Telematics Chapter 6: Network Layer - Freie Universität Berlin
Telematics Chapter 6: Network Layer - Freie Universität Berlin
Telematics Chapter 6: Network Layer - Freie Universität Berlin
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
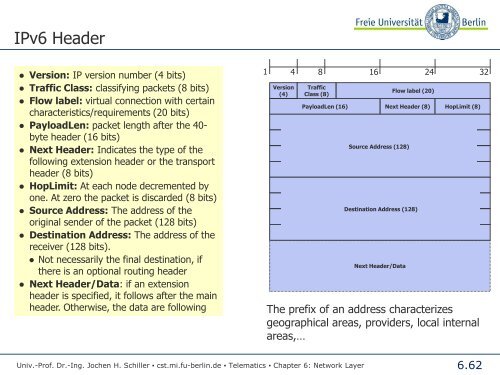
IPv6 Header<br />
● Version: IP version number (4 bits)<br />
● Traffic Class: classifying packets (8 bits)<br />
● Flow label: virtual connection with certain<br />
characteristics/requirements (20 bits)<br />
● PayloadLen: packet length after the 40byte<br />
header (16 bits)<br />
● Next Header: Indicates the type of the<br />
following extension header or the transport<br />
header (8 bits)<br />
● HopLimit: At each node decremented by<br />
one. At zero the packet is discarded (8 bits)<br />
● Source Address: The address of the<br />
original sender of the packet (128 bits)<br />
● Destination Address: The address of the<br />
receiver (128 bits).<br />
● Not necessarily the final destination, if<br />
there is an optional routing header<br />
● Next Header/Data: if an extension<br />
header is specified, it follows after the main<br />
header. Otherwise, the data are following<br />
1 4 8 16 24<br />
32<br />
Version<br />
(4)<br />
Traffic<br />
Class (8)<br />
PayloadLen (16)<br />
Univ.-Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen H. Schiller ▪ cst.mi.fu-berlin.de ▪ <strong>Telematics</strong> ▪ <strong>Chapter</strong> 6: <strong>Network</strong> <strong>Layer</strong><br />
Source Address (128)<br />
Next Header/Data<br />
Flow label (20)<br />
Destination Address (128)<br />
Next Header (8) HopLimit (8)<br />
The prefix of an address characterizes<br />
geographical areas, providers, local internal<br />
areas,…<br />
6.62