a review - Acta Technica Corviniensis
a review - Acta Technica Corviniensis
a review - Acta Technica Corviniensis
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
ROLE OF METAMODELING<br />
Detailed research has been carried out in using<br />
metamodeling techniques in design optimization.<br />
This research includes experimental design methods,<br />
metamodel types, model fitting techniques,<br />
application of metamodels in design optimization and<br />
reliability based design. Through literatures it has<br />
become clear that metamodeling provides a decision<br />
support role for all design engineers. The supporting<br />
functions that metamodels can provide are listed<br />
here with reference to the literatures [6]:<br />
a) Model approximation-models which replace the<br />
computationally expensive codes,<br />
b) Design space exploration-understanding the design<br />
problem in the whole design space by using<br />
metamodels,<br />
c) Optimization – e.g., global optimization, multiobjective<br />
optimization, multidisciplinary<br />
optimization, probabilistic optimization and so on.<br />
Metamodels are integrated to the above<br />
optimization problems to reduce the<br />
computational burden.<br />
d) Reliability based design- Reliability assessment is<br />
the prime function for Reliability based design.<br />
Metamodels are used to approximate the<br />
expensive constraint functions, or the limit state<br />
function.<br />
Figure 1 illustrates the support afforded by<br />
metamodels.<br />
Figure 1. Support provided by metamodels<br />
The evolution of metamodel based analysis is<br />
summarized in figure 2, which shows the number of<br />
publications related to metamodels over the past<br />
three decades. This data was obtained using the<br />
‘Scirus scientific research tool’ where we searched<br />
for occurrences of the word: “metamodels”(during<br />
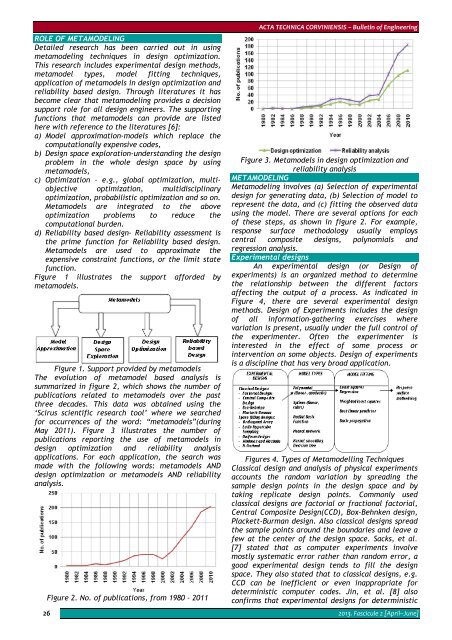
May 2011). Figure 3 illustrates the number of<br />
publications reporting the use of metamodels in<br />
design optimization and reliability analysis<br />
applications. For each application, the search was<br />
made with the following words: metamodels AND<br />
design optimization or metamodels AND reliability<br />
analysis.<br />
26<br />
Figure 2. No. of publications, from 1980 - 2011<br />
ACTA TECHNICA CORVINIENSIS – Bulletin of Engineering<br />
Figure 3. Metamodels in design optimization and<br />
reliability analysis<br />
METAMODELING<br />
Metamodeling involves (a) Selection of experimental<br />
design for generating data, (b) Selection of model to<br />
represent the data, and (c) fitting the observed data<br />
using the model. There are several options for each<br />
of these steps, as shown in figure 2. For example,<br />
response surface methodology usually employs<br />
central composite designs, polynomials and<br />
regression analysis.<br />
Experimental designs<br />
An experimental design (or Design of<br />
experiments) is an organized method to determine<br />
the relationship between the different factors<br />
affecting the output of a process. As indicated in<br />
Figure 4, there are several experimental design<br />
methods. Design of Experiments includes the design<br />
of all information-gathering exercises where<br />
variation is present, usually under the full control of<br />
the experimenter. Often the experimenter is<br />
interested in the effect of some process or<br />
intervention on some objects. Design of experiments<br />
is a discipline that has very broad application.<br />
Figures 4. Types of Metamodelling Techniques<br />
Classical design and analysis of physical experiments<br />
accounts the random variation by spreading the<br />
sample design points in the design space and by<br />
taking replicate design points. Commonly used<br />
classical designs are factorial or fractional factorial,<br />
Central Composite Design(CCD), Box-Behnken design,<br />
Plackett-Burman design. Also classical designs spread<br />
the sample points around the boundaries and leave a<br />
few at the center of the design space. Sacks, et al.<br />
[7] stated that as computer experiments involve<br />
mostly systematic error rather than random error, a<br />
good experimental design tends to fill the design<br />
space. They also stated that to classical designs, e.g.<br />
CCD can be inefficient or even inappropriate for<br />
deterministic computer codes. Jin, et al. [8] also<br />
confirms that experimental designs for deterministic<br />
2013. Fascicule 2 [April–June]