Varian Linatron High-Energy X-ray Applications 2007
Varian Linatron High-Energy X-ray Applications 2007
Varian Linatron High-Energy X-ray Applications 2007
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
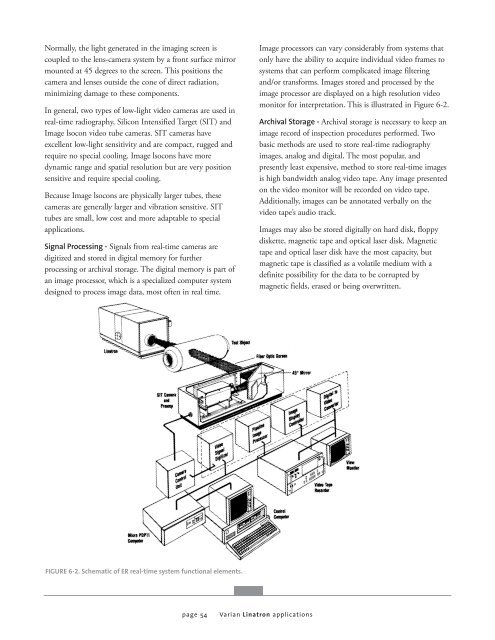
Normally, the light generated in the imaging screen is<br />
coupled to the lens-camera system by a front surface mirror<br />
mounted at 45 degrees to the screen. This positions the<br />
camera and lenses outside the cone of direct radiation,<br />
minimizing damage to these components.<br />
In general, two types of low-light video cameras are used in<br />
real-time radiography, Silicon Intensified Target (SIT) and<br />
Image lsocon video tube cameras. SIT cameras have<br />
excellent low-light sensitivity and are compact, rugged and<br />
require no special cooling. Image lsocons have more<br />
dynamic range and spatial resolution but are very position<br />
sensitive and require special cooling.<br />
Because Image lsocons are physically larger tubes, these<br />
cameras are generally larger and vibration sensitive. SIT<br />
tubes are small, low cost and more adaptable to special<br />
applications.<br />
Signal Processing - Signals from real-time cameras are<br />
digitized and stored in digital memory for further<br />
processing or archival storage. The digital memory is part of<br />
an image processor, which is a specialized computer system<br />
designed to process image data, most often in real time.<br />
FIGURE 6-2. Schematic of ER real-time system functional elements.<br />
page 54<br />
Image processors can vary considerably from systems that<br />
only have the ability to acquire individual video frames to<br />
systems that can perform complicated image filtering<br />
and/or transforms. Images stored and processed by the<br />
image processor are displayed on a high resolution video<br />
monitor for interpretation. This is illustrated in Figure 6-2.<br />
Archival Storage - Archival storage is necessary to keep an<br />
image record of inspection procedures performed. Two<br />
basic methods are used to store real-time radiography<br />
images, analog and digital. The most popular, and<br />
presently least expensive, method to store real-time images<br />
is high bandwidth analog video tape. Any image presented<br />
on the video monitor will be recorded on video tape.<br />
Additionally, images can be annotated verbally on the<br />
video tape’s audio track.<br />
Images may also be stored digitally on hard disk, floppy<br />
diskette, magnetic tape and optical laser disk. Magnetic<br />
tape and optical laser disk have the most capacity, but<br />
magnetic tape is classified as a volatile medium with a<br />
definite possibility for the data to be corrupted by<br />
magnetic fields, erased or being overwritten.<br />
<strong>Varian</strong> <strong>Linatron</strong> applications










![[MSDS 126] Dow Corning 200 Fluid, 5 CST Part Number ... - Varian](https://img.yumpu.com/5104917/1/190x245/msds-126-dow-corning-200-fluid-5-cst-part-number-varian.jpg?quality=85)