- Page 2 and 3:
a LANGE medical bookHarper’sIllus
- Page 4 and 5:
AuthorsDavid A. Bender, PhDSub-Dean
- Page 6 and 7:
x / PREFACE• The chapter on plasm
- Page 8 and 9:
iv / CONTENTS14. Lipids of Physiolo
- Page 10:
vi / CONTENTSSECTION VI. SPECIAL TO
- Page 14 and 15:
4 / CHAPTER 1in early 2001. It is a
- Page 16:
6 / CHAPTER 2H2eCH 3CH 2OHOHFigure
- Page 19 and 20:
WATER & pH / 9+ −[ H ][ OH ]−16
- Page 22 and 23:
12 / CHAPTER 2meq of alkali added p
- Page 24 and 25:
SECTION IStructures & Functionsof P
- Page 26 and 27:
16 / CHAPTER 3Table 3-1.L-α-Amino
- Page 28 and 29:
18 / CHAPTER 3pK a Values Vary With
- Page 30 and 31:
20 / CHAPTER 3121°OC117°122°120
- Page 32 and 33:
22 / CHAPTER 4RCFigure 4-1. Compone
- Page 34 and 35:
O24 / CHAPTER 4aliphatic polymers 3
- Page 36 and 37:
26 / CHAPTER 4NHOR′HNONH 2Phenyli
- Page 38 and 39:
28 / CHAPTER 4GENOMICS ENABLES PROT
- Page 40 and 41:
Proteins: Higher Orders of Structur
- Page 42 and 43:
32 / CHAPTER 50.54-nm pitch(3.6 res
- Page 44 and 45:
34 / CHAPTER 5COOHHHC αCHNHHNOC α
- Page 46 and 47:
36 / CHAPTER 5sures the absorbance
- Page 48 and 49:
38 / CHAPTER 5to a particular organ
- Page 50 and 51:
Proteins: Myoglobin & Hemoglobin 6V
- Page 52 and 53:
42 / CHAPTER 6Percent saturation100
- Page 54 and 55:
44 / CHAPTER 6T structureα 1 α 2O
- Page 56 and 57:
46 / CHAPTER 6Adaptation to High Al
- Page 58 and 59:
48 / CHAPTER 6Manning JM et al: Nor
- Page 60 and 61:
50 / CHAPTER 7132 2Enzyme site14Sub
- Page 62 and 63:
52 / CHAPTER 7independent of the co
- Page 64 and 65:
54 / CHAPTER 712OCAsp 102OAsp 102HO
- Page 66 and 67:
56 / CHAPTER 7NAD(P) + -Dependent D
- Page 68 and 69:
58 / CHAPTER 7+ -(Lactate)SH 2LACTA
- Page 70 and 71:
Enzymes: Kinetics 8Victor W. Rodwel
- Page 72 and 73:
62 / CHAPTER 8that anything which i
- Page 74 and 75:
64 / CHAPTER 8Hydrogen Ion Concentr
- Page 76 and 77:
66 / CHAPTER 8invertfactorand simpl
- Page 78 and 79:
68 / CHAPTER 8only one methylene ca
- Page 80 and 81:
70 / CHAPTER 8Increasing[S 2 ]S 11a
- Page 82 and 83:
Enzymes: Regulation of Activities 9
- Page 84 and 85:
74 / CHAPTER 9influenced both by ch
- Page 86 and 87:
76 / CHAPTER 9without affecting the
- Page 88 and 89:
78 / CHAPTER 9accounts for the freq
- Page 90 and 91:
SECTION IIBioenergetics & the Metab
- Page 92 and 93:
82 / CHAPTER 10Figure 10-4. Adenosi
- Page 94 and 95:
84 / CHAPTER 10(1) Glucose+P i →
- Page 96 and 97:
Biologic Oxidation 11Peter A. Mayes
- Page 98 and 99:
88 / CHAPTER 11H 3 CRNNOH 3 CRNHNOH
- Page 100 and 101:
90 / CHAPTER 11Amine oxidase, etcNA
- Page 102 and 103:
The Respiratory Chain &Oxidative Ph
- Page 104 and 105:
94 / CHAPTER 12AH 2 NAD + FpH 2A Fp
- Page 106 and 107:
96 / CHAPTER 12NADHSuccinateComplex
