- Page 1:
A 1 E=mc 2 This eBook is downloaded
- Page 4 and 5:
About the Authors Allyson Weseley h
- Page 6 and 7:
Perception Practice Questions 5 Sta
- Page 8:
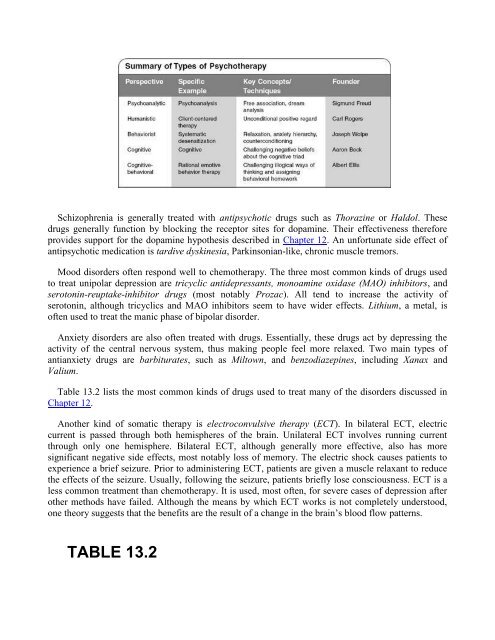
13 Treatment of Psychological Disor
- Page 11 and 12:
The College Board recently revised
- Page 13:
Overview of the AP Psychology Exam
- Page 16 and 17:
(A) negative reinforcement. (B) sha
- Page 18 and 19:
(B) 2 years (C) 4 years (D) 8 years
- Page 20 and 21:
(A) damage to her fovea. (B) place
- Page 22 and 23:
(A) humanistic. (B) sociocultural.
- Page 24 and 25:
48. In the past when Nuara’s comp
- Page 26 and 27:
(E) central 59. Which part of the b
- Page 28 and 29:
(D) 82 (E) 95 70. The typical age o
- Page 30 and 31:
(C) idiographic (D) sociocultural (
- Page 32 and 33:
(C) long-term memory. (D) echoic me
- Page 34 and 35:
Answer Key DIAGNOSTIC TEST 1. B 36.
- Page 36 and 37:
necessarily related to being creati
- Page 38 and 39:
uses magnetic fields to show both s
- Page 40 and 41:
the high school students taking AP
- Page 42 and 43:
when people’s preexisting beliefs
- Page 44 and 45:
of the trials but simply not had an
- Page 46 and 47:
76. (C) Group therapy tends to be l
- Page 48 and 49:
89. (D) The prefrontal cortex plays
- Page 50 and 51:
MULTIPLE-CHOICE ERROR ANALYSIS SHEE
- Page 52 and 53:
QUESTION 1 SCORING RUBRIC This is a
- Page 54 and 55:
eal-world violence” as the variab
- Page 56 and 57:
attention determines what informati
- Page 58 and 59:
Also, notice that this (fictional)
- Page 60 and 61:
History and Approaches CHAPTER 1 KE
- Page 62 and 63:
epression—the pushing down into t
- Page 64 and 65:
certain neurotransmitters in the br
- Page 66 and 67:
(D) focused entirely on human males
- Page 68 and 69:
13. Symbolic dream analysis might b
- Page 70 and 71:
10. (D) Watson referred to the cond
- Page 72 and 73:
Coercion Informed consent Anonymity
- Page 74 and 75:
the study and therefore are not par
- Page 76 and 77:
groups may possibly be due not to t
- Page 78 and 79:
irth onward. If I seek to control a
- Page 80 and 81:
since that value is in excess of ev
- Page 82 and 83:
perfect, negative correlation and +
- Page 84 and 85:
In both cases, you would be correct
- Page 86 and 87:
(A) sampling error. (B) the need to
- Page 88 and 89:
II. Having a computer generate a ra
- Page 90 and 91:
accredited commercial sources) and
- Page 92 and 93:
Biological Bases of Behavior CHAPTE
- Page 94 and 95:
Terminal buttons (also called end b
- Page 96 and 97:
Afferent Neurons (or Sensory Neuron
- Page 98 and 99:
heart rate, blood pressure, and res
- Page 100 and 101:
An electroencephalogram (EEG) detec
- Page 102 and 103:
Pons The pons (located just above t
- Page 104 and 105:
sensory messages and controls the m
- Page 106 and 107:
of each retina are processed in the
- Page 108 and 109:
separate families obviously share v
- Page 110 and 111:
(E) neurons, synapses, and cerebral
- Page 112 and 113:
2. (B) The motor cortex (which is l
- Page 114 and 115:
Sensation and Perception CHAPTER 4
- Page 116 and 117:
The first three senses listed here,
- Page 118 and 119:
enough bipolar cells fire, the next
- Page 120 and 121:
Figure 4.2. Cross section of the ea
- Page 122 and 123:
CHEMICAL SENSES Taste (or Gustation
- Page 124 and 125:
BODY POSITION SENSES Vestibular Sen
- Page 126 and 127:
Perceptual Theories Psychologists u
- Page 128 and 129:
Figure 4.5. Optical illusion. Gesta
- Page 130 and 131:
Depth Cues One of the most importan
- Page 132 and 133:
3. In a perception research lab, yo
- Page 134 and 135:
14. What behavior would be difficul
- Page 136 and 137:
is being filled in, instead of an i
- Page 138 and 139:
OVERVIEW While you are reading this
