
- Page 247 and 248:
Pro-Poly 4 Poly 4 sequesters iron a
- Page 249 and 250:
Res-Up Feeders This programmed feed
- Page 251 and 252:
Hach Test Kits Part # Description 4
- Page 253 and 254:
Notes 252 Hydrotech
- Page 255 and 256:
Commercial Products If you haven’
- Page 257 and 258:
Request for Commercial Bid Sales Ag
- Page 259 and 260:
FAF SERIES Commercial Water Softene
- Page 261 and 262:
FAF SERIES Commercial Water Softene
- Page 263 and 264:
FAF SERIES Commercial Softeners Eng
- Page 265 and 266:
TMI SERIES Commercial Water Softene
- Page 267 and 268:
LCS SERIES Commercial Water Softene
- Page 269 and 270:
DAF SERIES Commercial Chloride Anio
- Page 271 and 272:
DAF SERIES Chloride Anion Dealkaliz
- Page 273 and 274:
Commercial Water Filter Specificati
- Page 275 and 276:
Commercial Water Filter Engineered
- Page 277 and 278:
9000 Control Valve 9000 Features
- Page 279 and 280:
2750 Control Valve 2750 Features
- Page 281 and 282:
2900s Control Valve 2900s Features
- Page 283 and 284:
3900 Control Valve 3900 Features
- Page 285 and 286:
3200NXT Controller The 3200NXT Netw
- Page 287 and 288:
SXT Controller System Configuration
- Page 289 and 290:
WGR SERIES Commercial Reverse Osmos
- Page 291 and 292:
TWS SERIES Storage System Approx Pa
- Page 293 and 294:
AquaMatic ® Diaphragm Valves The A
- Page 295 and 296:
Sales & Marketing Materials All bro
- Page 297 and 298:
Sales & Marketing Materials Our web
- Page 299 and 300:
Pressure Loss of Water Due to Frict
- Page 301 and 302:
Pressure Drop per 1000 Feet of Sche
- Page 303 and 304:
Flow of Water Through PVC and CPVC
- Page 305 and 306:
Conversion Factors Multiply by To O
- Page 307 and 308:
Water Conditioning Glossary Absorpt
- Page 309 and 310:
Disinfection - A process in which p
- Page 311 and 312:
Nanometer - A measure of a waveleng
- Page 313 and 314:
Notes 312 Hydrotech