- Page 108 and 109:
98 / CHAPTER 12ADP+PiβαβATPγα
- Page 110 and 111:
100 / CHAPTER 12OUTERMEMBRANEINNERM
- Page 112 and 113:
Carbohydrates ofPhysiologic Signifi
- Page 114 and 115:
104 / CHAPTER 13HOCH 2HO HOHHOCH 2H
- Page 116 and 117:
106 / CHAPTER 13CH 2 OHCH 2 OHCOCH
- Page 118 and 119:
O108 / CHAPTER 136HOCH 2O6HOCH 2O4
- Page 120 and 121:
110 / CHAPTER 13Figure 13-15.contai
- Page 122 and 123:
112 / CHAPTER 1418:1;9 or ∆ 9 18:
- Page 124 and 125:
H114 / CHAPTER 14OCOO -more unsatur
- Page 126 and 127:
116 / CHAPTER 14Lysophospholipids A
- Page 128 and 129:
118 / CHAPTER 14“Chair” form“
- Page 130 and 131:
120 / CHAPTER 14RH R• R• ROO•
- Page 132 and 133:
Overview of Metabolism 15Peter A. M
- Page 134 and 135:
124 / CHAPTER 15(2) It is the precu
- Page 136 and 137:
126 / CHAPTER 15FFAGlucosei sl y si
- Page 138 and 139:
128 / CHAPTER 15enzyme-catalyzed re
- Page 140 and 141:
The Citric Acid Cycle:The Catabolis
- Page 142 and 143:
HO CH COO -CH 2 COO -L-MalateMALATE
- Page 144 and 145:
134 / CHAPTER 16HydroxyprolineSerin
- Page 146 and 147:
Glycolysis & the Oxidationof Pyruva
- Page 148 and 149:
GlycogenGlucose 1-phosphateHEXOKINA
- Page 150 and 151:
140 / CHAPTER 17lactate and oxidize
- Page 152 and 153:
142 / CHAPTER 17[ Acetyl-CoA ][ CoA
- Page 154 and 155:
144 / CHAPTER 17Boiteux A, Hess B:
- Page 156 and 157:
146 / CHAPTER 18Glycogen(1→4 and
- Page 158 and 159: 148 / CHAPTER 18PHOSPHORYLASEGLUCAN
- Page 160 and 161: 150 / CHAPTER 18Epinephrineβ Recep
- Page 162 and 163: 152 / CHAPTER 18Table 18-2. Glycoge
- Page 164 and 165: PiGLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATASEH 2 OGlucose
- Page 166 and 167: 156 / CHAPTER 19Table 19-1. Regulat
- Page 168 and 169: 158 / CHAPTER 19GLUCONEOGENESISP iA
- Page 170 and 171: 160 / CHAPTER 19Table 19-2. Glucose
- Page 172 and 173: 162 / CHAPTER 19due to hyperactivit
- Page 174 and 175: 164 / CHAPTER 20Glucose 6-phosphate
- Page 176 and 177: 166 / CHAPTER 20unit comprising car
- Page 178 and 179: 168 / CHAPTER 20H *CHHOHHCCCCOHOHHO
- Page 180 and 181: 170 / CHAPTER 20AGalactoseGlycogenG
- Page 182 and 183: 172 / CHAPTER 20inhibits the activi
- Page 184 and 185: 174 / CHAPTER 21CH 3 CO S CoAAcetyl
- Page 186 and 187: 176 / CHAPTER 21acids having an odd
- Page 188 and 189: 178 / CHAPTER 21crose is fed instea
- Page 190 and 191: Oxidation of Fatty Acids:Ketogenesi
- Page 192 and 193: 182 / CHAPTER 221CoAO3 2R CH2 CH2 C
- Page 194 and 195: 184 / CHAPTER 22CO 2OCH 3 C CH 2 CO
- Page 196 and 197: 186 / CHAPTER 22In extrahepatic tis
- Page 198 and 199: 188 / CHAPTER 22GlucoseBLOODFFAVLDL
- Page 200 and 201: Metabolism of Unsaturated FattyAcid
- Page 202 and 203: 192 / CHAPTER 2318O12 9C S CoALinol
