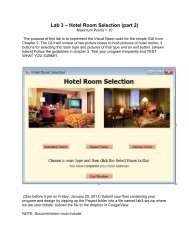
- Page 1:
High Level Assembler for z/OS & z/V
- Page 4 and 5:
Note!Before using this information
- Page 8 and 9:
|Open code . . . . . . . . . . . .
- Page 10 and 11:
Programming interface informationOr
- Page 12 and 13:
IBM High Level Assembler for z/OS &
- Page 14 and 15:
Syntax notationFormat▌A▐ ▌B
- Page 16 and 17:
Double-byte character set notationx
- Page 18:
Summary of changesxvi HLASM: V1R6 L
- Page 21 and 22:
Chapter 1. IntroductionA computer c
- Page 23 and 24:
Assembler languagev Macro instructi
- Page 25 and 26:
Assembler programProcessingConditio
- Page 27 and 28:
Coding made easierCoding made easie
- Page 29 and 30:
Chapter 2. Coding and structureThis
- Page 31 and 32:
Character setTable 4. Examples usin
- Page 33 and 34:
Assembler language coding conventio
- Page 35 and 36:
Assembler language coding conventio
- Page 37 and 38: Assembler language coding conventio
- Page 39 and 40: Assembler language structureThe mac
- Page 41 and 42: Assembler language structureMachine
- Page 43 and 44: Assembler language structureConditi
- Page 45 and 46: Mnemonic tags|||||||||For example,
- Page 47 and 48: Terms, literals, and expressions- T
- Page 49 and 50: Terms, literals, and expressionsAss
- Page 51 and 52: Terms, literals, and expressionsUsi
- Page 53 and 54: Terms, literals, and expressions|||
- Page 55 and 56: Terms, literals, and expressionsz/V
- Page 57 and 58: Terms, literals, and expressionsTab
- Page 59 and 60: Terms, literals, and expressions1.
- Page 61 and 62: Terms, literals, and expressions1.
- Page 63 and 64: Terms, literals, and expressions┌
- Page 65 and 66: Terms, literals, and expressionsA-Y
- Page 67 and 68: Chapter 3. Program structures and a
- Page 69 and 70: SourcemoduleA source module is comp
- Page 71 and 72: Beginning of a source modulev The S
- Page 73 and 74: Beginning of a source moduleReferen
- Page 75 and 76: Beginning of a source moduleNote: T
- Page 77 and 78: Beginning of a source moduleClass l
- Page 79 and 80: Beginning of a source modulez/VM an
- Page 81 and 82: AddressingBase Address Definition:
- Page 83 and 84: QualifiedDependentaddressingQualifi
- Page 85 and 86: Addressingz/VM and z/OSWhen you spe
- Page 87: Addressing..EX_SYM DC V(EXMOD1) Add
- Page 91 and 92: Part 2. Machine and assembler instr
- Page 93 and 94: Chapter 4. Machine instruction stat
- Page 95 and 96: Input/output operationsThe input or
- Page 97 and 98: Branching with extended mnemonic co
- Page 99 and 100: Statement formatsSymbolic operation
- Page 101 and 102: Operand entriesRegistersYou can spe
- Page 103 and 104: Operand entriesv Explicitly—in a
- Page 105 and 106: Operand entriesImmediateused by the
- Page 107 and 108: Examples of coded machine instructi
- Page 109 and 110: Examples of coded machine instructi
- Page 111 and 112: Examples of coded machine instructi
- Page 113 and 114: Examples of coded machine instructi
- Page 115 and 116: Chapter 5. Assembler instruction st
- Page 117 and 118: *PROCESS statementstatement, follow
- Page 119 and 120: ACONTROL instruction►►NOCOMPAT,
- Page 121 and 122: ACONTROL instructionFLAG(PAGE0)inst
- Page 123 and 124: ACONTROL instruction|||may be fetch
- Page 125 and 126: AINSERT instruction►►sequence_s
- Page 127 and 128: ALIAS instruction||||||The alias_st
- Page 129 and 130: AMODE instructionCATTR instruction
- Page 131 and 132: CATTR instructionRMODE(ANY)The text
- Page 133 and 134: CCW and CCW0 instructionssupport 31
- Page 135 and 136: CEJECT instructionIf number of line
- Page 137 and 138: CNOP instructionAfter the BALR inst
- Page 139 and 140:
COPY instructioncopied from either
- Page 141 and 142:
CSECT instructionsame section name
- Page 143 and 144:
CXD instructionZETA: the resulting
- Page 145 and 146:
DC instruction10EBP(7)L2’12’the
- Page 147 and 148:
DC instructionTable 17. Length attr
- Page 149 and 150:
DC instruction4. Double-byte data i
- Page 151 and 152:
DC instructionTable 19. Type codes
- Page 153 and 154:
DC instructionYou may omit the modi
- Page 155 and 156:
DC instructionfirst constant to be
- Page 157 and 158:
DC instructionTable 21. Specifying
- Page 159 and 160:
DC instruction—Character constant
- Page 161 and 162:
DC instruction—Character constant
- Page 163 and 164:
DC instruction—Graphic constantTa
- Page 165 and 166:
DC instruction—Fixed-point consta