- Page 140 and 141:
Sleep Cycle You may be familiar wit
- Page 142 and 143:
up until his graduation from high s
- Page 144 and 145:
Researcher Ernest Hilgard explained
- Page 146 and 147:
Practice Questions Directions: Each
- Page 148 and 149:
12. In the context of this unit, th
- Page 150 and 151:
activation-synthesis theory of drea
- Page 152 and 153:
Albert Bandura Edward Tolman Wolfga
- Page 154 and 155:
esponse to the white rat. Aversive
- Page 156 and 157:
B. F. Skinner, who coined the term
- Page 158 and 159:
things in the Skinner box or the ba
- Page 160 and 161:
and tend, instead, to bury the disk
- Page 162 and 163:
Tolman reasoned that these rats mus
- Page 164 and 165:
(B) aversive conditioning. (C) simu
- Page 166 and 167:
1. (B) The music before a scary eve
- Page 168 and 169:
important point: the word positive
- Page 170 and 171:
Functional fixedness Confirmation b
- Page 172 and 173:
with one person at a party but then
- Page 174 and 175:
One factor is the order in which th
- Page 176 and 177:
memory, is stored elsewhere in the
- Page 178 and 179:
THINKING AND CREATIVITY Describing
- Page 180 and 181:
very different than what the design
- Page 182 and 183:
(D) The words in each language affe
- Page 184 and 185:
(C) a child of normal mental abilit
- Page 186 and 187:
14. (C) The critical-period hypothe
- Page 188 and 189:
OVERVIEW In my psychology class, I
- Page 190 and 191:
motivation to return to the baselin
- Page 192 and 193:
hypothalamus act in opposition to c
- Page 194 and 195:
Sexual Response Cycle The famous la
- Page 196 and 197:
esponds best to can give managers a
- Page 198 and 199:
Schachter showed that people who ar
- Page 200 and 201:
Practice Questions Directions: Each
- Page 202 and 203:
(B) decreased motivation to perform
- Page 204 and 205:
equally active in work groups and m
- Page 206 and 207:
Konrad Lorenz Harry Harlow Mary Ain
- Page 208 and 209:
MOTOR/SENSORY DEVELOPMENT Reflexes
- Page 210 and 211:
MARY AINSWORTH Mary Ainsworth resea
- Page 212 and 213:
Sigmund Freud Historically, Freud w
- Page 214 and 215:
Integrity versus despair Toward the
- Page 216 and 217:
Formal operations (12 through adult
- Page 218 and 219:
During the next level of moral reas
- Page 220 and 221:
etween the sexes. However, biopsych
- Page 222 and 223:
(A) teratogens. (B) stress on the m
- Page 224 and 225:
(E) authoritative 15. Which of the
- Page 226 and 227:
Personality CHAPTER 10 KEY TERMS Pe
- Page 228 and 229:
Both the Oedipus and Electra crises
- Page 230 and 231:
• Biff continues to act as if he
- Page 232 and 233:
Impact of Freudian Theory Despite i
- Page 234 and 235:
BIOLOGICAL THEORIES Biological theo
- Page 236 and 237: HUMANISTIC THEORIES Many of the mod
- Page 238 and 239: psychologists, particularly cogniti
- Page 240 and 241: (C) identifying core principles by
- Page 242 and 243: 7. (C) Dr. Li is using the TAT (the
- Page 244 and 245: Testing and Individual Differences
- Page 246 and 247: same person, it clearly does not ac
- Page 248 and 249: Charles Spearman One fundamental is
- Page 250 and 251: created a test that would identify
- Page 252 and 253: NATURE VERSUS NURTURE: INTELLIGENCE
- Page 254 and 255: Practice Questions Directions: Each
- Page 256 and 257: 12. Although her score on the perso
- Page 258 and 259: 7. (C) Spearman argued that intelli
- Page 260 and 261: Abnormal Psychology CHAPTER 12 KEY
- Page 262 and 263: Disorders (DSM). Periodically, this
- Page 264 and 265: a situation in which one could emba
- Page 266 and 267: Dissociative identity disorder (DID
- Page 268 and 269: A growing body of evidence suggests
- Page 270 and 271: • Parkinson’s disease, characte