- Page 204 and 205: 194 / CHAPTER 23COOHO O Arachidonat
- Page 206 and 207: 196 / CHAPTER 23hepatorenal syndrom
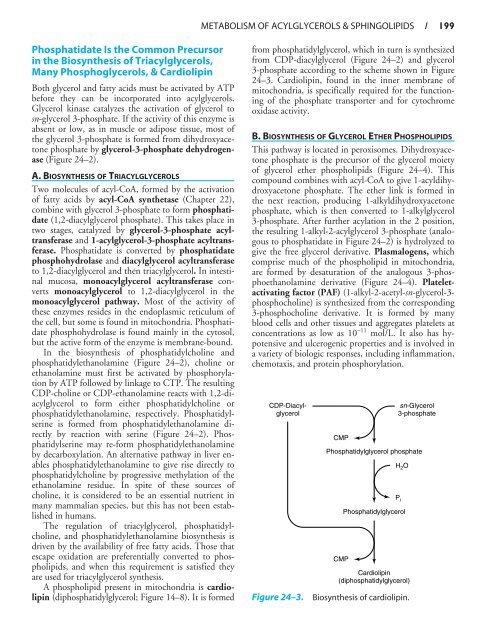
- Page 210 and 211: 200 / CHAPTER 24H 2 COHO CH 2 C O P
- Page 212 and 213: 202 / CHAPTER 24CH 3O(CH 2 ) 14 C S
- Page 214 and 215: 204 / CHAPTER 24SUMMARY• Triacylg
- Page 216 and 217: 206 / CHAPTER 25Table 25-1. Composi
- Page 218 and 219: •••208 / CHAPTER 25AIntestina
- Page 220 and 221: 210 / CHAPTER 25NascentVLDLB-100ELD
- Page 222 and 223: 212 / CHAPTER 25the fed state rathe
- Page 224 and 225: 214 / CHAPTER 25and may account for
- Page 226 and 227: 216 / CHAPTER 25Epinephrine,norepin
- Page 228 and 229: 218 / CHAPTER 25• Apolipoproteins
- Page 230 and 231: 220 / CHAPTER 26OCH 3 C S CoA2 Acet
- Page 232 and 233: 222 / CHAPTER 26OCH 3CH 3CH 3CSCoA-
- Page 234 and 235: 224 / CHAPTER 26CELL MEMBRANELDL (a
- Page 236 and 237: 226 / CHAPTER 2612 17Vitamin CNADP
- Page 238 and 239: 228 / CHAPTER 26lesterol into the c
- Page 240 and 241: 230 / CHAPTER 26Russell DW: Cholest
- Page 242 and 243: 232 / CHAPTER 27neogenesis. Those a
- Page 244 and 245: 234 / CHAPTER 27Table 27-1. Energy
- Page 246 and 247: 236 / CHAPTER 27CLINICAL ASPECTSIn
- Page 248 and 249: 238 / CHAPTER 28O- O O-NH+ 3- O O-O
- Page 250 and 251: 240 / CHAPTER 28CH 2 CH COO -+ NH 3
- Page 252 and 253: Catabolism of Proteins& of Amino Ac
- Page 254 and 255: 244 / CHAPTER 29of amino groups to
- Page 256 and 257: 246 / CHAPTER 29CO 22Mg-ATPN-Acetyl
- Page 258 and 259:
248 / CHAPTER 29Argininosuccinicaci
- Page 260 and 261:
250 / CHAPTER 30CONH 2H 2 O NH 4+CO
- Page 262 and 263:
252 / CHAPTER 30H 2 CNH 3+CHCO -H 4
- Page 264 and 265:
O -254+NH 3 O2CH O - 1 α-KG 1 GluC
- Page 266 and 267:
OOCCH 2CH 2COCO -H 2 OOCCH 2CH 2COC
- Page 268 and 269:
258 / CHAPTER 30HOHONH 2OCNH 3+NCH
- Page 270 and 271:
260 / CHAPTER 30CH 3NH 3+NH 3+NH 3+
- Page 272 and 273:
262 / CHAPTER 30OOH 2 C CC S CoACH
- Page 274 and 275:
Conversion of Amino Acidsto Special
- Page 276 and 277:
266 / CHAPTER 31PROTEINSNITRIC OXID
- Page 278 and 279:
+H 2 NHNHCNH 2NHCHCH 2CH 2 + H3 N C
- Page 280 and 281:
Porphyrins & Bile Pigments 32Robert
- Page 282 and 283:
272 / CHAPTER 32APAPPAAPAPAPUroporp
- Page 284 and 285:
274 / CHAPTER 32AHOOCH 2 CH 2 CNH 2
- Page 286 and 287:
276 / CHAPTER 32HemoproteinsProtein
- Page 288 and 289:
278 / CHAPTER 32indicated in Figure
- Page 290 and 291:
280 / CHAPTER 32Bilirubin formed in
- Page 292 and 293:
282 / CHAPTER 32MH 2 CMINHEOHOHMMH
- Page 294 and 295:
284 / CHAPTER 32Table 32-3. Laborat
- Page 296 and 297:
SECTION IVStructure, Function, & Re
- Page 298 and 299:
288 / CHAPTER 33Table 33-1. Bases,
- Page 300 and 301:
290 / CHAPTER 33NNH 2NNNTable 33-2.