- Page 167 and 168:
DC instruction—Fixed-point consta
- Page 169 and 170:
DC instruction—Decimal constantsD
- Page 171 and 172:
DC instruction—Address constants|
- Page 173:
DC instruction—Address constantsT
- Page 176 and 177:
DC instruction—Offset constantIn
- Page 178 and 179:
DC instruction—Hexadecimal floati
- Page 180 and 181:
DC instruction—Hexadecimal floati
- Page 182 and 183:
DC instruction—Hexadecimal floati
- Page 184 and 185:
DC instruction—Decimal floating-p
- Page 186 and 187:
Syntax of binary, decimal, and hexa
- Page 188 and 189:
DC instruction—Binary floating-po
- Page 190 and 191:
DROP instructionLabeledDependentIf
- Page 192 and 193:
DS instructionv An ordinary symbolv
- Page 194 and 195:
DS instructionthe data that follows
- Page 196 and 197:
DSECT instructionTo effect referenc
- Page 198 and 199:
DXD instructionnominal_valueis the
- Page 200 and 201:
END instructionNotes:1. If the END
- Page 202 and 203:
EQU instruction||||to the symbol in
- Page 204 and 205:
EQU instruction|FPR Register - Floa
- Page 206 and 207:
EXITCTL instructionSee the section
- Page 208 and 209:
ISEQ instruction►►sequence_symb
- Page 210 and 211:
LOCTR instructionA LOCTR name may b
- Page 212 and 213:
LTORG instructionAddressingDuplicat
- Page 214 and 215:
MNOTE instructionNote: The maximum
- Page 216 and 217:
OPSYN instruction||||||v An operati
- Page 218 and 219:
ORG instruction||||||||If symbol de
- Page 220 and 221:
ORG instructionThat is, the ORG ins
- Page 222 and 223:
PRINT instructionPRINT instructionT
- Page 224 and 225:
PRINT instructionexceeded the macro
- Page 226 and 227:
PUNCH instructionv A pair of single
- Page 228 and 229:
REPRO instruction||Notes:1. The ide
- Page 230 and 231:
RSECT instructionThe beginning of a
- Page 232 and 233:
TITLE instructionv Provides heading
- Page 234 and 235:
TITLE instructionIf the TITLE state
- Page 236 and 237:
USING instructioninstructions suppo
- Page 238 and 239:
USING instructionby means of anothe
- Page 240 and 241:
USING instructionLabeled USING inst
- Page 242 and 243:
USING instructionDomain of a labele
- Page 244 and 245:
USING instructionIf the dependent U
- Page 246 and 247:
XATTR instructionXATTR instruction
- Page 248 and 249:
XATTR instructionSCOPE(MODULE), abb
- Page 250 and 251:
232 HLASM: V1R6 Language Ref
- Page 252 and 253:
Name entry . . . . . . . . . . . .
- Page 254 and 255:
Macro definitionA macro definition
- Page 256 and 257:
Macro instructionThe macro instruct
- Page 258 and 259:
240 HLASM: V1R6 Language Ref
- Page 260 and 261:
Where to define a macro in a source
- Page 262 and 263:
Prototype statement|||||specified o
- Page 264 and 265:
Model statementsEach field or subfi
- Page 266 and 267:
Model statementsTable 37. Rules for
- Page 268 and 269:
Model statements||v Variable symbol
- Page 270 and 271:
Symbolic parametersPositionalKeywor
- Page 272 and 273:
Other conditional assembly instruct
- Page 274 and 275:
AREAD instruction||If no operand is
- Page 276 and 277:
MEXIT instructionThe MEXIT instruct
- Page 278 and 279:
System variable symbols1 macro2 get
- Page 280 and 281:
&SYSADATA_MEMBER System Variable Sy
- Page 282 and 283:
&SYSDATC System Variable SymbolYYYY
- Page 284 and 285:
&SYSECT System Variable Symbolv Sta
- Page 286 and 287:
&SYSIN_MEMBER System Variable Symbo
- Page 288 and 289:
&SYSLIB_DSN System Variable SymbolS
- Page 290 and 291:
&SYSLIN_DSN System Variable SymbolE
- Page 292 and 293:
&SYSLIST System Variable Symbolposi
- Page 294 and 295:
&SYSLOC System Variable Symbolinstr
- Page 296 and 297:
&SYSNDX System Variable Symbol1 MAC
- Page 298 and 299:
&SYSNDX System Variable SymbolState
- Page 300 and 301:
&SYSOPT_RENT System Variable Symbol
- Page 302 and 303:
&SYSPRINT_DSN System Variable Symbo
- Page 304 and 305:
&SYSPUNCH_DSN System Variable Symbo
- Page 306 and 307:
&SYSSEQF System Variable Symbol1. I
- Page 308 and 309:
&SYSTEM_ID System Variable SymbolNo
- Page 310 and 311:
&SYSTERM_VOLUME System Variable Sym
- Page 312 and 313:
&SYSVER System Variable Symbol294 H
- Page 314 and 315:
Macro instruction format|name_entry
- Page 316 and 317:
Macro instruction formatOperandYou
- Page 318 and 319:
Macro instruction formatAny keyword
- Page 320 and 321:
Macro instruction formatparameters
- Page 322 and 323:
Sublists in operandsTable 48. Relat
- Page 324 and 325:
Values in operandsUnquotedSpecial2.
