You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Process Scheduling<br />
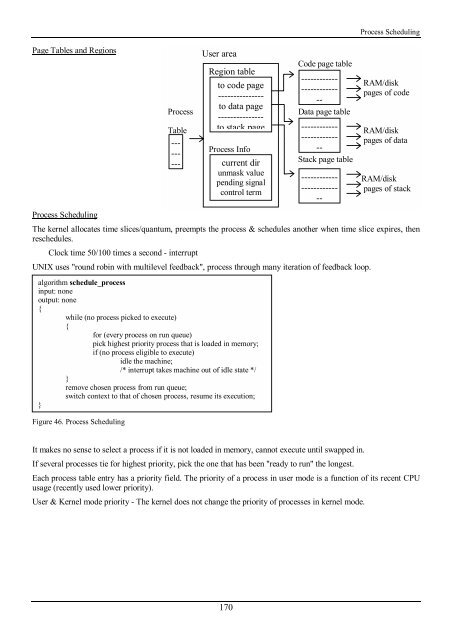
Page Tables and Regions<br />
Process<br />
Table<br />
---<br />
---<br />
---<br />
User area<br />
Region table<br />
to code page<br />
---------------<br />
to data page<br />
---------------<br />
to stack page<br />
Process Info<br />
current dir<br />
unmask value<br />
pending signal<br />
control term<br />
Code page table<br />
------------<br />
------------<br />
--<br />
Data page table<br />
------------<br />
------------<br />
--<br />
Stack page table<br />
------------<br />
------------<br />
--<br />
RAM/disk<br />
pages of code<br />
RAM/disk<br />
pages of data<br />
RAM/disk<br />
pages of stack<br />
Process Scheduling<br />
The kernel allocates time slices/quantum, preempts <strong>the</strong> process & schedules ano<strong>the</strong>r when time slice expires, <strong>the</strong>n<br />
reschedules.<br />
Clock time 50/100 times a second - interrupt<br />
UNIX uses "round robin <strong>with</strong> multilevel feedback", process through many iteration of feedback loop.<br />
algorithm schedule_process<br />
input: none<br />
output: none<br />
{<br />
while (no process picked to execute)<br />
{<br />
for (every process on run queue)<br />
pick highest priority process that is loaded in memory;<br />
if (no process eligible to execute)<br />
idle <strong>the</strong> machine;<br />
/* interrupt takes machine out of idle state */<br />
}<br />
remove chosen process from run queue;<br />
switch context to that of chosen process, resume its execution;<br />
}<br />
Figure 46. Process Scheduling<br />
It makes no sense to select a process if it is not loaded in memory, cannot execute until swapped in.<br />
If several processes tie for highest priority, pick <strong>the</strong> one that has been "ready to run" <strong>the</strong> longest.<br />
Each process table entry has a priority field. The priority of a process in user mode is a function of its recent CPU<br />
usage (recently used lower priority).<br />
User & Kernel mode priority - The kernel does not change <strong>the</strong> priority of processes in kernel mode.<br />
170