- Page 302 and 303:
292 / CHAPTER 33Pu/Py R O P O P OO
- Page 304 and 305:
294 / CHAPTER 34N 10 -Formyltetrahy
- Page 306 and 307:
296 / CHAPTER 34HNO-OOCNCHC COO - -
- Page 308 and 309:
298 / CHAPTER 34CO 2 + Glutamine +
- Page 310 and 311:
300 / CHAPTER 34OTHER DISORDERS OFP
- Page 312 and 313:
302 / CHAPTER 34REFERENCESBenkovic
- Page 314 and 315:
304 / CHAPTER 35O5′CH 2NNGNNHNH 2
- Page 316 and 317:
306 / CHAPTER 35dures allow for ver
- Page 318 and 319:
308 / CHAPTER 35O5′CH 2NNGNNHNH 2
- Page 320 and 321:
310 / CHAPTER 355′3′DNA3′5′
- Page 322 and 323:
312 / CHAPTER 35Region of hydrogenb
- Page 324 and 325:
DNA Organization, Replication,& Rep
- Page 326 and 327:
316 / CHAPTER 36understood. It is p
- Page 328 and 329:
318 / CHAPTER 36more extended chrom
- Page 330 and 331:
320 / CHAPTER 361 2 3 4 56 7 8 9 10
- Page 332 and 333:
322 / CHAPTER 36spersed repeats, in
- Page 334 and 335:
324 / CHAPTER 36Gγ Aγ δ βδ βG
- Page 336 and 337:
326 / CHAPTER 36contains an intersp
- Page 338 and 339:
328 / CHAPTER 36Table 36-5. Classes
- Page 340 and 341:
330 / CHAPTER 36with the other stra
- Page 342 and 343:
332 / CHAPTER 36lizing proteins bin
- Page 344 and 345:
334 / CHAPTER 36Improper spindledet
- Page 346 and 347:
336 / CHAPTER 36Table 36-9. Mechani
- Page 348 and 349:
338 / CHAPTER 363′5′3′5′3
- Page 350 and 351:
340 / CHAPTER 36Marians KJ: Prokary
- Page 352 and 353:
342 / CHAPTER 37Table 37-1. Classes
- Page 354 and 355:
344 / CHAPTER 37cule from the 5′
- Page 356 and 357:
346 / CHAPTER 37coordinately regula
- Page 358 and 359:
348 / CHAPTER 37site (from −3 to
- Page 360 and 361:
350 / CHAPTER 37Finally, this newly
- Page 362 and 363:
352 / CHAPTER 37activators are not
- Page 364 and 365:
354 / CHAPTER 37is accomplished by
- Page 366 and 367:
356 / CHAPTER 37(the histones are m
- Page 368 and 369:
Protein Synthesis & theGenetic Code
- Page 370 and 371:
360 / CHAPTER 38Table 38-2. Feature
- Page 372 and 373:
362 / CHAPTER 38Hemoglobin Illustra
- Page 374 and 375:
364 / CHAPTER 38NormalWild typemRNA
- Page 376 and 377:
Ternary complexformationFormation o
- Page 378 and 379:
368 / CHAPTER 38GTPG m TP—5′+P
- Page 380 and 381:
370 / CHAPTER 38Table 38-3. Evidenc
- Page 382 and 383:
372 / CHAPTER 38molecules. This dif
- Page 384 and 385:
Regulation of Gene Expression 39Dar
- Page 386 and 387:
376 / CHAPTER 39be regarded as a on
- Page 388 and 389:
378 / CHAPTER 39above sequence). At
- Page 390 and 391:
380 / CHAPTER 39AGene for repressor
- Page 392 and 393:
ProphageO R 3O R 2 O R 1RNA polymer
- Page 394 and 395:
384 / CHAPTER 39promoter dictates w
- Page 396 and 397:
386 / CHAPTER 39HMG PRDIV HMG PRDI-
- Page 398 and 399:
388 / CHAPTER 395′HREAREPORTER GE
