- Page 1 and 2:
Telematics Chapter 6: Network Layer
- Page 3 and 4:
Design Issues Connection principles
- Page 5 and 6:
Layers in the Network Application P
- Page 7 and 8:
Two Fundamental Philosophies ● Co
- Page 9 and 10:
Connection-Oriented Communication C
- Page 11 and 12:
Routing ● Most important function
- Page 13 and 14:
Routing - Connectionless Univ.-Prof
- Page 15 and 16:
Routing - Comparison Issue Connecti
- Page 17 and 18:
The Optimality Principle A subnet A
- Page 19 and 20:
Internet Univ.-Prof. Dr.-Ing. Joche
- Page 21 and 22:
On the Way to Today's Internet Stru
- Page 23 and 24:
ARPANET A node consists of ● an I
- Page 25 and 26:
Evolution by ARPANET Very fast evol
- Page 27 and 28: TCP/IP ● Developed 1974: ● Tran
- Page 29 and 30: From the ARPANET to the Internet
- Page 31 and 32: Evolution of the Internet Univ.-Pro
- Page 33 and 34: Internet ● What does it mean: “
- Page 35 and 36: The classical TCP/IP Protocol Suite
- Page 37 and 38: Internet Protocol (IP) Univ.-Prof.
- Page 39 and 40: Internet Protocol (IP) ● IP: conn
- Page 41 and 42: The IP Header (1) ● Version (4 bi
- Page 43 and 44: Fragmentation ● A too large or to
- Page 45 and 46: Internet Protocol (IP) Addressing U
- Page 47 and 48: IP Addresses 192.168.13.x 192.168.1
- Page 49 and 50: IP Addressing: Examples The represe
- Page 51 and 52: IP Addresses are scarce… ● Prob
- Page 53 and 54: IP Subnets ● Within an IP network
- Page 55 and 56: IP Subnets: Computation of the Dest
- Page 57 and 58: IPv6 Univ.-Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen H.
- Page 59 and 60: IPv6 ● Why changing the protocol,
- Page 61 and 62: IPv6: Characteristics ● Address s
- Page 63 and 64: IPv6 Header ● Packet size require
- Page 65 and 66: IPv6 Path MTU Discovery ● Path MT
- Page 67 and 68: IPv6 Extension Headers ● Optional
- Page 69 and 70: IPv6 Extension Headers ● Two exte
- Page 71 and 72: IPv6 Addresses (RFC 4291) ● IPv6
- Page 73 and 74: IPv6 Addresses: Representation of a
- Page 75 and 76: IPv6 Addresses: Representation of a
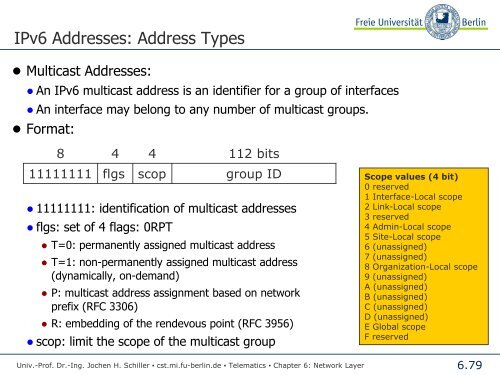
- Page 77: IPv6 Addresses: Address Types ● G
- Page 81 and 82: Transition from IPv4 to IPv6 ● IP
- Page 83 and 84: Transition from IPv4 to IPv6 ● Tr
- Page 85 and 86: Network Address Translation (NAT) U
- Page 87 and 88: Network Address Translation (NAT)
- Page 89 and 90: NAT Variants ● Disadvantages of s
- Page 91 and 92: Problems with NAPT ● NAPT works w
- Page 93 and 94: Auxiliary Protocols ARP, RARP, DHCP
- Page 95 and 96: Auxiliary Protocols ● IP serves o
- Page 97 and 98: Delivery of IP Packets ● Address
- Page 99 and 100: Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) O
- Page 101 and 102: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
- Page 103 and 104: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
- Page 105 and 106: How to realize Multicast with IPv4?