- Page 326 and 327:
Values in operands’SPACES ALLOWED
- Page 328 and 329:
Levels of macro call nestingLevels
- Page 330 and 331:
Levels of macro call nestingCOMPAT(
- Page 332 and 333:
Levels of macro call nesting&SYSSEQ
- Page 334 and 335:
SET symbolsSET symbolsSET symbols a
- Page 336 and 337:
SET symbolsTable 50. Features of SE
- Page 338 and 339:
SET symbolspreceding 999999 element
- Page 340 and 341:
Data attributesTable 51. Data attri
- Page 342 and 343:
Data attributesThe values of attrib
- Page 344 and 345:
Data attributesV R-, V-type address
- Page 346 and 347:
Data attributes|||||||||Notes:1. Or
- Page 348 and 349:
Data attributesv If the first opera
- Page 350 and 351:
Data attributesCount attribute (K')
- Page 352 and 353:
Data attributes||||||defined attrib
- Page 354 and 355:
Sequence symbolsparameter wherever
- Page 356 and 357:
LookaheadSequencelater defined by O
- Page 358 and 359:
GBLA, GBLB, and GBLC instructionsGB
- Page 360 and 361:
LCLA, LCLB, and LCLC instructions,
- Page 362 and 363:
Assigning values to SET symbolsLogi
- Page 364 and 365:
Assigning values to SET symbolsTabl
- Page 366 and 367:
SETA instructionTable 58. Variable
- Page 368 and 369:
SETA instructionB2A(’’) has val
- Page 370 and 371:
SETA instruction|||||||||||||||||||
- Page 372 and 373:
SETA instructionAfter the following
- Page 374 and 375:
SETA instruction10. An arithmetic e
- Page 376 and 377:
SETA instructionarithmetic value
- Page 378 and 379:
SETB instructionv A logical express
- Page 380 and 381:
SETB instructionOR Format: Logical-
- Page 382 and 383:
SETC instructionSETCinstructionThe
- Page 384 and 385:
SETC instruction|LCLC &C1,&C2LCLC &
- Page 386 and 387:
Substring notationv When e2 has a v
- Page 388 and 389:
Substring notation||||ExamplesA2D(0
- Page 390 and 391:
Substring notationC2X Format: Funct
- Page 392 and 393:
Substring notationSuppose the SETC
- Page 394 and 395:
Substring notationX2C(’’) has v
- Page 396 and 397:
Substring notationFor example, eith
- Page 398 and 399:
Substring notationStatement 1 assig
- Page 400 and 401:
SETAF instruction►► variable_sy
- Page 402 and 403:
AIF instructionsequence_symbolis a
- Page 404 and 405:
AIF instructionAIFB—synonym of th
- Page 406 and 407:
ACTR instruction►►sequence_symb
- Page 408 and 409:
390 HLASM: V1R6 Language Ref
- Page 410 and 411:
MHELP optionsparameters are dumped
- Page 412 and 413:
394 HLASM: V1R6 Language Ref
- Page 414 and 415:
396 HLASM: V1R6 Language Ref
- Page 416 and 417:
Assembler instructions and statemen
- Page 418 and 419:
Assembler instructions and statemen
- Page 420 and 421:
Assembler instructions and statemen
- Page 422 and 423:
Summary of constantsTable 65. Summa
- Page 424 and 425:
Macro and conditional assembly lang
- Page 426 and 427:
Macro and conditional assembly lang
- Page 428 and 429:
Macro and conditional assembly lang
- Page 430 and 431:
Macro and conditional assembly lang
- Page 432 and 433:
Macro and conditional assembly lang
- Page 434 and 435:
Macro and conditional assembly lang
- Page 436 and 437:
Standard character set code tableHe
- Page 438 and 439:
Standard character set code tableHe
- Page 440 and 441:
NoticesPURPOSE. Some states do not
- Page 442 and 443:
z/VM: CP Planning and Administratio
- Page 444 and 445:
ALIAS instruction 108maximum operan
- Page 446 and 447:
comment statements (continued)ordin
- Page 448 and 449:
GG-type graphic constant 144GBLA in
- Page 450 and 451:
macro instructions (continued)opera
- Page 452 and 453:
eference constant (R) 154reference
- Page 454 and 455:
UUHEADPRINT instruction 206unary op
- Page 456:
Readers’ Comments — We’d Like