- Page 400 and 401:
390 / CHAPTER 39protein of E coli),
- Page 402 and 403:
392 / CHAPTER 39GAL4 +1ActiveAUASGA
- Page 404 and 405:
394 / CHAPTER 39mouse amylase and m
- Page 406 and 407:
Molecular Genetics, RecombinantDNA,
- Page 408 and 409:
398 / CHAPTER 40DNA 5′Regulatoryr
- Page 410 and 411:
400 / CHAPTER 40A. Sticky or stagge
- Page 412 and 413:
402 / CHAPTER 40Table 40-4. Cloning
- Page 414 and 415:
404 / CHAPTER 40Southern Northern W
- Page 416 and 417:
406 / CHAPTER 40STARTCYCLE 1CYCLE 2
- Page 418 and 419:
408 / CHAPTER 40∋Gγ Aγ Ψβ δ
- Page 420 and 421:
410 / CHAPTER 40A. MstII restrictio
- Page 422 and 423:
412 / CHAPTER 40percentage of genes
- Page 424 and 425:
414 / CHAPTER 40Primosome: The mobi
- Page 426 and 427:
416 / CHAPTER 41products, and toxic
- Page 428 and 429:
418 / CHAPTER 41hydrophobic regions
- Page 430 and 431:
420 / CHAPTER 41Table 41-2. Enzymat
- Page 432 and 433:
422 / CHAPTER 41attack by nucleases
- Page 434 and 435:
424 / CHAPTER 41Transportedmolecule
- Page 436 and 437:
426 / CHAPTER 41Table 41-4. Some pr
- Page 438 and 439:
428 / CHAPTER 41INSIDEATPADP+P i3 N
- Page 440 and 441:
430 / CHAPTER 41broblasts, for exam
- Page 442 and 443:
432 / CHAPTER 41Table 41-5. Some di
- Page 444 and 445:
The Diversity of theEndocrine Syste
- Page 446 and 447:
436 / CHAPTER 42◆❁❁✪✴ ❖
- Page 448 and 449:
438 / CHAPTER 42Hormones Are Chemic
- Page 450 and 451:
440 / CHAPTER 42HOABCCCDC C CC CCCh
- Page 452 and 453:
442 / CHAPTER 42the gonads and acts
- Page 454 and 455:
444 / CHAPTER 42OHOH5α-REDUCTASENA
- Page 456 and 457:
446 / CHAPTER 42Sunlight7-Dehydroch
- Page 458 and 459:
448 / CHAPTER 42FOLLICULAR SPACE WI
- Page 460 and 461:
450 / CHAPTER 4220NH 2 -Ala Leu Pro
- Page 462 and 463:
452 / CHAPTER 42AngiotensinogenAsp-
- Page 464 and 465:
454 / CHAPTER 42Table 42-5. Diversi
- Page 466 and 467:
Hormone Action &Signal Transduction
- Page 468 and 469:
458 / CHAPTER 43−Cytoplasm−++TR
- Page 470 and 471:
460 / CHAPTER 43NNHEEα sGDPγβCNo
- Page 472 and 473:
462 / CHAPTER 43Activeadenylylcycla
- Page 474 and 475:
464 / CHAPTER 43A number of critica
- Page 476 and 477:
466 / CHAPTER 43RECOGNITION(HYPERGL
- Page 478 and 479:
468 / CHAPTER 43C. THE NF-B PATHWAY
- Page 480 and 481:
470 / CHAPTER 43A/BCDEFNAF-1DBDHing
- Page 482 and 483:
472 / CHAPTER 43Table 43-5. Nuclear
- Page 484 and 485:
SECTION VISpecial TopicsNutrition,
- Page 486 and 487:
INTESTINALLUMEN1AcylPANCREATICAcylL
- Page 488 and 489:
478 / CHAPTER 44Iron Absorption Is
- Page 490 and 491:
480 / CHAPTER 44growing children ar
- Page 492 and 493:
482 / CHAPTER 45Table 45-1. The vit
- Page 494 and 495:
484 / CHAPTER 45H 3 CH 3 CH 3 CH 3
- Page 496 and 497:
486 / CHAPTER 45tration of calcium.