- Page 107 and 108: Internet Group Management Protocol
- Page 109 and 110: Multicast Groups: Example Network w
- Page 111 and 112: Internet Control Message Protocol (
- Page 113 and 114: ICMP: Header ● ICMP message field
- Page 115 and 116: ICMP: Applications ● Some very po
- Page 117 and 118: Some Tools Univ.-Prof. Dr.-Ing. Joc
- Page 119 and 120: Some Tools: Route ● Route ● Dis
- Page 121 and 122: Some Tools: Traceroute ● Tracerou
- Page 123 and 124: Some Tools: Pathping (2) Computing
- Page 125 and 126: Internet Layer ● Raw division int
- Page 127 and 128: Routing in the Internet ● The Int
- Page 129 and 130:
Routing in a Sub-Network ● Sub-ne
- Page 131 and 132:
Routing Algorithms: Graph abstracti
- Page 133 and 134:
Routing Algorithms: Taxonomy static
- Page 135 and 136:
Static Routing ● Source Routing
- Page 137 and 138:
Static Routing ● Flooding Princip
- Page 139 and 140:
Local Estimation Procedure in Via L
- Page 141 and 142:
Probabilistic Routing ● Router de
- Page 143 and 144:
Routing: Shortest Path ● Static v
- Page 145 and 146:
Shortest Path: Dijkstra (1) ● Alg
- Page 147 and 148:
Shortest Path: Dijkstra (3) A 2 6 B
- Page 149 and 150:
Shortest Path: Dijkstra (5) A 2 6 B
- Page 151 and 152:
Shortest Path: Dijkstra (7) A 2 6 B
- Page 153 and 154:
Shortest Path: Dijkstra (9) A 6 2 B
- Page 155 and 156:
Implementation of Dijkstra (2) do {
- Page 157 and 158:
Distance Vector Routing ● Problem
- Page 159 and 160:
Distance Vector Routing Distance Ve
- Page 161 and 162:
Distance Vector Routing: Example A
- Page 163 and 164:
Distance Vector Routing: Example B
- Page 165 and 166:
Distance Vector Routing: Example Ro
- Page 167 and 168:
Distance Vector Routing: Example Fr
- Page 169 and 170:
Distance Vector Routing: Example Fr
- Page 171 and 172:
Distance Vector Routing: Connection
- Page 173 and 174:
Distance Vector Routing: Connection
- Page 175 and 176:
Distance Vector Routing: Connection
- Page 177 and 178:
Distance Vector Routing: Connection
- Page 179 and 180:
Distance Vector Routing: The Bounci
- Page 181 and 182:
Distance Vector Routing: The Bounci
- Page 183 and 184:
Distance Vector Routing: Count to I
- Page 185 and 186:
Distance Vector Routing: Count to I
- Page 187 and 188:
Routing Routing Information Protoco
- Page 189 and 190:
Information Exchange 1.) Exchange o
- Page 191 and 192:
Link State Routing ● Every router
- Page 193 and 194:
Link State Routing ● Second step:
- Page 195 and 196:
Packet Buffer for Router B ● Four
- Page 197 and 198:
Route Enquiry ● Fifth step: Decis
- Page 199 and 200:
Routing Tables ● Problem: extensi
- Page 201 and 202:
Hierarchical Routing Region 1 1A 3A
- Page 203 and 204:
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) ●
- Page 205 and 206:
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) ●
- Page 207 and 208:
Intermediate System to Intermediate
- Page 209 and 210:
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) ● G
- Page 211 and 212:
Size of BGP routing tables (bgp.pot
- Page 213 and 214:
Average AS path length Univ.-Prof.
- Page 215:
Summary ● TCP/IP reference model