- Page 272 and 273: Paraphilias or psychosexual disorde
- Page 274 and 275: Practice Questions Directions: Each
- Page 276 and 277: (C) cognitive (D) behavioral (E) so
- Page 278 and 279: psychologists would locate the caus
- Page 280 and 281: Albert Ellis OVERVIEW Just as there
- Page 282 and 283: of Consciousness,” is an altered
- Page 284 and 285: the doctor’s office. His mother m
- Page 288 and 289: The most intrusive and rarest form
- Page 290 and 291: 2. Coretta’s therapist says littl
- Page 292 and 293: (B) client-centered (C) aversive co
- Page 294 and 295: 9. (B) Transference is when patient
- Page 296 and 297: Stanley Milgram Irving Janis Philli
- Page 298 and 299: already said that the boring task w
- Page 300 and 301: attribution error. Say that you go
- Page 302 and 303: Origin of Stereotypes and Prejudice
- Page 304 and 305: that good-looking people are percei
- Page 306 and 307: TABLE 14.1 Group polarization is th
- Page 308 and 309: (C) modeling. (D) diffusion of resp
- Page 310 and 311: 14. On the first day of class, Mr.
- Page 312 and 313: error is a different attributional
- Page 314 and 315: Here’s another example: A psychol
- Page 316 and 317: (E) Table manners are learned by re
- Page 318 and 319: Answering Free-Response Questions C
- Page 320 and 321: 6. When asked about a psychological
- Page 322 and 323: INTERPRETING THE RUBRIC Notice how
- Page 324 and 325: Point 4 — Not awarded—The stude
- Page 326 and 327: (E) PTSD. 5. Which psychological pe
- Page 328 and 329: (A) social facilitation (B) deindiv
- Page 330 and 331: (B) contextual intelligence (C) div
- Page 332 and 333: 34. Which of the following statisti
- Page 334 and 335: (E) adult genital stage. 45. Daniel
- Page 336 and 337:
(D) the fundamental attribution err
- Page 338 and 339:
64. Matt’s research design could
- Page 340 and 341:
(C) the social role hypothesis. (D)
- Page 342 and 343:
(A) social facilitation. (B) confor
- Page 344 and 345:
(D) James-Lange theory (E) opponent
- Page 346 and 347:
Answer Key PRACTICE TEST #1 1. D 36
- Page 348 and 349:
6. (C) Pascale would best be classi
- Page 350 and 351:
18. (B) Counterconditioning lies at
- Page 352 and 353:
29. (E) Of the disorders listed, ma
- Page 354 and 355:
40. (E) Jamie’s printer problems
- Page 356 and 357:
ethics. People with low self-esteem
- Page 358 and 359:
take the energy from impulses they
- Page 360 and 361:
Genna’s right hemisphere was dama
- Page 362 and 363:
SSRIs (serotonin selective reuptake
- Page 364 and 365:
effect would not be particularly he
- Page 366 and 367:
Question 1 Scoring Rubric This is a
- Page 368 and 369:
Part B Point 4 — Yerkes-Dodson la
- Page 370 and 371:
(A) hearing (B) touch (C) balance (
- Page 372 and 373:
(A) proximity and similarity (B) to
- Page 374 and 375:
(C) primary (physical) and secondar
- Page 376 and 377:
(C) unconditional positive regard (
- Page 378 and 379:
(E) Dreams reflect variations in br
- Page 380 and 381:
(C) median (D) mean (E) normal curv
- Page 382 and 383:
(B) semantic memory (C) procedural
- Page 384 and 385:
(D) disorganized, paranoid, cataton
- Page 386 and 387:
(C) Operant conditioning is used to
- Page 388 and 389:
(B) to explain the biomedical sympt
- Page 390 and 391:
Answer Key PRACTICE TEST #2 1. C 36
- Page 392 and 393:
nondamaged parts of the brain and r
- Page 394 and 395:
28. (D) Stimulation of the lateral
- Page 396 and 397:
48. (A) Psychotherapies all involve
- Page 398 and 399:
67. (D) Generalization occurs in cl
- Page 400 and 401:
hybrid cars” and “don’t own h
- Page 402 and 403:
Multiple-Choice Error Analysis Shee
- Page 404 and 405:
Point 3 — Students need to briefl
- Page 406 and 407:
SAMPLE STUDENT RESPONSE ESSAY 2 SCO