- Page 498 and 499:
488 / CHAPTER 45OCH 3HO 3Phylloquin
- Page 500 and 501:
490 / CHAPTER 45FMN. The main dieta
- Page 502 and 503:
492 / CHAPTER 45H 3 CH 2 NCOCH 2 CH
- Page 504 and 505:
494 / CHAPTER 45droxymethyltransfer
- Page 506 and 507:
496 / CHAPTER 45CH 2 OHCH 2 OHCH 2
- Page 508 and 509:
Intracellular Traffic & Sortingof P
- Page 510 and 511:
Plasma membraneCytosolEarlyendosome
- Page 512 and 513:
502 / CHAPTER 4612GTP3GDPTargeting
- Page 514 and 515:
504 / CHAPTER 46at their amino term
- Page 516 and 517:
506 / CHAPTER 46NNNCNCCNNEXTRACYTOP
- Page 518 and 519:
508 / CHAPTER 46Table 46-4. Some se
- Page 520 and 521:
510 / CHAPTER 46Coated3 vesicle4t-S
- Page 522 and 523:
512 / CHAPTER 46Membrane proteinExt
- Page 524 and 525:
Glycoproteins 47Robert K. Murray, M
- Page 526 and 527:
516 / CHAPTER 47Table 47-4. The pri
- Page 528 and 529:
518 / CHAPTER 47animal origin are n
- Page 530 and 531:
520 / CHAPTER 47NO-glycan chainTand
- Page 532 and 533:
522 / CHAPTER 47α2,3 or 2,6Sialic
- Page 534 and 535:
524 / CHAPTER 47Man α1,2 GlcNAc P
- Page 536 and 537:
526 / CHAPTER 47Table 47-10. Summar
- Page 538 and 539:
528 / CHAPTER 47Additional constitu
- Page 540 and 541:
530 / CHAPTER 47ABCDBaselineRolling
- Page 542 and 543:
532 / CHAPTER 47Mutations in DNAMut
- Page 544 and 545:
534 / CHAPTER 47• The structures
- Page 546 and 547:
536 / CHAPTER 48Table 48-1. Types o
- Page 548 and 549:
538 / CHAPTER 48this matrix are the
- Page 550 and 551:
540 / CHAPTER 48other gene for fibr
- Page 552 and 553:
542 / CHAPTER 48other plasma protei
- Page 554 and 555:
544 / CHAPTER 48β1,4 β1,3Hyaluron
- Page 556 and 557:
546 / CHAPTER 48Table 48-7. Biochem
- Page 558 and 559:
548 / CHAPTER 48(see above), where
- Page 560 and 561:
550 / CHAPTER 48Blood capillaryNucl
- Page 562 and 563:
552 / CHAPTER 48in structurally abn
- Page 564 and 565:
554 / CHAPTER 48mal trunk size, mac
- Page 566 and 567:
Muscle & the Cytoskeleton 49Robert
- Page 568 and 569:
558 / CHAPTER 49H bandA. ExtendedI
- Page 570 and 571:
560 / CHAPTER 49Myosins constitute
- Page 572 and 573:
562 / CHAPTER 49123Thick filamentLM
- Page 574 and 575:
564 / CHAPTER 49Depolarization of n
- Page 576 and 577:
566 / CHAPTER 49Table 49-2. Some ot
- Page 578 and 579:
568 / CHAPTER 49Table 49-3. Some di
- Page 580 and 581:
570 / CHAPTER 49cardiomyopathy. In
- Page 582 and 583:
572 / CHAPTER 49Table 49-7. Actin-m
- Page 584 and 585:
574 / CHAPTER 49Table 49-8. Summary
- Page 586 and 587:
576 / CHAPTER 49carbonate) loading,
- Page 588 and 589:
578 / CHAPTER 49disappearing during
- Page 590 and 591:
Plasma Proteins & Immunoglobulins 5
- Page 592 and 593:
582 / CHAPTER 50AC+ -Albumin α 1
- Page 594 and 595:
584 / CHAPTER 50tively early in con
- Page 596 and 597:
586 / CHAPTER 50the level of the en
- Page 598 and 599:
588 / CHAPTER 50Copper Is a Cofacto
- Page 600 and 601:
