CSP Gateway Configuration Guide - InterSystems Documentation
CSP Gateway Configuration Guide - InterSystems Documentation
CSP Gateway Configuration Guide - InterSystems Documentation
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
CGI Environment Variables<br />
The client principal name (or client username) is that of the <strong>Gateway</strong> host. This is the name used to identify the key in the<br />
Kerberos Key Table. Assign this principal the necessary privileges in the Caché server to allow the <strong>Gateway</strong>’s service to<br />
operate.<br />
2.3 CGI Environment Variables<br />
CGI Environment Variables are derived both from the client’s HTTP request headers and from the environment in which<br />
the Web server is operating. The <strong>CSP</strong> <strong>Gateway</strong> transmits the common environment variables to Caché with each and every<br />
request. If extra environment variables are required by the application, they must be explicitly requested in the <strong>CSP</strong> <strong>Gateway</strong><br />
configuration (via the Extra CGI Environment Variables setting in the Application Access section of the configuration)<br />
[Home] > [<strong>Configuration</strong>] > [<strong>CSP</strong> <strong>Gateway</strong> Managment] and select Application Access<br />
The list of environment variables transmitted is shown in the table below together with a brief description of each. Further<br />
documentation can be obtained from standard Web text books. See also the section “CgiEnvs Property and CGI Environment<br />
Variables” in Using Caché Server Pages.<br />
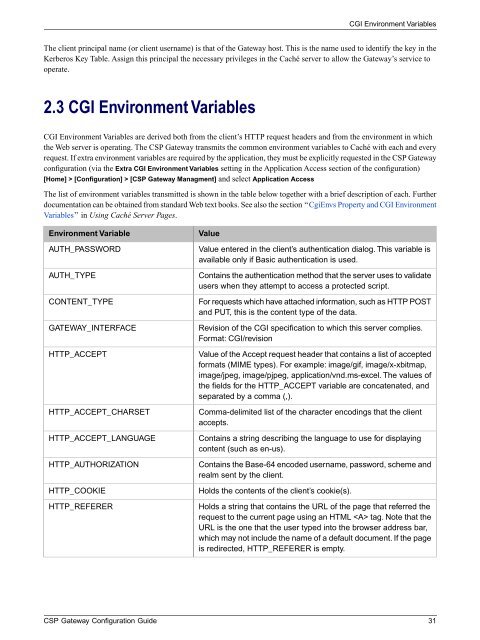
Environment Variable<br />
AUTH_PASSWORD<br />
AUTH_TYPE<br />
CONTENT_TYPE<br />
GATEWAY_INTERFACE<br />
HTTP_ACCEPT<br />
HTTP_ACCEPT_CHARSET<br />
HTTP_ACCEPT_LANGUAGE<br />
HTTP_AUTHORIZATION<br />
HTTP_COOKIE<br />
HTTP_REFERER<br />
Value<br />
Value entered in the client’s authentication dialog. This variable is<br />
available only if Basic authentication is used.<br />
Contains the authentication method that the server uses to validate<br />
users when they attempt to access a protected script.<br />
For requests which have attached information, such as HTTP POST<br />
and PUT, this is the content type of the data.<br />
Revision of the CGI specification to which this server complies.<br />
Format: CGI/revision<br />
Value of the Accept request header that contains a list of accepted<br />
formats (MIME types). For example: image/gif, image/x-xbitmap,<br />
image/jpeg, image/pjpeg, application/vnd.ms-excel. The values of<br />
the fields for the HTTP_ACCEPT variable are concatenated, and<br />
separated by a comma (,).<br />
Comma-delimited list of the character encodings that the client<br />
accepts.<br />
Contains a string describing the language to use for displaying<br />
content (such as en-us).<br />
Contains the Base-64 encoded username, password, scheme and<br />
realm sent by the client.<br />
Holds the contents of the client’s cookie(s).<br />
Holds a string that contains the URL of the page that referred the<br />
request to the current page using an HTML tag. Note that the<br />
URL is the one that the user typed into the browser address bar,<br />
which may not include the name of a default document. If the page<br />
is redirected, HTTP_REFERER is empty.<br />
<strong>CSP</strong> <strong>Gateway</strong> <strong>Configuration</strong> <strong>Guide</strong> 31