Solar Drying: Fundamentals,Applications and Innovations - National ...
Solar Drying: Fundamentals,Applications and Innovations - National ...
Solar Drying: Fundamentals,Applications and Innovations - National ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Fadhel - Recent Advancements in <strong>Solar</strong> <strong>Drying</strong><br />
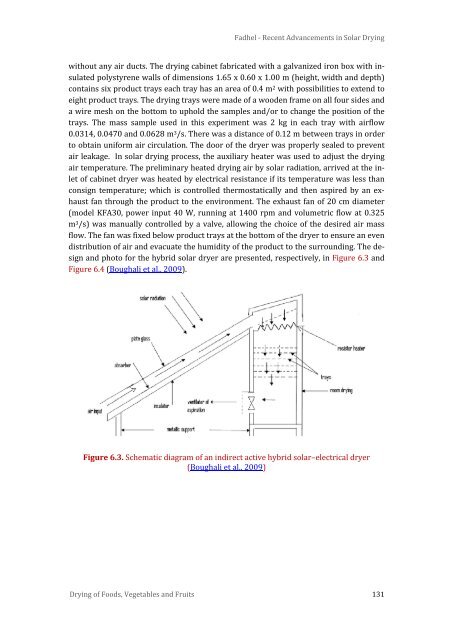
without any air ducts. The drying cabinet fabricated with a galvanized iron box with insulated<br />
polystyrene walls of dimensions 1.65 x 0.60 x 1.00 m (height, width <strong>and</strong> depth)<br />
contains six product trays each tray has an area of 0.4 m 2 with possibilities to extend to<br />
eight product trays. The drying trays were made of a wooden frame on all four sides <strong>and</strong><br />
a wire mesh on the bottom to uphold the samples <strong>and</strong>/or to change the position of the<br />
trays. The mass sample used in this experiment was 2 kg in each tray with airflow<br />
0.0314, 0.0470 <strong>and</strong> 0.0628 m 3 /s. There was a distance of 0.12 m between trays in order<br />
to obtain uniform air circulation. The door of the dryer was properly sealed to prevent<br />
air leakage. In solar drying process, the auxiliary heater was used to adjust the drying<br />
air temperature. The preliminary heated drying air by solar radiation, arrived at the inlet<br />
of cabinet dryer was heated by electrical resistance if its temperature was less than<br />
consign temperature; which is controlled thermostatically <strong>and</strong> then aspired by an exhaust<br />
fan through the product to the environment. The exhaust fan of 20 cm diameter<br />
(model KFA30, power input 40 W, running at 1400 rpm <strong>and</strong> volumetric flow at 0.325<br />
m 3 /s) was manually controlled by a valve, allowing the choice of the desired air mass<br />
flow. The fan was fixed below product trays at the bottom of the dryer to ensure an even<br />
distribution of air <strong>and</strong> evacuate the humidity of the product to the surrounding. The design<br />
<strong>and</strong> photo for the hybrid solar dryer are presented, respectively, in Figure 6.3 <strong>and</strong><br />
Figure 6.4 (Boughali et al., 2009).<br />
Figure 6.3. Schematic diagram of an indirect active hybrid solar–electrical dryer<br />
(Boughali et al., 2009)<br />
<strong>Drying</strong> of Foods, Vegetables <strong>and</strong> Fruits 131