590 / CHAPTER 50disease). In this c
- Page 602 and 603:
592 / CHAPTER 50+ H3 N+ H3 NV LFabS
- Page 604 and 605:
594 / CHAPTER 50Table 50-8. Major f
- Page 606 and 607:
596 / CHAPTER 50Myeloma cellHybrido
- Page 608 and 609:
Hemostasis & Thrombosis 51Margaret
- Page 610 and 611:
600 / CHAPTER 51Table 51-1. Numeric
- Page 612 and 613:
602 / CHAPTER 51PrethrombinCa 2+ Ca
- Page 614 and 615:
604 / CHAPTER 51disease because fac
- Page 616 and 617:
606 / CHAPTER 51Table 51-3. Compari
- Page 618 and 619:
608 / CHAPTER 51dothelial cells, bu
- Page 620 and 621:
610 / CHAPTER 52Table 52-1. Summary
- Page 622 and 623:
612 / CHAPTER 52Table 52-2. Summary
- Page 624 and 625:
614 / CHAPTER 52Mutations in the ge
- Page 626 and 627:
616 / CHAPTER 52Table 52-6. Princip
- Page 628 and 629:
618 / CHAPTER 52antibodies. For pur
- Page 630 and 631:
620 / CHAPTER 52Table 52-7. Laborat
- Page 632 and 633:
622 / CHAPTER 52Table 52-11. Exampl
- Page 634 and 635:
624 / CHAPTER 52Table 52-12. Protei
- Page 636 and 637:
Metabolism of Xenobiotics 53Robert
- Page 638 and 639:
628 / CHAPTER 53smooth endoplasmic
- Page 640 and 641:
630 / CHAPTER 53This reaction helps
- Page 642 and 643:
632 / CHAPTER 53human genome, a new
- Page 644 and 645:
634 / CHAPTER 5420 30 30 20 25cMGen
- Page 646 and 647:
636 / CHAPTER 54DETERMINATION OF TH
- Page 648 and 649:
638 / CHAPTER 54the proteome), incl
- Page 650 and 651:
640 / APPENDIXOffice of Rare Diseas
- Page 652 and 653:
IndexNote: Page numbers in bold fac
- Page 654 and 655:
INDEX / 645Alpha-amino nitrogen. Se
- Page 656 and 657:
INDEX / 647Aromatase enzyme complex
- Page 658 and 659:
INDEX / 649Bronze diabetes, 587Brow
- Page 660 and 661:
INDEX / 651CFU-E. See Colony-formin
- Page 662 and 663:
INDEX / 653immunoglobulin heavy cha
- Page 664 and 665:
INDEX / 655Detoxification, 626cytoc
- Page 666 and 667:
INDEX / 657EcoRI, 398, 399t, 401fEc
- Page 668 and 669:
INDEX / 659Extrinsic pathway of blo
- Page 670 and 671:
INDEX / 661∆G F , 61enzymes affec
- Page 672 and 673:
INDEX / 663Glutamine analogs, purin
- Page 674 and 675:
INDEX / 665Heat, free energy libera
- Page 676 and 677:
INDEX / 667Hybridomas, 595-596, 596
- Page 678 and 679:
INDEX / 669Intracellular signals, 4
- Page 680 and 681:
INDEX / 671Ligand-receptor complex,
- Page 682 and 683:
INDEX / 673Melting point, of amino
- Page 684 and 685:
INDEX / 675regulation ofactin-based
- Page 686 and 687:
INDEX / 677Nucleus (cell), importin
- Page 688 and 689:
INDEX / 679Phenylisothiocyanate (Ed
- Page 690 and 691:
INDEX / 681Positive regulators, of
- Page 692 and 693:
INDEX / 683transport, 454-455, 454t
- Page 694 and 695:
INDEX / 685Reversed-phase high-pres
- Page 696 and 697:
INDEX / 687Skinessential fatty acid
- Page 698 and 699:
INDEX / 689Tertiary structure, 33-3
- Page 700 and 701:
INDEX / 691Troponin I, 562Troponin
- Page 702:
INDEX / 693Wilson disease, 432t, 58